Introduction to Lion's Mane Mushroom Cultivation
Lion's Mane mushroom (Hericium erinaceus) represents one of the most distinctive and valuable medicinal and culinary mushrooms available to home and commercial cultivators. With its cascading white tendrils resembling a lion's mane—or alternatively, a pom-pom, monkey's head, or bearded tooth mushroom—this fungus has captured increasing attention for both its unique appearance and impressive health benefits. Native to North America, Europe, and Asia, Lion's Mane grows naturally on hardwood trees, particularly American beech, but has been successfully adapted to various cultivation methods accessible to growers of all experience levels.
Unlike many gourmet mushrooms that require precise environmental controls, Lion's Mane offers reasonable forgiveness for cultivation mistakes, making it an excellent choice for beginners while still providing enough complexity to engage experienced mycologists. Its growing popularity stems not only from its relative ease of cultivation but also from its remarkable nutritional and medicinal properties, including support for cognitive function, nerve regeneration, immune modulation, and digestive health.
This comprehensive guide to Lion's Mane mushroom cultivation provides a structured approach to growing this exceptional fungus, from understanding its basic biology and lifecycle to mastering advanced cultivation techniques. Whether you're a hobbyist looking to produce small quantities for personal use, an urban farmer interested in supplying local markets, or a commercial grower seeking to scale production, this guide offers the practical knowledge needed to successfully cultivate Lion's Mane mushrooms in various settings and with different resources.

Understanding Lion's Mane Mushroom Biology
Before beginning cultivation, it's essential to understand the basic biology and lifecycle of Lion's Mane mushrooms, as this knowledge forms the foundation for successful growing practices.
Taxonomy and Identification
Lion's Mane belongs to a distinct family of fungi with unique characteristics:
- Scientific classification: Hericium erinaceus, belonging to the family Hericiaceae
- Related species: H. americanum, H. coralloides, and H. abietis, which share similar appearance and growing requirements
- Distinguishing features: Cascading white spines or "teeth" instead of the typical cap and gills structure
- Growth pattern: Produces a single clump of dangling spines rather than multiple fruiting bodies
- Natural color: Typically snow-white when fresh, yellowing slightly with age
- Spore print: White to cream-colored
Understanding these characteristics helps ensure proper identification and selection of cultivation strains.
Lifecycle and Growth Stages
The Lion's Mane lifecycle follows the typical pattern of most cultivated fungi:
- Spore germination: Spores develop into primary mycelium
- Mycelial growth: Primary mycelium expands, forming a network throughout the substrate
- Primordia formation: Small white bumps appear, signaling the beginning of fruiting body development
- Fruiting body development: Primordia develop into the characteristic spine-covered structures
- Spore production: Mature fruiting bodies release spores, completing the lifecycle
Each stage requires specific environmental conditions for optimal development, which will be addressed in cultivation practices.
Natural Habitat and Substrate Preferences
In nature, Lion's Mane displays specific preferences that inform cultivation practices:
- Host trees: Primarily grows on hardwoods, particularly American beech, oak, maple, and walnut
- Growth position: Typically fruits on dead or dying trees, both standing and fallen
- Timing: Usually fruits in late summer through fall in temperate climates
- Substrate composition: Prefers partially decomposed wood with specific lignin/cellulose ratios
- Environmental conditions: Thrives in humid, moderately cool forest environments
- Competitive strategy: Specialized decomposer that often appears after primary decomposers
These natural preferences provide important clues for creating optimal cultivation conditions.
Equipment and Supplies for Lion's Mane Cultivation
Successful Lion's Mane cultivation requires specific equipment and supplies, which vary depending on the chosen cultivation method and scale.
Basic Equipment for Beginners
For those just starting, these essential items provide a foundation:
- Pressure cooker/autoclave: For sterilizing substrates (minimum 15-quart capacity recommended)
- Spray bottles: For maintaining humidity and misting fruiting chambers
- Thermometer/hygrometer: For monitoring temperature and humidity
- Heat mat with controller: For maintaining optimal mycelium incubation temperature
- Clean work surface: For inoculation procedures
- Isopropyl alcohol (70%): For sanitizing surfaces and tools
- Nitrile gloves: For handling substrates and maintaining cleanliness
- Mason jars or polypropylene bags: For containing substrate during colonization
- Micropore tape or synthetic filter discs: For allowing gas exchange while preventing contamination
These items allow for small-scale cultivation using simple methods.
Intermediate Equipment
As experience grows, these additional items enhance success:
- HEPA filter: For creating clean air during inoculation procedures
- Still air box or flow hood: For reducing contamination during transfers
- Impulse sealer: For sealing substrate bags
- Humidity controller: For automated humidity management in fruiting chambers
- CO2 monitor: For tracking gas exchange in fruiting environments
- Specialized fruiting chambers: Modified containers designed specifically for mushroom cultivation
- pH meter: For monitoring substrate acidity
- Scale: For precise measurement of substrate ingredients
This equipment improves consistency and reduces contamination issues.
Advanced Commercial Equipment
For large-scale or commercial production:
- Laboratory-grade laminar flow hood: For sterile work environment
- Industrial autoclave: For bulk substrate sterilization
- Automated environmental control systems: For maintaining precise growing conditions
- Specialized incubation rooms: For large-scale mycelium development
- Commercial fruiting rooms: With controlled humidity, temperature, and airflow
- Humidification systems: For maintaining consistent humidity levels
- HVAC systems with HEPA filtration: For clean air circulation
- Automated monitoring and alert systems: For immediate notification of environmental changes
This equipment facilitates scaled production with consistent results.
Substrate Materials
The foundation of Lion's Mane cultivation relies on appropriate substrates:
- Hardwood sawdust: Preferably oak, maple, or beech (primary substrate component)
- Supplemental nutrients: Wheat bran, rice bran, or spent brewer's grain (20-25% of substrate mix)
- Calcium supplements: Gypsum or agricultural lime (1-2% of substrate mix)
- Moisture management: Vermiculite or perlite (optional, 5-10% of substrate mix)
- Water: For achieving proper moisture content (60-65% total moisture)
- pH adjusters: Typically calcium carbonate for raising pH if needed
- Hardwood fuel pellets: Convenient alternative to raw sawdust
- Straw or sugar cane bagasse: Alternative substrates for certain methods
The quality and composition of these materials significantly impact cultivation success.
Cultivation Methods for Lion's Mane Mushrooms
Several proven cultivation methods exist for Lion's Mane, each with advantages and challenges.
Log Cultivation
The most traditional approach mimics Lion's Mane's natural growth habitat:
- Log selection: Freshly cut hardwood logs, 4-8 inches in diameter, 3-4 feet long
- Wood types: Oak, maple, beech, and other hardwoods (avoid softwoods)
- Timing: Logs cut during dormant season (late fall to early spring) when sugar content is highest
- Inoculation method: Drilling holes and inserting sawdust spawn or plug spawn
- Hole pattern: Typically diamond pattern with holes 6-8 inches apart
- Sealing: Covering inoculation sites with wax to prevent contamination
- Incubation: Stacking logs in shaded, humid location for 6-12 months
- Fruiting induction: Soaking logs in cold water for 24 hours
- Production lifespan: 3-5 years of periodic fruiting
This method requires patience but offers long-term production with minimal maintenance.
Sawdust Block Method
The most common commercial method, offering reliable and relatively quick results:
- Substrate formula: 75-80% hardwood sawdust, 20-25% nutritional supplements (wheat bran, etc.), 1-2% gypsum
- Moisture content: Adjusting to 60-65% moisture (substrate should form a ball when squeezed but not drip water)
- Container: Polypropylene bags with filter patch for gas exchange
- Block size: Typically 2.5-5 pounds per bag
- Sterilization: Pressure cooking at 15 PSI for 2-2.5 hours
- Inoculation: Adding grain spawn at 5-10% of substrate weight
- Incubation: 21-30 days at 70-75°F (21-24°C) until fully colonized
- Fruiting initiation: Cutting X-shaped openings in the bag and exposing to fruiting conditions
- Multiple harvests: Typically 2-3 flushes before substrate is exhausted
This method balances efficiency with reasonable yields and is suitable for both hobbyists and commercial growers.
Supplemented Straw Technique
An alternative method using more readily available materials:
- Substrate preparation: Chopping straw into 1-3 inch pieces
- Pasteurization: Hot water bath at 160-170°F (71-77°C) for 1-2 hours
- Supplementation: Adding 10-20% wheat bran after cooling
- Container options: Bags, buckets with holes, or column systems
- Inoculation rate: 10-15% spawn to substrate ratio
- Colonization period: 14-21 days at 70-75°F (21-24°C)
- Fruiting requirements: Similar to sawdust blocks but may produce smaller fruits
- Yield expectations: Generally lower than hardwood substrates but faster colonization
This technique offers a lower-cost entry point but typically produces smaller yields than hardwood methods.
Mason Jar Cultivation
A beginner-friendly method ideal for small-scale production:
- Container: Quart or half-gallon mason jars with modified lids for gas exchange
- Substrate: Similar to sawdust block formula but in smaller quantities
- Sterilization: Pressure cooking jars at 15 PSI for 90-120 minutes
- Inoculation: Adding grain spawn through modified lid using sterile technique
- Incubation: Keeping jars at 70-75°F (21-24°C) until fully colonized (2-3 weeks)
- Fruiting initiation: Removing lids and placing in humidity chamber
- Expected yield: 1-2 ounces fresh weight per quart jar
- Advantages: Low startup cost, easy monitoring of colonization progress
This method is excellent for beginners or those with limited space and resources.

Step-by-Step Cultivation Process
Following a systematic approach to Lion's Mane cultivation increases success rates and productivity.
Spawn Production
Starting with quality spawn provides the foundation for successful cultivation:
- Selecting cultures: Beginning with proven strains from reputable suppliers
- Culture media: Preparing malt extract agar plates or slants
- Tissue culture: Taking tissue samples from healthy specimens (if starting from fresh mushrooms)
- Spore germination: Alternative starting method using spore prints or syringes
- Mother culture maintenance: Transferring and maintaining viable mycelium on agar
- Grain selection: Choosing appropriate grain (rye, wheat, or millet) for spawn
- Grain preparation: Washing, soaking, and draining grain properly
- Sterilization protocol: Pressure cooking prepared grain at 15 PSI for 90 minutes
- Inoculation technique: Transferring culture to sterilized grain using sterile technique
- Incubation conditions: Maintaining 70-75°F (21-24°C) during colonization
- Shaking schedule: Shaking containers at 30% and 70% colonization to distribute mycelium
- Storage considerations: Using fully colonized spawn promptly or refrigerating briefly
Quality spawn production is critical but can be bypassed by purchasing ready-made spawn from commercial suppliers.
Substrate Preparation
Proper substrate preparation significantly impacts cultivation success:
- Material selection: Choosing appropriate hardwood sawdust and supplements
- Measurement ratio: Combining ingredients by weight (typically 75-80% sawdust, 20-25% supplements)
- Hydration technique: Adding water gradually to achieve 60-65% moisture content
- Moisture testing: Performing the squeeze test (ball forms but only a few drops emerge)
- pH adjustment: Ensuring substrate pH between 5.5-6.5, adjusting if necessary
- Bagging procedure: Filling polypropylene bags with filter patches
- Compaction level: Filling without excessive compaction
- Bag sealing: Folding top and securing with clips or heat sealing
- Sterilization: Processing filled bags at 15 PSI for 2-2.5 hours
- Cooling period: Allowing bags to return to room temperature before inoculation
Following these steps creates an optimal growing medium for Lion's Mane mushrooms.
Inoculation Techniques
Proper inoculation minimizes contamination risk while efficiently introducing spawn:
- Work environment preparation: Cleaning and disinfecting all surfaces
- Air quality management: Working in still air box, flow hood, or exceptionally clean environment
- Personal hygiene: Washing hands thoroughly and wearing gloves, mask, and clean clothing
- Tool sterilization: Flaming or alcohol-sterilizing all tools
- Spawn distribution: Adding 5-10% spawn by substrate weight
- Mixing method: Shaking bags or using sterile technique to distribute spawn
- Closing procedure: Properly sealing bags after inoculation
- Labeling system: Marking bags with date and strain information
- Initial placement: Transferring to incubation area with appropriate temperature
Careful attention to sterile technique during this phase dramatically reduces contamination issues.
Incubation Process
Proper incubation ensures complete colonization of the substrate:
- Temperature maintenance: Keeping consistent temperature between 70-75°F (21-24°C)
- Placement considerations: Arranging bags to allow air circulation
- Lighting requirements: Maintaining indirect light or darkness during colonization
- Progress monitoring: Checking for white mycelial growth throughout substrate
- Contamination inspection: Looking for off-colors, unusual odors, or irregular growth patterns
- Shaking schedule: Optionally breaking up mycelium at 30-40% colonization to accelerate growth
- Incubation duration: Allowing 3-4 weeks for complete colonization
- Colonization verification: Confirming substrate appears uniformly white
- Pre-fruiting assessment: Looking for early signs of primordia formation
Patient and proper incubation establishes the foundation for successful fruiting.
Fruiting Conditions
Creating the optimal environment for fruiting body development:
- Temperature adjustment: Reducing to 60-65°F (15-18°C) to initiate fruiting
- Humidity requirements: Maintaining 85-95% relative humidity
- Fresh air exchange: Ensuring adequate ventilation (3-5 air exchanges per hour)
- Light exposure: Providing indirect light (approximately 500-1000 lux)
- Initiating fruiting: Creating 1-2 inch X-shaped cuts in fully colonized bags
- Primordia formation: Observing small white bumps forming at opening (5-10 days)
- Development monitoring: Watching primordia develop into characteristic spine-covered structures
- Growth period: Allowing 5-14 days for full development
- Maturity indicators: Harvesting when spines are well-formed but before yellowing
Maintaining these conditions consistently results in healthy, well-formed Lion's Mane fruiting bodies.
Harvesting and Post-Harvest Handling
Proper harvesting and handling maintains quality and extends shelf life:
- Timing determination: Harvesting when fruiting body is fully developed but before deterioration
- Cutting technique: Using sharp, clean knife to cut at the base of the fruiting body
- Handling precautions: Minimizing touching of the delicate spines
- Cleaning process: Gently removing any substrate debris
- Refrigeration: Storing at 34-38°F (1-3°C) in breathable container
- Shelf life expectations: Typically 5-7 days when properly refrigerated
- Drying option: Slicing into 1/4 inch pieces and dehydrating at 115-125°F (46-52°C)
- Packaging considerations: Using paper bags for fresh mushrooms or airtight containers for dried
- Second flush preparation: Rehydrating substrate block and returning to fruiting conditions
Careful harvesting and proper handling maximize both quality and marketability.
Optimizing Growing Conditions
Fine-tuning environmental conditions significantly impacts yield and quality.
Temperature Management
Temperature affects both growth rate and fruiting quality:
- Spawn run optimal range: 70-75°F (21-24°C) promotes rapid colonization
- Fruiting temperature range: 60-65°F (15-18°C) stimulates primordia formation
- Temperature fluctuation: Slight daily fluctuations (5-10°F) can stimulate fruiting
- Cold shock technique: Brief exposure to lower temperatures (50-55°F) to trigger fruiting
- Heat stress avoidance: Preventing temperatures above 80°F (27°C) which inhibit growth
- Seasonal adjustments: Adapting growing environment to compensate for seasonal changes
- Monitoring frequency: Checking temperatures at least twice daily
- Temperature gradient considerations: Ensuring even temperatures throughout growing area
Consistent temperature management prevents many common cultivation problems.
Humidity Control
Proper humidity levels are critical, especially during fruiting:
- Optimal colonization humidity: 65-75% relative humidity during spawn run
- Fruiting humidity requirements: 85-95% relative humidity for proper development
- Humidity generation methods: Ultrasonic humidifiers, foggers, or manual misting
- Measurement tools: Digital hygrometers for accurate monitoring
- Excessive moisture warning signs: Water droplets forming on fruiting bodies
- Humidity chambers: SGFC (Shotgun Fruiting Chamber), Martha tents, or commercial chambers
- Air exchange balance: Maintaining humidity while ensuring adequate fresh air
- Microclimate considerations: Creating optimal conditions directly around fruiting blocks
Balancing humidity with proper air exchange prevents both drying and bacterial contamination.
Light Requirements
Understanding Lion's Mane's light needs improves fruiting:
- Spectrum preference: Blue spectrum light (5000-6500K) stimulates proper development
- Intensity requirements: Moderate indirect light (500-1000 lux)
- Duration recommendation: 12/12 hour light/dark cycle during fruiting
- Light sources: LED, fluorescent, or indirect natural light
- Positioning considerations: Ensuring even light distribution without heat buildup
- Light during colonization: Minimal light requirements during incubation
- Directional growth response: Fruiting bodies grow toward light source
- Color development impact: Proper lighting enhances white coloration
While not as critical as humidity and temperature, proper lighting improves both yield and appearance.
Air Exchange and Ventilation
Proper gas exchange is essential for healthy fruiting bodies:
- Carbon dioxide sensitivity: High CO2 levels cause elongated, thin fruiting bodies
- Exchange rate: 3-5 fresh air exchanges per hour during fruiting
- Ventilation methods: Fans, hole patterns, or automated systems
- Natural vs. forced air: Considerations for different growing environments
- Air purification: HEPA filtration to reduce contaminants
- Circulation patterns: Ensuring even air movement without direct drafts
- Monitoring options: CO2 meters for precise management
- Relationship to humidity: Balancing air exchange with humidity maintenance
Proper air exchange prevents deformities and enhances overall mushroom development.
Troubleshooting Common Cultivation Issues
Even experienced growers encounter problems; knowing how to address them is essential.
Contamination Identification and Management
Recognizing and addressing common contaminants:
- Green mold (Trichoderma): Appears as green patches, requires immediate isolation
- Black mold (Aspergillus): Dark spots with powdery appearance
- Bacterial contamination: Wet, slimy areas with foul odor
- Cobweb mold (Hypomyces): Gray, wispy growth that spreads rapidly
- Lipstick mold (Sporendonema): Bright red or pink coloration
- Contamination prevention: Improving sterile technique and air quality
- Isolation protocols: Removing contaminated blocks to prevent spread
- Sterilization validation: Checking pressure cooker function and timing
- Environmental sanitization: Regular cleaning of growing areas
Early identification and isolation minimize losses from contamination.
Growth Rate Problems
Addressing slow or stalled mycelial growth:
- Temperature imbalance: Verifying temperatures remain in optimal range
- Moisture issues: Checking for overly wet or dry substrate
- Spawn quality: Ensuring spawn was viable and fresh when used
- Gas exchange limitations: Confirming adequate filter patch function
- Nutrient deficiencies: Evaluating substrate composition
- pH imbalance: Testing substrate pH if growth stalls
- Incubation duration expectations: Understanding normal colonization timeframes
- Substrate compaction: Avoiding excessive density that limits mycelial penetration
Systematic evaluation of these factors typically resolves growth rate issues.
Fruiting Difficulties
Solving problems with initiation and development of fruiting bodies:
- Primordia formation failure: Ensuring proper temperature drop and humidity increase
- Aborted fruiting bodies: Addressing fluctuating conditions or contaminants
- Deformed growth: Correcting excessive CO2 or insufficient light
- Delayed fruiting: Implementing cold shock or adjusting fruiting triggers
- Small fruiting bodies: Improving nutrition or adjusting harvest timing
- Yellowing or browning: Addressing age, humidity issues, or bacterial contamination
- Excessive moisture on fruiting bodies: Increasing air exchange while maintaining humidity
- Multiple fruiting sites vs. single site: Controlling where fruiting occurs for larger specimens
Most fruiting issues can be resolved through environmental adjustments.
Pest Management
Identifying and controlling common mushroom pests:
- Fungus gnats: Small flies whose larvae damage mycelium and fruiting bodies
- Fungus beetles: Small beetles that feed on mushroom tissue
- Mites: Microscopic arachnids that can devastate cultures
- Prevention strategies: Maintaining cleanliness and screening air intakes
- Sticky traps: Using for monitoring and reducing flying insect populations
- Biological controls: Introducing beneficial nematodes or predatory mites
- Physical barriers: Implementing fine mesh screens on ventilation openings
- Chemical interventions: Using as last resort and only with food-safe products
Prevention through cleanliness and physical barriers is most effective for pest management.
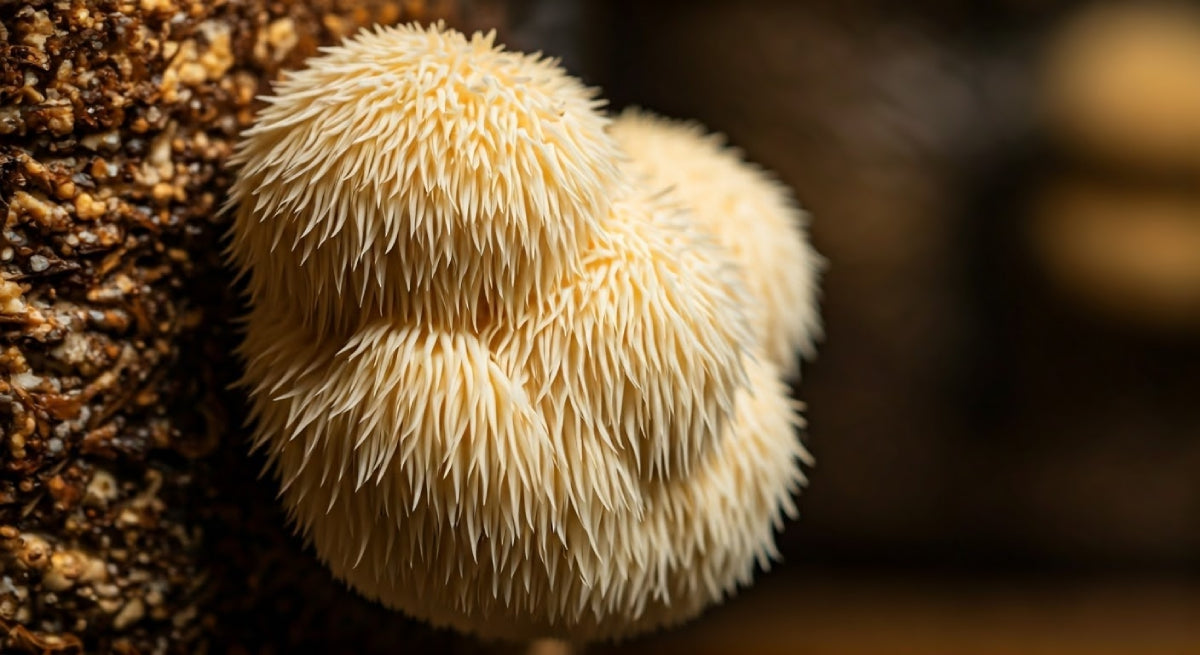

Advanced Cultivation Techniques
Experienced growers can implement these techniques to enhance production.
Strain Selection and Development
Working with genetics to improve cultivation outcomes:
- Commercial strain comparison: Testing different strains for performance
- Wild strain domestication: Isolating promising traits from wild specimens
- Sector selection: Choosing vigorous mycelial growth patterns from plates
- Clone propagation: Taking tissue cultures from exceptional fruiting bodies
- Spore germination: Creating new genetic combinations through spore isolation
- Selection criteria: Evaluating colonization speed, yield, fruiting reliability, and morphology
- Strain preservation: Maintaining cultures on slants, in liquid nitrogen, or other long-term storage
- Strain vigor maintenance: Periodically refreshing cultures through tissue culture or single-spore isolation
Dedicated work with genetics can significantly improve cultivation results over time.
Liquid Culture Techniques
Using liquid culture to increase efficiency and speed:
- Media formulation: Creating appropriate liquid nutrition (often malt extract or potato dextrose)
- Sterilization protocol: Pressure cooking liquid media with proper venting
- Inoculation method: Adding mycelium from clean cultures
- Incubation parameters: Maintaining optimal temperature with periodic agitation
- Growth assessment: Observing for healthy, rhizomorphic growth patterns
- Contamination identification: Checking for unusual colors, odors, or growth patterns
- Usage timing: Utilizing at peak vigor before nutrient depletion
- Storage limitations: Understanding shelf life constraints
- Scaling advantages: Producing large volumes of inoculum efficiently
Liquid culture can dramatically accelerate and scale up production processes.
Supplementation Strategies
Fine-tuning substrate nutrition for optimal yields:
- Supplement timing: Adding at mixing vs. delayed supplementation techniques
- Nitrogen sources: Comparing wheat bran, rice bran, soybean meal, and other options
- Mineral additions: Testing gypsum, calcium carbonate, and other minerals
- Carbohydrate enhancement: Adding molasses, flour, or other carbohydrate sources
- Balanced formulation: Creating optimal carbon-to-nitrogen ratios
- Supplement sterilization: Addressing higher contamination risks with enriched substrates
- Commercial supplement options: Evaluating pre-formulated supplements like Master's Mix
- Cost-benefit analysis: Balancing increased yields against higher input costs
Strategic supplementation can increase yields by 50-100% when properly implemented.
Commercial Scale Production
Considerations for scaling to commercial production:
- Workflow design: Creating efficient systems for substrate preparation, inoculation, and harvesting
- Labor management: Identifying bottlenecks and labor-intensive processes
- Equipment scaling: Selecting appropriate equipment for increased volume
- Contamination control: Implementing industrial hygiene practices
- Supply chain development: Securing reliable sources for bulk materials
- Production scheduling: Creating staggered production for consistent harvest
- Yield benchmarks: Establishing realistic production targets
- Efficiency metrics: Tracking biological efficiency (fresh mushroom weight/dry substrate weight)
- Market development: Identifying and developing sales channels
Successful scaling requires systematic planning and investment in appropriate infrastructure.
Post-Harvest Processing and Usage
Maximizing the value of harvested Lion's Mane mushrooms through proper handling and processing.
Storage and Preservation Methods
Extending shelf life and preserving nutritional value:
- Refrigeration parameters: Storing at 34-38°F (1-3°C) in breathable containers
- Dehydration technique: Slicing into 1/4 inch pieces and drying at 115-125°F (46-52°C)
- Freeze-drying advantages: Maintaining texture and medicinal compounds
- Cryogenic preservation: Flash-freezing for optimal texture retention
- Vacuum sealing: Extending shelf life of dried product
- Alcohol tinctures: Extracting and preserving medicinal compounds
- Powdering methods: Creating convenient powder from dried mushrooms
- Storage containers: Using airtight, moisture-proof containers for dried products
Proper preservation maintains both culinary quality and medicinal benefits.
Value-Added Product Development
Creating products that increase profitability:
- Medicinal extracts: Dual-extraction methods for both water and alcohol-soluble compounds
- Capsule production: Encapsulating powdered mushroom or extract
- Culinary preparations: Creating ready-to-use products like seasoning blends
- Ready-to-fruit kits: Developing kits for home growers
- Educational materials: Creating guides and resources as complementary products
- Specialty foods: Developing mushroom-infused products like chocolates, coffee, or snacks
- Beauty and wellness items: Creating topical applications using mushroom extracts
- Pet products: Developing supplements for animal health
Diversification through value-added products can significantly increase revenue per pound of mushrooms.
Culinary Applications
Highlighting Lion's Mane's unique culinary attributes:
- Flavor profile: Understanding the delicate seafood-like flavor
- Texture considerations: Working with the unique meat-like texture
- Cooking methods: Sautéing, roasting, and simmering techniques
- Seafood substitute applications: Creating "crab cakes" and similar dishes
- Absorption properties: Utilizing its ability to absorb flavors in marinades
- Pairing suggestions: Complementary flavors and ingredients
- Recipe development: Creating signature dishes highlighting unique qualities
- Chef education: Providing information on working with this unusual mushroom
Educating customers about culinary uses increases demand and perceived value.
Medicinal Preparation Methods
Optimizing extraction of beneficial compounds:
- Water extraction: Simmering dried mushrooms for polysaccharide extraction
- Alcohol extraction: Using ethanol to extract triterpenes and other compounds
- Dual-extraction process: Combining both methods for full-spectrum extracts
- Extraction ratios: Understanding concentration factors
- Decoction techniques: Traditional methods for medicinal preparation
- Tincture formulation: Creating alcohol-based extracts with proper dilution
- Powdered extract production: Spray-drying or other concentration methods
- Dosage considerations: Understanding appropriate usage amounts
Proper extraction methods maximize the bioavailability of Lion's Mane's beneficial compounds.
Sustainable and Ecological Considerations
Implementing environmentally responsible cultivation practices.
Waste Management and Recycling
Minimizing environmental impact through proper waste handling:
- Spent substrate applications: Using as garden soil amendment or compost
- Circular systems: Integrating mushroom production with other agricultural activities
- Vermicomposting integration: Feeding spent substrate to worms for casting production
- Animal feed potential: Using spent substrate as supplemental livestock feed
- Packaging considerations: Selecting biodegradable or recyclable materials
- Water conservation: Implementing systems to reduce water usage
- Energy efficiency: Optimizing sterilization and environmental control for lower energy use
- Carbon footprint assessment: Evaluating and reducing overall environmental impact
Responsible waste management transforms byproducts into resources rather than waste.
Organic Cultivation Practices
Implementing chemical-free growing methods:
- Organic substrate sourcing: Finding certified organic hardwood and supplements
- Natural pest management: Using biological controls rather than chemicals
- Certification requirements: Understanding local organic certification standards
- Documentation systems: Maintaining records for organic verification
- Cleaning product selection: Using approved sanitizers compatible with organic certification
- Cross-contamination prevention: Separating organic from conventional production
- Marketing advantages: Leveraging organic certification for market positioning
- Price premium considerations: Balancing higher costs with increased market value
Organic cultivation practices often command premium prices while reducing environmental impact.
Biodiversity and Conservation
Contributing to mushroom conservation and diversity:
- Wild strain preservation: Maintaining cultures from diverse geographic origins
- Habitat restoration: Using cultivation knowledge for ecological restoration projects
- Education initiatives: Teaching about fungal ecology and importance
- Spawn donation: Supporting community cultivation projects
- Citizen science participation: Contributing to mushroom research and mapping
- Traditional knowledge documentation: Preserving cultural practices around mushroom use
- Genetic diversity maintenance: Preventing narrowing of commercial strain genetics
- Research support: Contributing to scientific understanding of Hericium species
These activities support both business sustainability and ecological health.
Frequently Asked Questions About Lion's Mane Cultivation
What are the most common mistakes beginners make when growing Lion's Mane?
Beginners often encounter several predictable challenges when first cultivating Lion's Mane mushrooms. The most common errors include insufficient sterilization of substrates, which leads to contamination; inadequate humidity during the fruiting stage, causing slow growth or deformed fruiting bodies; poor air exchange, resulting in elongated, stringy growth; harvesting too late, after the mushroom has begun to yellow and develop off-flavors; and impatience during the incubation period, leading to premature initiation of fruiting conditions. Additionally, many newcomers underestimate the importance of temperature control during different growth phases or use substrate formulations without adequate nutrition for healthy fruiting body development. Addressing these common pitfalls—through proper sterilization techniques, maintaining 85-95% humidity during fruiting, ensuring 3-5 air exchanges per hour, harvesting when spines are well-formed but still white, allowing complete colonization before introducing fruiting conditions, maintaining specific temperature ranges for incubation (70-75°F) and fruiting (60-65°F), and using proven substrate recipes with 20-25% nutritional supplements—dramatically improves success rates for beginning cultivators.
How long does the entire Lion's Mane cultivation process take from inoculation to harvest?
The timeline for Lion's Mane cultivation varies somewhat depending on environmental conditions, substrate formulation, and specific strain genetics, but follows a generally predictable pattern. Starting with ready-made spawn, the process typically requires:
- Substrate colonization: 14-21 days for mycelium to fully colonize the substrate
- Primordia formation: 3-7 days after introducing fruiting conditions
- Fruiting body development: 5-14 days from primordia to mature harvest
- Total time to first harvest: Approximately 3-6 weeks from inoculation
After the first harvest, subsequent flushes may occur every 10-14 days, with most substrate blocks producing 2-3 flushes before becoming exhausted. The entire productive life cycle of a substrate block typically spans 2-3 months. Factors that can extend this timeline include lower incubation temperatures, less nutritious substrates, or contamination issues that slow growth. Conversely, optimal conditions, highly nutritious substrates, and vigorous strains may shorten the time to harvest. For planning purposes, most cultivators work with a 4-week estimate from inoculation to first harvest.
Can Lion's Mane be grown outdoors like oyster mushrooms?
Yes, Lion's Mane can be grown outdoors, though it requires slightly different approaches than outdoor oyster mushroom cultivation. The most successful outdoor method for Lion's Mane is log cultivation, which closely mimics its natural growing habitat. For this approach, freshly cut hardwood logs (preferably oak, maple, or beech) are inoculated with Lion's Mane spawn in spring or fall, then placed in shaded, humid locations. These logs typically take 9-12 months before the first fruiting, considerably longer than indoor methods, but can continue producing for 3-5 years.
Unlike oyster mushrooms, Lion's Mane is less suited to straw-based outdoor cultivation methods, as it strongly prefers woody substrates. While totem methods (stacking inoculated hardwood discs) can work well, Lion's Mane generally doesn't perform as reliably in outdoor beds or straw installations as oyster mushrooms. Outdoor cultivation also makes Lion's Mane more susceptible to pest damage, particularly from slugs and insects attracted to its soft texture. For these reasons, while outdoor cultivation is possible and can be rewarding for patient growers, most commercial Lion's Mane production occurs indoors where environmental conditions can be more precisely controlled.
What yields can I expect from Lion's Mane cultivation?
Yields from Lion's Mane cultivation vary based on substrate formulation, growing conditions, and cultivation method, but typical results can be estimated for planning purposes. Using the standard sawdust block method with supplemented hardwood substrate:
- A 5-pound (wet weight) substrate block typically yields 1-1.5 pounds of fresh mushrooms in the first flush
- Total yield across all flushes usually ranges from 1.5-2.5 pounds of fresh mushrooms per block
- This represents a biological efficiency (BE) of 30-50% (fresh mushroom weight/dry substrate weight)
- Higher supplementation levels (25-30% wheat bran or similar) can increase yields to 2-3+ pounds per block
- Master's Mix formulations (50% hardwood, 50% soybean hulls) often achieve biological efficiencies of 75-100%
For log cultivation, yields are lower per substrate weight but continue longer:
- A 40-pound log might produce 2-4 pounds of mushrooms annually for 3-5 years
- Production is seasonal and weather-dependent rather than controlled
Commercially, experienced growers typically achieve 1.5-2 pounds of fresh Lion's Mane per 5-pound block consistently, with top producers reaching 2.5-3 pounds through optimized conditions and substrate formulations. These yields make Lion's Mane moderately productive compared to oyster mushrooms (which can achieve higher BEs) but more productive than shiitake on similar substrates.
How do I know when Lion's Mane mushrooms are ready to harvest?
Determining the optimal harvest time for Lion's Mane requires observation of several key indicators. The ideal moment to harvest is when the fruiting body has fully developed its characteristic cascading spines (teeth), but before it begins to discolor or dry out. Specific signs that Lion's Mane is ready for harvest include:
- The fruiting body has reached a substantial size, typically 4-6 inches in diameter
- The spines have elongated to at least 1/2 inch in length and hang downward
- The entire structure remains white to cream-colored, with no significant yellowing or browning
- The texture is firm and resilient when gently pressed
- The edges of the fruiting body have developed fully but haven't started to curl or dry
Harvesting too early results in underdeveloped spines and reduced yield, while harvesting too late leads to yellowing, browning, and potential bitterness. Lion's Mane does not release spores visibly like many gilled mushrooms, so spore release cannot be used as a harvest indicator. The transition from perfect ripeness to overmaturity can happen quickly, sometimes within 1-2 days, particularly in environments with lower humidity or higher air movement. Therefore, daily monitoring of developing fruiting bodies is recommended during the final stages of growth. When in doubt, it's generally better to harvest slightly early rather than too late, as youth preserves the delicate flavor and medicinal properties better than overmaturity.
Conclusion
Lion's Mane mushroom cultivation represents an accessible yet rewarding endeavor that bridges practical agriculture with the fascinating world of fungal biology. From small-scale home production to commercial operations, the principles outlined in this guide provide a framework for successful cultivation of this unique and valuable mushroom. The relative forgivingness of Lion's Mane compared to more demanding species makes it an excellent entry point for beginning cultivators, while its distinctive appearance and impressive nutritional and medicinal properties ensure sustained interest and market value.
As interest in functional foods and natural health solutions continues to grow, Lion's Mane mushrooms occupy a special niche at the intersection of culinary delight and wellness support. Their documented benefits for cognitive function, nerve health, immune modulation, and digestive support create multiple market opportunities beyond conventional mushroom sales. Whether cultivated for personal use, local markets, or commercial distribution, Lion's Mane offers significant potential returns on investment in terms of both economic value and personal satisfaction.
By understanding the fundamental biological needs of Hericium erinaceus, implementing appropriate cultivation techniques, and continuously refining methods through experience, cultivators can achieve consistent success with this remarkable fungus. The patience and attention required for mushroom cultivation generally—and Lion's Mane specifically—rewards practitioners with not only a valuable harvest but also deeper insight into the fascinating kingdom of fungi that plays such a crucial role in our planet's ecosystems and, increasingly, in human health and wellness.













Share:
How to Grow Lion’s Mane Mushrooms at Home: A Simple Step-by-Step Guide
Turkey Tail Mushroom Benefits: Boost Your Wellness Naturally and Strengthen Immunity