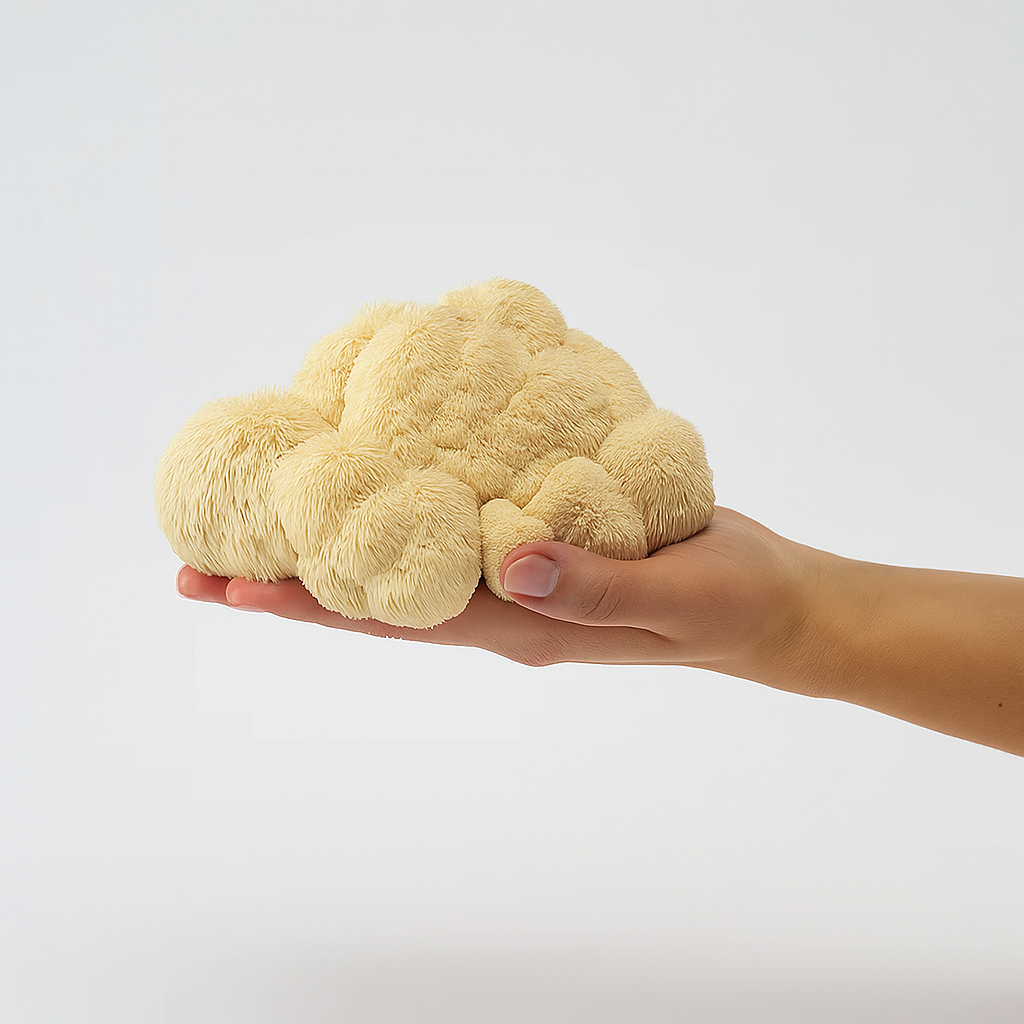
Lion's Mane mushrooms represent one of nature's most fascinating and beneficial fungi, earning recognition as both a culinary delicacy and a powerful medicinal superfood. Known scientifically as Hericium erinaceus, these distinctive white, shaggy mushrooms resemble a lion's mane as they grow, hence their memorable name. With their unique appearance featuring long, cascading spines that dangle downward, Lion's Mane mushrooms are unmistakable in both the wild and cultivated settings.
These remarkable fungi have captured the attention of health enthusiasts, researchers, and chefs worldwide due to their exceptional combination of brain-supporting compounds, impressive nutritional profile, and distinctive seafood-like flavor. Lion's Mane mushrooms have been treasured in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries, where they were reserved for royalty and considered a symbol of wisdom and longevity.
Understanding Lion's Mane Mushroom: Nature's Unique Creation
Physical Characteristics and Identification
Lion's Mane mushrooms are large, white, globe-shaped fungi that have long, shaggy spines extending from their surface. These distinctive mushrooms typically look like white pom-poms and can grow quite substantial in size, with individual specimens sometimes weighing as much as half a kilogram. The spines, or "teeth," begin short but become longer with age, creating the characteristic cascading appearance that gives the mushroom its lion-like moniker.
These unique-looking mushrooms are found growing on rotting hardwood trees and logs throughout the northern hemisphere and are native to Asia, Europe, and North America. Unlike many mushrooms that grow in clusters, Lion's Mane typically develops as individual large masses, making them easily identifiable for foragers and cultivators alike.
Species Variations and Scientific Classification
Although they're generally thought of as a single type of mushroom, there are actually three different species of Lion's Mane. Hericium erinaceus is the one that's most widely available and commonly used for both culinary and medicinal purposes. The other species include Hericium americanum and Hericium coralloides, which share similar appearances and properties but are less commonly encountered in commercial cultivation.
Natural Habitat and Growth Patterns
In their natural environment, Lion's Mane mushrooms grow as saprophytic fungi on the trunks of dead hardwood trees such as oak, beech, and maple. They typically appear in late summer and fall, thriving in the humid conditions that follow seasonal rainfall. The mushrooms serve as decomposers in forest ecosystems, breaking down dead wood and returning nutrients to the soil.

Exceptional Health Benefits of Lion's Mane Mushroom
Cognitive Enhancement and Brain Health
The most celebrated Lion's Mane mushrooms benefits center around their remarkable impact on brain health and cognitive function. Studies have found that Lion's Mane mushrooms contain two special compounds that can stimulate the growth of brain cells: hericenones and erinacines. These unique bioactive compounds have the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and stimulate the synthesis of nerve growth factor (NGF), a protein essential for the growth, maintenance, and survival of neurons.
Research has demonstrated that Lion's Mane may help protect against Alzheimer's disease, a degenerative brain disease that causes progressive memory loss. In fact, Lion's Mane mushroom and its extracts have been shown to reduce symptoms of memory loss in mice, as well as prevent neuronal damage caused by amyloid-beta plaques, which accumulate in the brain during Alzheimer's disease.
Human studies have shown promising results as well. A 2020 study of people with mild Alzheimer's disease found that supplementation with 1 gram of Lion's Mane mushroom daily for 49 weeks significantly improved cognitive test scores compared with a placebo. Additionally, research in adults with mild memory problems associated with aging found that those taking Lion's Mane mushrooms had better brain function compared with participants who did not consume Lion's Mane mushrooms.
Memory and Mental Performance Enhancement
Lion's Mane mushrooms have demonstrated remarkable effects on memory and mental performance in multiple studies. In one study of 30 older adults with mild cognitive impairment, those who took tablets containing Hericium erinaceus powder for 4 months showed a temporary improvement on cognitive tests. The participants experienced significant between-group differences in cognitive function scales at weeks 8, 12, and 16 of supplementation.
Recent research has also explored the acute effects of Lion's Mane supplementation. A 2023 study concluded that Lion's Mane might improve cognitive function, with participants who took a single dose demonstrating quicker performance on cognitive tasks, indicating that it may potentially improve processing speed.
Mood Support and Mental Health Benefits
Lion's Mane extracts have shown significant potential in treating mental health conditions, particularly anxiety and depression. Research suggests that Lion's Mane mushrooms may improve mood, depressive symptoms, and anxiety by helping the body and mind adapt to stress and stressful situations.
A 2023 study examined the effects of 28 days of Lion's Mane supplementation in 41 healthy adults aged 18-45. Participants reported signs of reduced stress, which researchers suggested could be linked to Lion's Mane's ability to stimulate nerve growth factor (NGF), a protein associated with mood regulation. Similarly, a 2022 animal study found that combining chlorella and Lion's Mane mushroom had an antidepressant-like effect by increasing dopamine levels in mice.
In another significant study, researchers randomized 30 menopausal individuals to receive either a placebo or Lion's Mane (four 500 mg supplements daily for four weeks). Those who took Lion's Mane had a significant reduction in depression compared to the placebo group, demonstrating its potential for mood support during challenging life transitions.
Immune System Enhancement
Research indicates that Lion's Mane mushrooms can significantly boost immune system function through multiple pathways. Studies on mice suggest that Lion's Mane mushrooms may boost the activity of the intestinal immune system, while other research indicates that a protein in Lion's Mane mushrooms encourages the growth of beneficial gut bacteria that strengthen immunity.
The mushrooms contain potent antioxidants, which are substances that limit the damage of free radicals and help combat chronic inflammation. Many health conditions, including heart disease, arthritis, and cancer, involve chronic inflammation and the effects of unstable molecules called free radicals, making Lion's Mane's antioxidant properties particularly valuable.
Digestive Health and Gut Protection
Lion's Mane mushrooms offer significant benefits for digestive health, particularly in protecting the stomach lining and reducing inflammation in the digestive tract. Several older studies have found that Lion's Mane extract can prevent the growth of H. pylori in test tubes, a bacteria linked with many stomach ulcers.
Animal studies have demonstrated that Lion's Mane extract was more effective at preventing alcohol-induced stomach ulcers than traditional acid-lowering drugs, and without any negative side effects. The extract can also reduce inflammation and prevent tissue damage in other intestinal areas, potentially helping treat inflammatory bowel diseases like ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
Nutritional Profile and Bioactive Compounds
Essential Vitamins and Minerals
Lion's Mane mushrooms are rich in essential nutrients that support overall health and wellbeing. They contain significant amounts of thiamine, riboflavin, and niacin, important B-vitamins that support energy metabolism and nervous system function. The mushrooms are also a good source of essential minerals such as manganese, zinc, and potassium, which play crucial roles in various physiological processes.
These mushrooms are also packed with plant compounds and are low in calories and salt, making them an excellent addition to health-conscious diets. The protein content of Lion's Mane mushrooms is notable for a fungal source, providing essential amino acids that support muscle maintenance and overall health.
Unique Bioactive Compounds
The therapeutic effects of Lion's Mane mushrooms stem from their unique collection of bioactive compounds. The most important of these are hericenones and erinacines, which are responsible for the mushroom's neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties. These compounds are unique to the Hericium genus and are not found in other mushroom species.
Additionally, Lion's Mane contains beta-glucan polysaccharides, which contribute to immune system support and overall health benefits. The mushrooms also contain various phenolic acids, lectins, proteins, fatty acids, and sterols that work synergistically to provide the full spectrum of health benefits.
Culinary Applications and Flavor Profile
Distinctive Taste and Texture
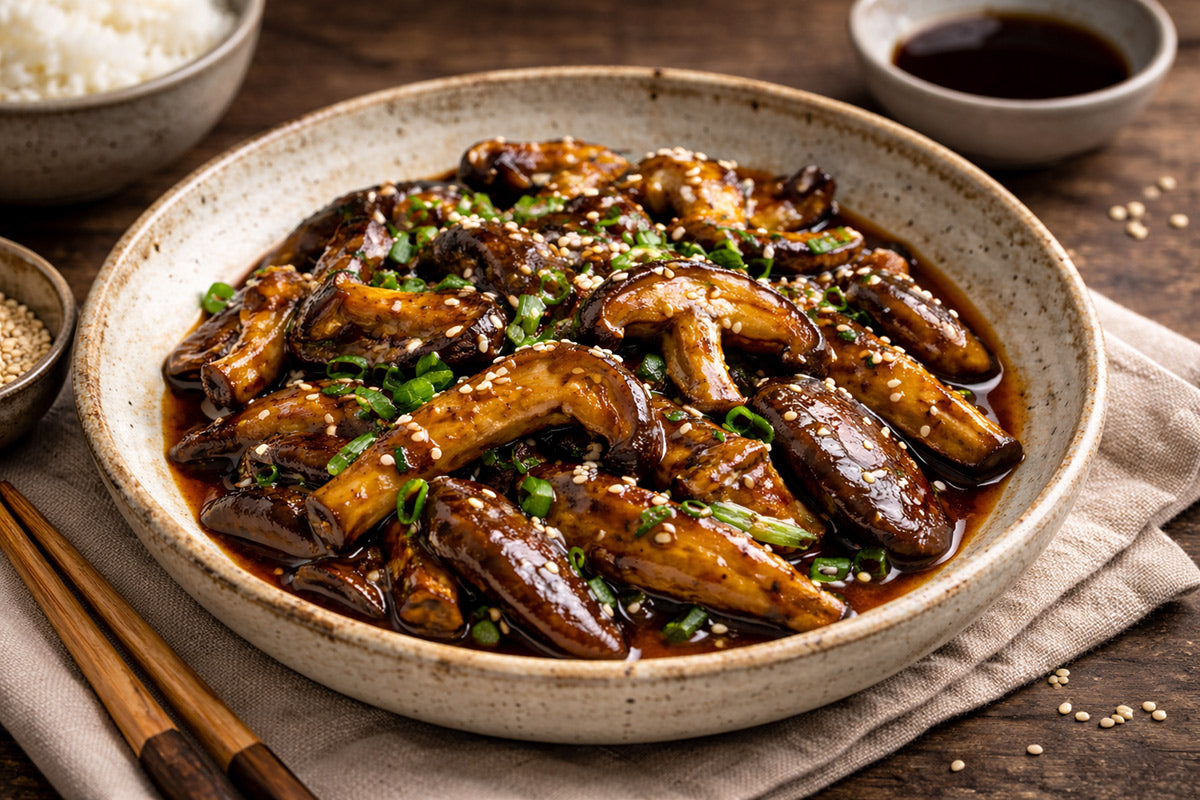
Lion's Mane mushrooms have earned acclaim in culinary circles for their distinctive flavor and texture that many describe as remarkably similar to seafood, particularly crab or lobster. This unique characteristic makes them an exceptional plant-based substitute for seafood in various recipes, earning them particular appreciation among vegetarian and vegan cooks.
The texture of Lion's Mane is dense and meaty when cooked properly, with a satisfying bite that holds up well to various cooking methods. Raw Lion's Mane has a subtly sweet flavor, but cooking transforms it into something much more complex and savory, developing umami-rich notes that enhance any dish.
Preparation and Cooking Methods
Basic Preparation Techniques
When preparing Lion's Mane mushrooms, proper cleaning is essential. Clean off any dirt from your mushrooms using a mushroom brush or a damp piece of kitchen roll, but avoid soaking them as they can absorb too much liquid and become soggy. Cut off the bottoms of the mushrooms, then slice them into 1/4 to 1/2 inch pieces, depending on your intended use.
Sautéing Method
The most popular cooking method involves sautéing sliced Lion's Mane in a dry pan over medium-high heat initially to allow excess moisture to evaporate. Once the mushrooms reduce in size, add butter and oil, cooking until they become golden brown on both sides. This process typically takes 5-7 minutes total and results in perfectly caramelized mushrooms with concentrated flavors.
Pan-Searing Technique
For a more substantial preparation, cut Lion's Mane into thick "steaks" and sear them in a hot cast-iron skillet. Season both sides with salt, pepper, and a light dusting of flour before searing. Cook for 3-4 minutes per side until golden brown, then finish with butter, garlic, and fresh herbs for an elegant presentation.
Popular Recipe Applications
Seafood Substitutes
Lion's Mane's seafood-like flavor makes it perfect for "crab" cakes, where the mushroom is broken into chunks, mixed with traditional crab cake seasonings, formed into patties, and pan-fried until golden. Many people find Lion's Mane mushrooms to be an excellent imitator of lobster when fried in a pan and dipped in melted butter.
Meat Alternatives
The mushrooms work exceptionally well as chicken substitutes in various dishes, from stir-fries to pasta preparations. Their ability to absorb flavors makes them versatile additions to curries, soups, and stews where they take on the surrounding flavors while contributing their own unique taste and substantial texture.
Gourmet Preparations
High-end restaurants often feature Lion's Mane as the star ingredient in sophisticated preparations, serving them as "steaks" over creamy polenta or incorporating them into elegant risottos and pasta dishes where their unique texture and flavor can be fully appreciated.
Growing Lion's Mane Mushroom at Home
Indoor Cultivation Methods
Growing Lion's Mane mushrooms at home has become increasingly popular due to the availability of high-quality growing kits and the substantial cost savings compared to purchasing fresh mushrooms at retail prices. The mushrooms are reasonably easy to cultivate, though they require more attention than some other common varieties.
Using Growing Kits
The easiest way for beginners to start growing Lion's Mane is with commercial growing kits. These kits contain pre-colonized substrate blocks that are ready to fruit. Simply remove the kit from its packaging, cut an "X" into the plastic bag, and mist 2-3 times daily with the included spray bottle. Mushrooms typically begin forming within 1-2 weeks and are ready to harvest 2-5 days after pin formation.
Substrate Preparation
For more advanced growers, Lion's Mane grows best on supplemented hardwood sawdust, typically supplemented with wheat bran at 10-20%. The substrate should be sterilized before inoculation to prevent contamination, and higher spawn rates are recommended to increase the chances of successful colonization.
Environmental Requirements
Lion's Mane mushrooms prefer specific environmental conditions for optimal growth. During the growing phase, maintain temperatures between 60-85°F (15-30°C) with humidity levels around 80-90%. The mushrooms need adequate fresh air exchange, as poor ventilation can result in stringy, malformed growth.
Outdoor Log Cultivation
Log Selection and Preparation
For outdoor cultivation, select freshly cut hardwood logs from oak, maple, or beech trees. The logs should be 3-8 inches in diameter and 3-4 feet in length. Allow fresh logs to rest for 2-6 weeks before inoculation to let the tree's natural antifungal compounds dissipate.
Inoculation Process
Drill holes in the logs at regular intervals and insert Lion's Mane spawn plugs or sawdust spawn. Seal the holes with food-grade wax to prevent contamination and moisture loss. Place the inoculated logs in a shaded area with protection from wind and direct sunlight.
Long-term Management
Outdoor log cultivation is a longer-term project, with mushrooms typically appearing 6-12 months after inoculation, depending on log size and environmental conditions. However, properly maintained logs can continue producing mushrooms for several years, providing a sustainable source of fresh Lion's Mane.
Harvesting and Storage
Optimal Harvest Timing
Harvest Lion's Mane mushrooms when they reach full size but before the spines begin to turn yellow or brown. The mushrooms should feel firm and have a bright white color throughout. Younger mushrooms can be harvested for a more tender texture, while more mature specimens offer stronger flavor.
Proper Storage Methods
Fresh Lion's Mane mushrooms should be stored in the refrigerator in a paper bag or paper towel-lined container to maintain proper moisture levels while allowing air circulation. They typically keep for up to one week when stored properly. For longer storage, mushrooms can be dried, frozen, or processed into extracts.

Lion's Mane Supplements and Products
Available Forms and Types
Lion's Mane supplements come in numerous forms to accommodate different preferences and needs. As a supplement, the mushroom comes in powders, liquids, and capsules, each offering distinct advantages for various applications.
Powder Forms
Powdered Lion's Mane mushrooms can be easily incorporated into smoothies, teas, coffee, or recipes. This form is especially convenient for those who want to control their dosage precisely and enjoy the flexibility of mixing the supplement into their favorite beverages or foods.
Capsule Supplements
Capsules provide the most convenient and precise dosing option, making them ideal for consistent daily supplementation. High-quality capsule supplements are made from organic mushroom extracts with guaranteed levels of beneficial compounds like beta-glucans.
Liquid Extracts and Tinctures
Liquid extracts offer rapid absorption and can be taken directly or added to beverages. These concentrated forms often provide higher potency than powder or capsule forms and may include both water and alcohol extractions to capture the full spectrum of bioactive compounds.
Quality Considerations and Standards
Source and Processing
When selecting Lion's Mane supplements, prioritize products made from organic mushroom fruiting bodies rather than mycelium grown on grain. Fruiting body extracts contain higher concentrations of beneficial compounds and avoid the starch content found in mycelium products.
Standardization and Testing
Look for supplements that provide guaranteed levels of beta-glucans, typically 25-30% or higher. Reputable manufacturers test their products for heavy metals, agricultural chemicals, and microbial contamination to ensure safety and purity.
Extraction Methods
The best Lion's Mane supplements use dual extraction methods, combining both water and alcohol extraction to capture both water-soluble and alcohol-soluble compounds. This comprehensive approach ensures maximum bioavailability of the mushroom's beneficial components.
Dosage Guidelines and Usage
General Dosage Recommendations
Because Lion's Mane mushrooms haven't undergone extensive human studies, there's no standardized dose, and different amounts have been used in various research studies. For example, older adults with mild cognitive impairment in one study took 250 milligrams of mushroom powder three times daily, totaling less than 1 gram per day.
Other studies have used higher doses, with some research using 1.5-2 grams daily for various health applications. A 2023 study investigating cognitive effects used 1.8 grams daily, showing that this dosage was well-tolerated and produced measurable benefits.
Timing and Administration
Lion's Mane supplements can be taken with or without food, though some people find better digestive tolerance when taken with meals. For cognitive benefits, many users prefer taking their supplement in the morning to support mental clarity throughout the day.

Safety Profile and Considerations
General Safety and Side Effects
Lion's Mane mushrooms are generally recognized as safe for most people and have not been linked to serious adverse effects. No adverse effects have been seen in animal studies, even at doses as high as 2.3 grams per pound of body weight per day for extended periods.
In human studies, side effects are typically mild and may include stomach discomfort, nausea, and occasionally skin rash. These effects are generally temporary and resolve when the supplement is discontinued or the dose is reduced.
Important Precautions and Contraindications
Allergic Reactions
Anyone who is allergic or sensitive to mushrooms should avoid Lion's Mane since it's a mushroom species. There have been documented cases of people experiencing difficulty breathing or skin rashes after exposure to Lion's Mane mushrooms, likely related to mushroom allergies.
Autoimmune Conditions
Lion's Mane mushroom might cause the immune system to become more active, which could increase the symptoms of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other conditions. People with these conditions should consult healthcare providers before using Lion's Mane supplements.
Blood Clotting and Surgery
Lion's Mane mushroom might slow blood clotting, which could increase the chances of bruising and bleeding in people with bleeding conditions. Additionally, it might interfere with blood sugar control during and after surgery, so users should stop taking Lion's Mane at least 2 weeks before scheduled surgery.
Drug Interactions
Diabetes Medications
Lion's Mane mushroom might lower blood sugar levels, so taking it along with diabetes medications might cause blood sugar to drop too low. People with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar closely when using Lion's Mane supplements.
Blood-Thinning Medications
Taking Lion's Mane mushroom along with medications that slow blood clotting might increase the risk of bruising and bleeding. This includes medications like warfarin, aspirin, and other anticoagulants.
Immunosuppressant Medications
Since Lion's Mane can increase immune system activity, it might decrease the effectiveness of medications used to suppress the immune system, such as those prescribed after organ transplants.
Research and Future Directions
Current Scientific Understanding
The scientific research on Lion's Mane mushrooms continues to expand, with studies investigating both their traditional uses and new potential applications. Most current research has been conducted in laboratory settings and animal models, with limited but promising human studies showing cognitive and mood benefits.
Recent research has focused on understanding the mechanisms behind Lion's Mane's neuroprotective effects, particularly how hericenones and erinacines stimulate nerve growth factor production and support brain health. These findings provide a scientific foundation for the traditional uses of Lion's Mane in cognitive support.
Emerging Research Areas
Cancer Research
Preliminary studies have shown that Lion's Mane extracts demonstrate antiproliferative and antimetastatic activities in preclinical cancer models. While these results are promising, human studies are needed to determine whether these effects translate to clinical applications.
Metabolic Health
Emerging research suggests that Lion's Mane may have benefits for metabolic health, including blood sugar regulation and lipid metabolism. Some studies indicate potential benefits for individuals with metabolic syndrome and related conditions.
Gut-Brain Connection
Scientists are increasingly interested in Lion's Mane's effects on the gut-brain axis, particularly how its impact on gut bacteria diversity might influence cognitive function and mood. Clinical findings suggest Lion's Mane may increase diversity of the gut microbiome, which could explain some of its cognitive benefits.
Future Clinical Applications
As research continues to validate the traditional uses of Lion's Mane mushrooms, we may see development of standardized extracts for specific clinical applications. Areas of particular interest include age-related cognitive decline, mood disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases.
The growing body of research supports the potential for Lion's Mane to become an important tool in integrative medicine approaches to brain health, though larger, well-designed clinical trials are needed to establish definitive therapeutic protocols.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Lion's Mane Mushroom
Lion's Mane mushrooms represent a remarkable convergence of culinary excellence and therapeutic potential, offering benefits that extend far beyond their distinctive appearance and delicious flavor. From their traditional use in ancient Chinese medicine to modern scientific validation of their cognitive-enhancing properties, these unique fungi continue to demonstrate why they deserve their reputation as nature's brain-boosting superfood.
Whether you're drawn to Lion's Mane mushrooms for their potential to support memory and cognitive function, their ability to enhance mood and reduce stress, or simply their exceptional culinary versatility as a seafood substitute, these remarkable fungi offer something valuable for almost everyone. The growing body of scientific research continues to validate many traditional uses while uncovering new potential applications for human health.
For those interested in incorporating Lion's Mane into their wellness routine, the various forms available—from fresh mushrooms for cooking to standardized supplements for consistent dosing—make it easy to find an approach that fits individual needs and preferences. Whether grown at home using simple growing kits or purchased from reputable supplement manufacturers, Lion's Mane offers an accessible way to support both brain health and overall wellbeing.
As research continues to explore the full potential of Lion's Mane mushrooms, their role in supporting cognitive health, immune function, and overall vitality becomes increasingly clear. For those seeking natural approaches to brain health and wellness, Lion's Mane mushrooms represent one of nature's most promising and well-researched options, backed by both centuries of traditional use and growing scientific validation.
The future of Lion's Mane mushrooms looks bright, with ongoing research likely to uncover even more applications and benefits. For now, those who choose to embrace these remarkable fungi can feel confident in their decision to support their health with one of nature's most unique and beneficial mushrooms.













Share:
Shiitake Mushrooms: A Culinary and Nutritional Powerhouse
King Oyster Mushroom - Meaty Texture and Rich Flavor