Understanding lion's mane mushroom growth stages is essential for successful cultivation, whether you're a beginner home grower or experienced mycologist. This comprehensive guide explores the fascinating 5-stage development process of Hericium erinaceus, from invisible spores to the iconic white, cascading fruiting bodies that make this "smart mushroom" so distinctive and valuable.
Quick Answer: Lion's mane mushrooms develop through 5 distinct growth stages: spore germination (days 1-3), mycelium colonization (14-21 days), primordia formation/pinning (3-7 days), fruiting body development (5-10 days), and maturation/spore release (14-25 days total). Each stage requires specific environmental conditions for optimal development.

Overview of Lion's Mane Development Lifecycle
Complete Growth Timeline
Lion's mane mushrooms follow a predictable development pattern that typically spans 4-6 weeks under optimal conditions. Understanding this timeline helps growers provide appropriate care at each critical stage.
Total Development Timeline:
-
Week 1-3: Mycelium colonization and establishment
-
Week 3-4: Primordia formation and early pinning
-
Week 4-5: Rapid fruiting body development
-
Week 5-6: Maturation and harvest readiness
Environmental Factors Affecting Timeline:
-
Temperature: Optimal ranges vary by growth stage
-
Humidity: Critical for proper development
-
Fresh air exchange: Prevents deformities
-
Light exposure: Triggers fruiting initiation
-
Substrate quality: Affects colonization speed
Learn advanced cultivation techniques in our comprehensive Lion's Mane cultivation guide.
Stage 1: Spore Germination and Initial Mycelium Development (Days 1-7)
The Invisible Beginning
Lion's mane cultivation typically begins with spore germination or the introduction of established mycelium through liquid culture or grain spawn. This initial stage sets the foundation for the entire growth cycle.
Spore Germination Process:
-
Spore activation: Triggered by moisture and nutrients
-
Germ tube formation: First visible sign of growth (microscopic)
-
Primary mycelium development: Initial thread-like structures
-
Branching begins: Mycelium starts expanding outward
Optimal Conditions for Stage 1:
-
Temperature: 70-75°F (21-24°C)
-
Humidity: 80-85% relative humidity
-
Light: Minimal to no light required
-
Air exchange: Limited fresh air exchange
-
Substrate: Sterile, nutrient-rich growing medium
Common Starting Methods
Liquid Culture Inoculation: Most efficient method using mycelium suspended in nutrient solution. Explore detailed techniques in our Lion's Mane liquid culture guide.
Grain Spawn: Pre-colonized grains provide vigorous starting material for substrate inoculation.
Spore Syringes: Direct spore introduction requires sterile technique and longer development time.
The Lykyn Smart Mushroom Grow Chamber maintains optimal conditions automatically during this critical early stage.
Stage 2: Mycelium Colonization (Days 7-21)
Substrate Takeover Phase
This stage represents the most crucial development period where lion's mane mycelium spreads throughout the growing substrate, establishing the foundation for future fruiting.
Colonization Characteristics:
-
Appearance: Pure white, fluffy mycelial growth
-
Pattern: Uniform spread throughout substrate
-
Texture: Cotton-like or web-like structures
-
Growth rate: Visible daily progress under optimal conditions
Visual Indicators of Healthy Colonization:
-
Color: Bright white, clean appearance
-
Density: Thick, vigorous mycelial mass
-
Coverage: Even distribution across substrate surface
-
Odor: Pleasant, earthy mushroom scent
-
Firmness: Substrate becomes more solid and cohesive
Environmental Requirements
Temperature Management:
-
Optimal range: 70-75°F (21-24°C)
-
Consistency: Avoid temperature fluctuations
-
Monitoring: Daily temperature checks recommended
Humidity Control:
-
Target range: 80-90% relative humidity
-
Consistency: Maintain steady moisture levels
-
Ventilation: Minimal air exchange during colonization
Contamination Prevention:
-
Sterile conditions: Critical during this vulnerable stage
-
Visual monitoring: Daily checks for unusual colors or odors
-
Isolation: Keep colonizing substrates separate from fruiting areas
Timeline Variations
Factors Affecting Colonization Speed:
-
Substrate type: Hardwood sawdust vs. enriched blocks
-
Inoculation rate: Higher spawn ratios speed colonization
-
Temperature consistency: Stable conditions accelerate growth
-
Moisture levels: Proper hydration essential for mycelial expansion
-
Spawn quality: Vigorous cultures colonize faster
Typical Timelines:
-
Sawdust blocks: 14-21 days full colonization
-
Log inoculation: 6-12 months initial colonization
-
Ready-to-fruit blocks: May arrive pre-colonized
Stage 3: Primordia Formation and Pinning (Days 21-28)
The Transition Phase
Primordia formation, commonly called "pinning," marks the transition from vegetative mycelium growth to reproductive fruiting body development. This stage is environmentally sensitive and requires specific condition changes.
What are Primordia?
-
Definition: Small, white nodular formations
-
Size: Pencil eraser to marble-sized bumps
-
Appearance: Dense, compact white masses
-
Location: Surface of colonized substrate
-
Function: Early-stage fruiting bodies
Environmental Triggers for Pinning:
-
Temperature drop: Reduce from 75°F to 65-70°F
-
Increased humidity: Raise to 90-95% relative humidity
-
Light introduction: 12 hours indirect light daily
-
Fresh air exchange: Increase oxygen levels significantly
Critical Pinning Requirements
Humidity Management:
-
Target: 90-95% relative humidity
-
Method: Regular misting or automated humidification
-
Monitoring: Hygrometer readings multiple times daily
-
Consistency: Avoid humidity fluctuations
Fresh Air Exchange (FAE):
-
Importance: Prevents carbon dioxide buildup
-
Method: Gentle air circulation or ventilation
-
Balance: Maintain humidity while providing fresh air
-
Signs of inadequate FAE: Elongated, stringy growth patterns
Light Requirements:
-
Type: Indirect natural light or LED grow lights
-
Duration: 12 hours daily light cycle
-
Intensity: Low to moderate light levels
-
Purpose: Triggers proper fruiting body formation
Common Pinning Problems
Insufficient Pinning:
-
Causes: Low humidity, poor air exchange, incorrect temperature
-
Solutions: Adjust environmental conditions gradually
-
Prevention: Monitor conditions consistently
Excessive Pinning:
-
Result: Many small, underdeveloped mushrooms
-
Management: Remove excess pins to allow larger development
-
Optimization: Balance environmental conditions
Learn troubleshooting techniques in our detailed Lion's Mane home growing guide.
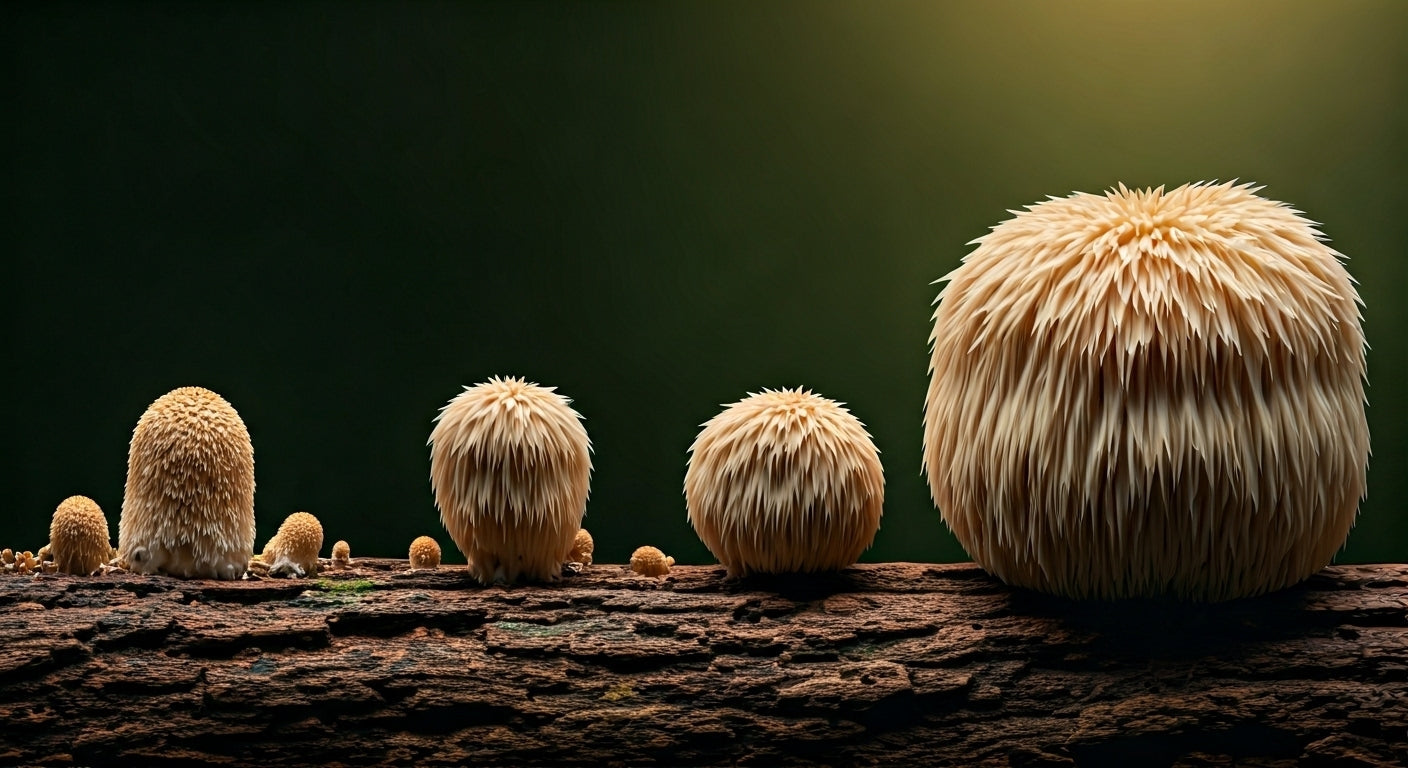
Stage 4: Fruiting Body Development (Days 28-35)
Rapid Growth Phase
This stage showcases lion's mane's most dramatic development as tiny primordia transform into the characteristic cascading white fruiting bodies within 5-10 days.
Fruiting Body Formation:
-
Initial structure: Small white bumps expand rapidly
-
Spine development: Characteristic teeth/spines begin forming
-
Size increase: Mushrooms can double in size daily
-
Shape emergence: Classic "lion's mane" or "pom-pom" appearance develops
Growth Characteristics:
-
Speed: Visible size changes within hours
-
Pattern: Cascading white spines elongate downward
-
Density: Spines become more numerous and prominent
-
Color: Pure white when healthy and developing properly
Optimal Fruiting Conditions
Temperature Requirements:
-
Ideal range: 65-70°F (18-21°C)
-
Slightly cooler: Than colonization temperature
-
Consistency: Stable temperatures prevent stress
-
Monitoring: Temperature fluctuations can cause deformities
Humidity Management:
-
High humidity: 85-95% relative humidity
-
Consistent moisture: Regular misting if needed
-
Air circulation: Prevent stagnant humid conditions
-
Balance: Maintain moisture without oversaturation
Fresh Air Exchange:
-
Critical importance: Prevents elongated, coral-like growth
-
Proper ventilation: Ensures normal spine development
-
CO2 management: Remove excess carbon dioxide
-
Visual indicators: Normal "pom-pom" shape vs. branching coral patterns
Growth Monitoring
Daily Observation:
-
Size tracking: Measure diameter increase
-
Spine development: Monitor length and density
-
Color assessment: Maintain pure white coloration
-
Shape evaluation: Ensure proper rounded formation
Quality Indicators:
-
Healthy growth: Dense, white, fluffy appearance
-
Proper spine formation: Cascading, well-developed teeth
-
Uniform development: Even growth across fruiting body
-
Clean color: No yellowing, browning, or discoloration
Stage 5: Maturation and Harvest Timing (Days 35-42)
Peak Development Phase
The final growth stage determines harvest timing, flavor quality, and medicinal potency. Proper timing ensures optimal taste, texture, and beneficial compound concentration.
Maturation Indicators:
-
Spine development: Spines reach 1-2 centimeters length
-
Growth plateau: Size increase slows significantly
-
Density increase: Fruiting body becomes more compact
-
Color stability: Maintains pure white appearance
Harvest Timing Signals:
-
Optimal window: Spines fully developed but still white
-
Size maximum: Growth rate significantly decreases
-
Texture firmness: Maintains spongy, dense feel
-
No yellowing: Harvest before any color changes occur
Harvest Quality Factors
Peak Harvest Characteristics:
-
Appearance: Dense white "pom-pom" with well-developed spines
-
Size: Typically 4-8 inches diameter when mature
-
Texture: Firm but slightly spongy to touch
-
Aroma: Pleasant, mild mushroom scent
-
Weight: Can reach 1+ pound for large specimens
Signs of Over-Maturity:
-
Color changes: Yellowing or browning of spines
-
Texture deterioration: Soft, mushy, or hollow feeling
-
Spine elongation: Excessively long, thin spines
-
Bitterness development: Off-flavors from aging
-
Spore release: White dust indicates over-maturity
Harvesting Techniques
Proper Harvesting Method:
-
Clean cutting: Use sharp, sterile knife
-
Cut location: Close to substrate base
-
Substrate protection: Avoid damaging growing medium
-
Immediate handling: Process or refrigerate quickly
-
Second flush preparation: Allow substrate to rest
Post-Harvest Care:
-
Refrigeration: Store at 34-38°F (1-3°C)
-
Humidity control: Use breathable containers
-
Processing timeline: Use within 1-2 weeks fresh
-
Preservation options: Dehydrate, freeze, or cook immediately
Explore preservation techniques in our comprehensive Lion's Mane cultivation guide.
Environmental Control Throughout Growth Stages
Stage-Specific Requirements Summary
Colonization Stage (Days 1-21):
-
Temperature: 70-75°F (21-24°C)
-
Humidity: 80-90% RH
-
Light: Minimal/darkness preferred
-
Air exchange: Limited FAE
Pinning Stage (Days 21-28):
-
Temperature: 65-70°F (18-21°C)
-
Humidity: 90-95% RH
-
Light: 12 hours indirect daily
-
Air exchange: Moderate FAE increase
Fruiting Stage (Days 28-42):
-
Temperature: 65-70°F (18-21°C)
-
Humidity: 85-95% RH
-
Light: Continued 12-hour cycle
-
Air exchange: High FAE critical
Advanced Environmental Management
Automated Systems: The Lykyn Smart Mushroom Grow Chamber automatically adjusts conditions throughout all growth stages, ensuring optimal development without manual intervention.
Manual Control Methods:
-
Temperature: Room selection, heating/cooling devices
-
Humidity: Misting, humidifiers, humidity chambers
-
Air exchange: Fans, ventilation systems, natural airflow
-
Light: LED grow lights, indirect natural lighting
Common Growth Stage Problems and Solutions
Colonization Issues
Slow Colonization:
-
Causes: Low temperature, poor substrate nutrition, weak spawn
-
Solutions: Increase temperature, improve substrate quality, use vigorous cultures
Contamination During Colonization:
-
Prevention: Sterile technique, quality substrates, proper storage
-
Identification: Unusual colors, off odors, competing growth
-
Response: Isolate affected areas, improve sterile practices
Pinning Problems
No Pin Formation:
-
Causes: Insufficient environmental changes, poor conditions
-
Solutions: Adjust temperature, humidity, light exposure
-
Timeline: Allow adequate colonization time before forcing
Excessive Pinning:
-
Management: Thin pins to allow larger development
-
Prevention: Optimize environmental conditions for balanced pinning
Fruiting Difficulties
Elongated Growth (Coral Formation):
-
Cause: Insufficient fresh air exchange
-
Solution: Increase ventilation immediately
-
Prevention: Monitor air exchange during fruiting
Slow Development:
-
Causes: Suboptimal temperature, humidity, or air circulation
-
Solutions: Fine-tune environmental conditions
-
Patience: Allow adequate development time
Optimizing Growth for Maximum Yield
Substrate Quality Impact
Substrate Types:
-
Hardwood sawdust: Preferred natural substrate
-
Supplemented sawdust: Enhanced with nutrients
-
Hardwood pellets: Convenient, consistent option
-
Log cultivation: Long-term, natural growing method
Nutrient Supplementation:
-
Wheat bran: Common nitrogen source
-
Soybean meal: High-protein supplement
-
Corn meal: Additional carbohydrate source
-
Balanced nutrition: Avoid over-supplementation
Multiple Flush Management
Second Flush Preparation:
-
Rest period: 7-10 days after first harvest
-
Rehydration: Soak substrate if needed
-
Environmental reset: Return to pinning conditions
-
Yield expectations: Subsequent flushes typically smaller
Substrate Longevity:
-
Total flushes: 2-4 flushes typical
-
Diminishing returns: Each flush produces less
-
Exhaustion signs: Poor pinning, slow growth, contamination
-
Disposal: Compost spent substrate
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How long does it take for lion's mane mushrooms to grow from start to harvest? A: Complete development from inoculation to harvest typically takes 4-6 weeks. This includes 2-3 weeks for colonization, 1 week for pinning, and 1-2 weeks for fruiting body development. Timeline varies based on environmental conditions and growing methods.
Q: What are the most critical environmental factors during lion's mane growth stages? A: Temperature, humidity, and fresh air exchange are most critical. Colonization needs 70-75°F with 80-90% humidity and minimal air exchange. Fruiting requires 65-70°F with 85-95% humidity and high fresh air exchange to prevent deformed growth.
Q: How can I tell when lion's mane is ready for harvest? A: Harvest when the fruiting body stops growing significantly, spines are 1-2cm long, and the mushroom maintains pure white color. The texture should be firm but spongy. Harvest before any yellowing or browning appears for best flavor and potency.
Q: Why do my lion's mane mushrooms look like coral instead of pom-poms? A: Coral-like growth indicates insufficient fresh air exchange during fruiting. Lion's mane requires high airflow to develop proper rounded shape with cascading spines. Increase ventilation immediately to prevent further deformation.
Q: Can I get multiple harvests from one growing block? A: Yes, lion's mane typically produces 2-4 flushes from a single substrate block. After harvesting, allow 7-10 days rest, maintain proper conditions, and new pins should form. Each subsequent flush will be smaller than the previous one.
Q: What's the difference between mycelium and fruiting body stages? A: Mycelium is the vegetative growth stage where thread-like structures colonize substrate, requiring darkness and moderate humidity. Fruiting body stage produces the edible mushrooms, triggered by environmental changes including light exposure, temperature drops, and increased humidity.
Summary
Lion's mane mushroom growth stages follow a predictable 5-phase development cycle spanning 4-6 weeks from inoculation to harvest. Understanding each stage's specific environmental requirements—from colonization at 70-75°F with minimal air exchange to fruiting at 65-70°F with high fresh air exchange—enables successful cultivation. Proper timing of environmental changes triggers healthy progression from mycelium colonization through pinning to mature fruiting bodies ready for harvest.
Master Lion's Mane Cultivation Today
Ready to optimize your lion's mane growing success? Understanding growth stages is just the beginning—proper environmental control throughout development ensures consistent, high-quality harvests. The Lykyn Smart Mushroom Grow Chamber automatically manages temperature, humidity, and airflow transitions between growth stages, eliminating guesswork and maximizing yield potential.
Explore our comprehensive Lion's Mane growing resources to master advanced cultivation techniques and discover why understanding growth stages transforms amateur attempts into professional-quality harvests. Transform your cultivation knowledge into consistent success with every growing cycle—your journey to mushroom growing mastery begins with understanding each critical development phase.













Share:
Lion's Mane Tincture Recipe: Master the Double Extraction Method for Maximum Potency
When to Harvest Pink Oyster Mushrooms: Your Complete Timing Guide