Introduction to Black Trumpet Mushrooms
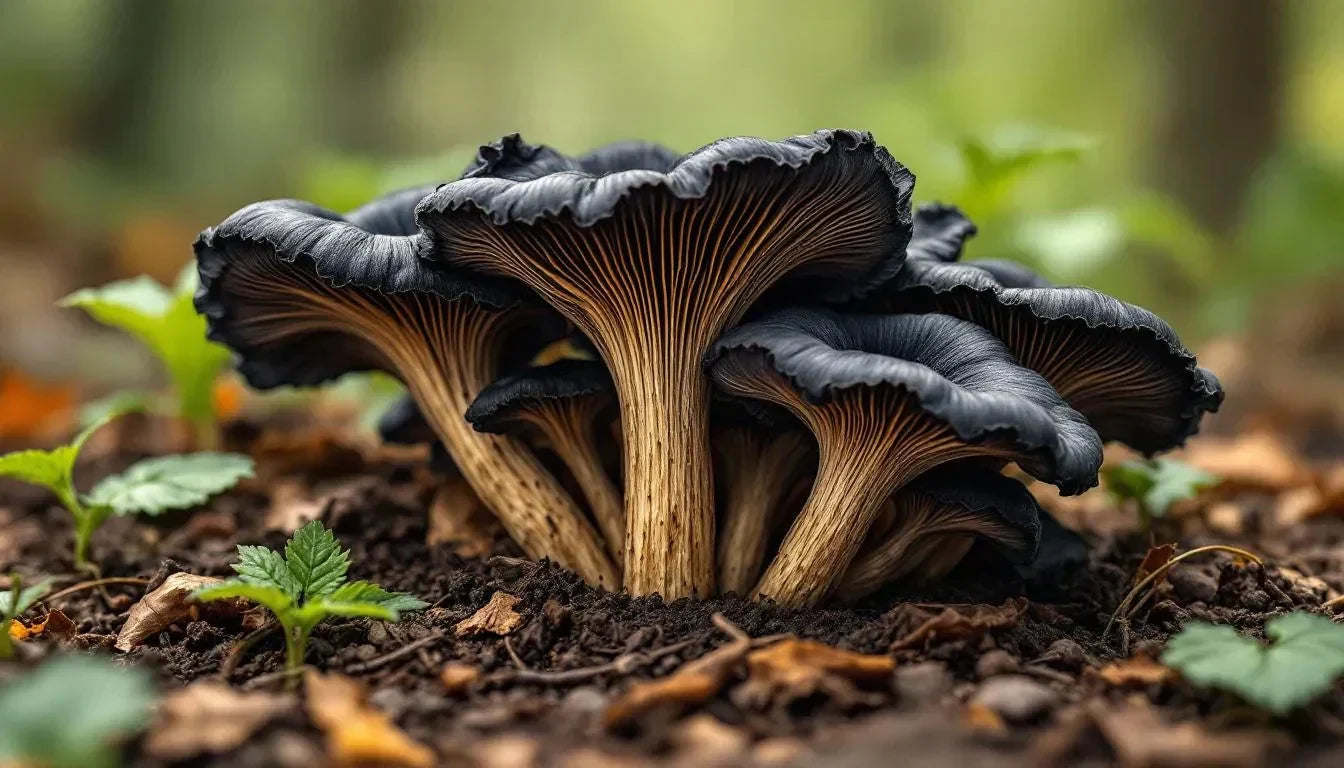
Black trumpet mushrooms (Craterellus cornucopioides), also known as the horn of plenty or trumpet of death, are among the most distinctive and prized wild mushrooms in the culinary world. Despite their somewhat ominous alternate name, these mushrooms are completely safe to eat and highly sought after by chefs and mushroom enthusiasts alike. Their unique appearance—resembling dark, trumpet-shaped funnels—and their extraordinary flavor profile make them one of the most coveted wild mushrooms in gourmet cuisine.
These woodland treasures belong to the Cantharellaceae family, making them relatives of the more commonly known chanterelle mushrooms. However, black trumpets possess a more intense flavor and aroma than their golden cousins, earning them special status among culinary experts. What makes black trumpet mushrooms particularly interesting is their ability to hide in plain sight—their dark coloration blends perfectly with the forest floor, making them one of the most challenging mushrooms to forage.
Physical Characteristics and Identification
Distinctive Features
Black trumpet mushrooms have several defining characteristics that distinguish them from other wild mushrooms:
- Color: Deep brownish-black to nearly black exterior with a lighter, grayish interior
- Shape: Hollow, trumpet or funnel-shaped with wavy, flared edges
- Size: Typically 2-4 inches tall and 1-3 inches wide at the opening
- Texture: Thin-fleshed and somewhat fragile, with a slightly velvety surface
- Stem: No distinct stem; the entire fruiting body forms a continuous hollow tube
- Spore surface: Smooth or slightly wrinkled outer surface (lacks gills, pores, or teeth)
- Spore color: Pale cream to whitish
Identification Tips
For those interested in foraging, properly identifying black trumpet mushrooms is essential. Look for these key features:
- The complete hollow tube from top to bottom (when cut lengthwise)
- The absence of true gills (unlike many mushrooms that have distinct gill structures)
- The thin, almost papery flesh when mature
- A slight bluish or purplish tint in some specimens
- A fragrant, fruity aroma often compared to apricots or black tea
- Growth in clusters or scattered groups, rarely as single specimens
Look-alikes and Differentiation
Black trumpet mushrooms have few dangerous look-alikes, which makes them relatively safe for foraging. However, several similar mushrooms might cause confusion:
- Devil's Urn (Urnula craterium): Appears in early spring rather than summer/fall, has a more cup-like shape, and lacks the fruity aroma
- Black Elfin Saddle (Helvella lacunosa): Has a distinct stem and saddle-shaped cap, not truly trumpet-shaped
- False Chanterelle (Hygrophoropsis aurantiaca): Orange-yellow with true gills, not black and smooth
- Dead Man's Fingers (Xylaria polymorpha): Club-shaped, not hollow, and grows on wood rather than soil
Habitat and Distribution
Natural Growing Conditions
Black trumpet mushrooms thrive in specific ecological conditions that knowledgeable foragers learn to recognize:
- Forest type: Primarily hardwood forests, especially those with oak, beech, or maple trees
- Soil conditions: Rich, moist, well-draining soil with accumulated leaf litter
- Moss association: Often found growing among moss patches
- Terrain: Preference for sloped terrain, hillsides, and water runoff paths
- Moisture levels: Require consistent moisture but not saturated conditions
- Light conditions: Deeply shaded areas where direct sunlight rarely penetrates
Geographical Distribution
While black trumpet mushrooms can be found across several continents, their distribution varies:
- North America: Throughout eastern regions from Canada to the southern United States; also along the Pacific Northwest coast
- Europe: Widespread across temperate European forests, particularly in France, Italy, and Spain
- Asia: Found in temperate regions, though less commonly documented
- Seasonality: Typically fruit from late summer through fall, though regional variations exist
Mycorrhizal Relationships
Black trumpet mushrooms form mycorrhizal relationships with certain tree species, meaning they live in a mutually beneficial relationship with tree roots. This symbiotic relationship involves:
- The mushroom providing minerals and water to the tree
- The tree providing carbohydrates to the mushroom
- An interconnected network often called the "wood wide web"
- Preference for mature, established forests over younger woodlands

Culinary Qualities and Flavor Profile
Distinctive Flavor Characteristics
Black trumpet mushrooms are treasured for their exceptional flavor profile, which is more complex than many other wild mushrooms:
- Base notes: Rich, earthy, and smoky
- Secondary notes: Fruity undertones reminiscent of apricots or black currants
- Aromatic qualities: Fragrant with hints of black tea and truffle
- Flavor intensity: Concentrated and potent, especially when dried
- Umami factor: Exceptionally high, contributing to its meat-like satisfaction
- Finish: Long-lasting with a slight peppery quality
Texture and Cooking Properties
The unique physical structure of black trumpet mushrooms influences their culinary applications:
- Raw texture: Slightly firm yet fragile
- Cooked texture: Tender without becoming mushy
- Liquid absorption: Excellent absorption of cooking fats and flavors
- Rehydration: Exceptional rehydration when dried, retaining shape and texture
- Cooking methods: Responsive to various cooking techniques, from quick sautéing to slow braising
- Color impact: Imparts a striking dark hue to dishes, often used for visual impact
Culinary Complementary Ingredients
Black trumpet mushrooms pair exceptionally well with certain ingredients that highlight their unique qualities:
- Dairy: Cream, butter, and soft cheeses
- Proteins: Chicken, veal, and delicate seafood
- Herbs: Thyme, marjoram, and tarragon
- Alcohols: Dry sherry, cognac, and white wine
- Starches: Risotto, polenta, and egg pasta
- Vegetables: Leeks, fennel, and celery root
Nutritional Profile and Health Benefits
Nutrient Composition
Black trumpet mushrooms offer an impressive nutritional profile, particularly when considering their wild origins:
- Protein: Higher protein content than many cultivated mushrooms
- Fiber: Excellent source of dietary fiber
- Vitamins: Rich in B vitamins, particularly riboflavin (B2) and niacin (B3)
- Minerals: Contains potassium, copper, and selenium
- Antioxidants: High levels of antioxidant compounds
- Calories: Low in calories, making them diet-friendly
Potential Health Benefits
Research into wild mushrooms suggests black trumpets may offer several health advantages:
- Immune support: Contains beta-glucans that may support immune function
- Antioxidant activity: Helps combat oxidative stress through various compounds
- Anti-inflammatory properties: May help reduce inflammatory responses
- Prebiotic potential: Supports beneficial gut bacteria through indigestible fiber
- Mineral absorption: Contains compounds that may enhance mineral absorption
- Protein quality: Provides all essential amino acids, rare for plant-based foods
Traditional and Historical Uses
Historically, black trumpet mushrooms have been valued beyond their culinary applications:
- Traditional medicine: Used in European folk medicine for digestive issues
- Seasonal tonic: Consumed as a seasonal health tonic in some cultures
- Dye production: Used as a natural fabric dye in traditional textile arts
- Forest indicators: Their presence used as indicators of forest health and biodiversity

Foraging and Identification Tips
When and Where to Look
Successful black trumpet mushroom foraging requires understanding their growth patterns:
- Prime season: Late summer through fall (varies by region)
- Weather conditions: Often appear after periods of rain followed by warm days
- Growth patterns: May reappear in the same location for multiple years
- Time of day: More visible during overcast days when contrast is higher
- Specific habitats: Check moss-covered areas, water runoff paths, and around decaying logs
- Tree associations: Focus on areas near oak, beech, and maple trees
Sustainable Harvesting Practices
Responsible foraging ensures black trumpet populations remain viable:
- Selective picking: Harvest only mature specimens, leaving smaller ones to develop
- Cutting vs. pulling: Cut mushrooms at the base rather than pulling to minimize soil disturbance
- Spore dispersal: Carry harvested mushrooms in mesh bags to spread spores while walking
- Percentage harvesting: Take no more than 50% of mushrooms from any single patch
- Rotation: Avoid harvesting from the same exact location in consecutive years
- Environmental awareness: Stay on established paths to minimize forest floor damage
Safety Considerations
While black trumpets are considered safe, foraging requires proper precautions:
- Positive identification: Always be 100% certain of identification before consumption
- Expert verification: Have finds verified by experienced foragers when beginning
- Testing: Try small amounts first when eating for the first time
- Clean harvesting: Avoid specimens growing near polluted areas or roadsides
- Proper cleaning: Clean thoroughly to remove debris, insects, and contaminants
- Land regulations: Be aware of legal restrictions on foraging in certain areas
Preparation and Cooking Methods
Cleaning and Preparation
Black trumpet mushrooms require special attention when cleaning due to their trumpet shape:
- Debris removal: Gently tap to remove loose forest debris
- Initial inspection: Examine for insects hiding inside the trumpet
- Dry brushing: Use a soft mushroom brush or pastry brush for initial cleaning
- Water technique: If necessary, brief water immersion followed by immediate drying
- Slicing: Cut lengthwise to inspect and clean the interior surface
- Drying: Thoroughly dry on paper towels before cooking
Classic Cooking Methods
Several cooking techniques showcase black trumpet mushrooms' exceptional qualities:
Dry Sautéing
- Heat a heavy pan without oil until hot
- Add cleaned mushrooms and cook until they release their moisture
- Once moisture evaporates, add butter or oil and seasonings
- Continue cooking until edges begin to crisp slightly
Cream-Based Preparations
- Sauté mushrooms in butter until tender
- Add minced shallots and garlic, cooking until fragrant
- Deglaze with white wine or sherry
- Add heavy cream and reduce until thickened
- Finish with fresh herbs and black pepper
Infusions and Broths
- Combine mushrooms with aromatics in water or stock
- Simmer gently to extract flavors
- Strain for clear broth or blend for creamy soup
- Season with complementary herbs and spices
Preservation Methods
To enjoy black trumpet mushrooms year-round, several preservation methods work well:
- Drying: Air-dry or use a food dehydrator at low temperature until completely crisp
- Freezing: Sauté first, then cool and freeze in portion-sized containers
- Oil preservation: Store in olive oil with herbs (refrigerate and use within 1 month)
- Powder production: Grind dried mushrooms into powder for seasoning
- Compound butter: Mix chopped sautéed mushrooms into butter, roll, and freeze
- Pickling: Prepare in vinegar-based brine with complementary spices
Commercial Availability and Selection
Market Forms
Black trumpet mushrooms are available commercially in several forms:
- Fresh: Seasonal availability at farmers' markets, specialty grocers, and gourmet shops
- Dried: Most common year-round form, typically packaged in small quantities
- Frozen: Less common but available from some specialty suppliers
- Powdered: Ground dried mushrooms sold as seasoning
- Preserved: Occasionally available in oil, vinegar, or as part of prepared foods
- Online sources: Specialty mushroom retailers offering various forms
Quality Indicators
When purchasing black trumpet mushrooms, look for these quality signs:
- Fresh mushrooms: Flexible not brittle, clean without excessive dirt, aromatic
- Dried mushrooms: Intense fragrance, completely dry with no moisture, uniform color
- Packaging: Proper packaging that protects from moisture and damage
- Source information: Transparent information about origin and harvest methods
- Certifications: Organic or wild-harvested certifications when available
- Price: Be wary of prices that seem too low, as quality wild mushrooms command premium prices
Storage Recommendations
Proper storage extends the usability of black trumpet mushrooms:
- Fresh: Refrigerate in paper bag for 3-5 days maximum
- Dried: Store in airtight container in cool, dark place for up to 1 year
- Rehydrated: Use immediately, do not store after rehydration
- Frozen: Maintain at 0°F (-18°C) for up to 6 months
- Powdered: Keep in sealed container away from light and moisture for up to 1 year
- Preserved in oil: Refrigerate and use within 1 month
Culinary Applications and Recipe Ideas
Signature Dishes
Black trumpet mushrooms shine in several classic preparations:
- Black Trumpet Risotto: The earthiness complements the creamy rice perfectly
- Trumpet and Truffle Pasta: Combined with light cream sauce and fresh pasta
- Wild Mushroom Tart: Featured with other wild mushrooms in a savory pastry
- Black Trumpet Soup: Showcased in a velvety puréed soup
- Mushroom Conserva: Preserved in herbed oil as an antipasto
- Trumpet-Crusted Meats: Used as a flavorful coating for meats before roasting
Creative Modern Uses
Innovative chefs have developed contemporary applications:
- Black Trumpet Butter: Compound butter for finishing steaks or vegetables
- Mushroom Tea: Steeped as an aromatic broth or consommé
- Infused Oils: Flavoring oils for dressing and finishing dishes
- Trumpet Powder Rubs: Dried and ground for use in spice blends
- Fermented Preparations: Lacto-fermented for probiotic benefits
- Dessert Applications: Paired with chocolate or caramel in adventurous desserts
Home Cook-Friendly Recipes
Accessible recipes for home cooks to showcase black trumpet mushrooms:
Black Trumpet and Chicken Pot Pie
Incorporating rehydrated trumpets into the classic comfort dish adds depth and sophistication.
Simple Black Trumpet Crostini
- Sauté mushrooms with shallots and garlic
- Deglaze with white wine
- Mount with butter and herbs
- Serve on toasted baguette slices with optional soft cheese
Black Trumpet Scrambled Eggs
Adding sautéed black trumpets to soft scrambled eggs creates a luxurious breakfast or light dinner.
Cultural Significance and History
Historical Usage
Black trumpet mushrooms have a rich history in various culinary traditions:
- French cuisine: Long prized in French cooking, particularly in rural regions
- Italian traditions: Featured in risottos and pasta dishes throughout northern Italy
- Eastern European foraging: Important seasonal food source in Slavic countries
- Native American usage: Documented use by indigenous peoples in North America
- Medieval Europe: Mentioned in historical texts as foraged food during autumn
Cultural Representations
These distinctive mushrooms appear in cultural contexts beyond the plate:
- Folklore: Featured in European fairy tales and folklore
- Artistic depictions: Represented in still life paintings from the Renaissance onward
- Seasonal celebrations: Associated with autumn harvest festivals in some regions
- Modern gastronomy: Celebrated in contemporary fine dining as a marker of seasonal cooking
- Foraging revival: Central to the modern wild food and foraging movement
Conclusion: The Allure of Black Trumpet Mushrooms
Black trumpet mushrooms represent one of nature's most remarkable culinary treasures. Their distinctive appearance, exceptional flavor profile, and relative rarity contribute to their mystique and desirability. From forest floor to fine dining, these mushrooms connect us to ancient foraging traditions while simultaneously inspiring modern culinary innovation.
For the home cook, experimenting with black trumpet mushrooms offers an opportunity to explore flavors and textures that cannot be replicated by cultivated varieties. Their intense umami qualities and complex aromatics can transform even simple dishes into memorable dining experiences. Whether foraged personally or purchased from specialty suppliers, black trumpet mushrooms deserve their reputation as one of the most prized wild edibles.
As interest in wild foods continues to grow, the black trumpet mushroom stands as a prime example of the exceptional flavors that can only be found in nature. By respecting sustainable harvesting practices and preserving traditional knowledge about these remarkable fungi, we can ensure that future generations will also have the opportunity to discover the unique pleasures of the black trumpet mushroom.















Share:
Mushroom Seasoning: The Complete Guide to Nature's Umami Flavor Enhancer
Seeding Microgreens: The Complete Guide to Growing Nutrient-Dense Greens at Home