Mycelium contamination is every mushroom grower's nightmare, but it doesn't have to derail your cultivation journey. Whether you're a beginner working with your first grow kit or an experienced cultivator managing multiple projects, understanding contamination is crucial for consistent, successful harvests.
This comprehensive guide will teach you everything you need to know about identifying contamination early, preventing it from occurring, and recovering when things go wrong. By mastering these techniques, you'll save time, money, and frustration while achieving the clean, productive grows you're aiming for.

Understanding Mycelium Contamination: What Every Grower Needs to Know
Mycelium contamination occurs when unwanted microorganisms—bacteria, mold, or yeast—invade your growing environment and compete with your desired mushroom mycelium. These contaminants can completely destroy your substrate, waste weeks of growing time, and potentially spread to other projects.
The key to successful mushroom cultivation lies in creating conditions that favor your mushroom mycelium while suppressing competing organisms. This requires understanding both the biology of contamination and the practical techniques that prevent it.
Common Types of Contamination in Mushroom Growing
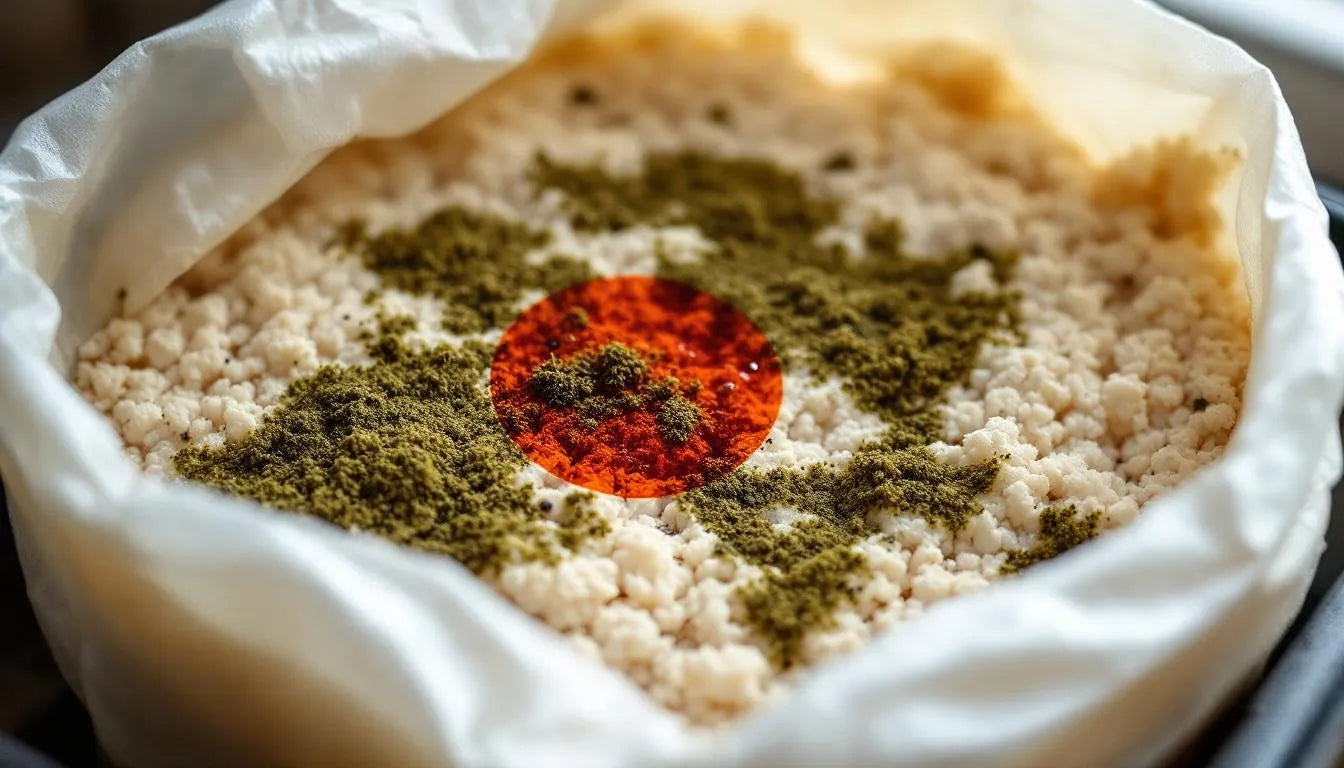
Trichoderma (Green Mold) The most aggressive and common contaminant, trichoderma appears as bright green patches that spread rapidly. This mold thrives in warm, humid conditions and can overtake healthy mycelium within days.
Penicillium (Blue-Green Mold) Often mistaken for trichoderma, penicillium presents as blue-green fuzzy growth. While less aggressive than trichoderma, it still poses significant threats to mushroom cultivation.
Bacterial Contamination Bacteria create slimy, wet areas with foul odors. Bacterial contamination often appears as dark, wet spots and can cause substrate to become mushy and smell rotten.
Yeast Contamination Yeast contamination produces alcoholic or sweet fermentation odors. The substrate may appear overly wet or develop unusual bubbling.
Aspergillus (Black Mold) Black aspergillus appears as dark, powdery patches and can be particularly dangerous to human health. Any suspected aspergillus contamination should be disposed of immediately.
Early Detection: Recognizing Contamination Before It Spreads
Quick identification saves entire projects and prevents contamination from spreading to other grows. Learning to spot early warning signs allows you to take immediate action.
Visual Indicators of Contamination
Color Changes Healthy mycelium is pure white, cream-colored, or occasionally light yellow as it ages. Any green, blue, black, pink, or orange colors indicate contamination. Even small colored spots require immediate attention.
Texture Differences Contaminated areas often feel different from healthy mycelium. Look for slimy patches, overly wet areas, or sections that feel mushy when gently pressed.
Growth Patterns Contaminants often display different growth patterns than mushroom mycelium. Powdery surfaces, circular patches, or fuzzy growths that seem separate from your main mycelium network suggest contamination.
Smell Tests for Contamination Detection
Your nose is one of your most valuable contamination detection tools. Each type of contamination produces distinct odors that trained growers can identify quickly.
Healthy Mycelium Scents Fresh mushroom mycelium should smell earthy, pleasant, and slightly sweet. Lion's Mane Mushroom Liquid Culture typically has a mild, pleasant mushroom scent when healthy.
Warning Odors
- Sour or fermented smells indicate yeast contamination
- Rotten or putrid odors suggest bacterial infection
- Sharp, ammonia-like smells point to advanced bacterial contamination
- Sweet, alcoholic scents indicate yeast fermentation

Prevention Strategies: Building Contamination-Resistant Growing Systems
Prevention remains far more effective than treatment when dealing with mycelium contamination. Implementing proper sterile techniques and environmental controls creates conditions that strongly favor your mushroom mycelium.
Sterile Technique Fundamentals
Workspace Preparation Clean your growing area thoroughly before each session. Use 70% isopropyl alcohol to wipe down all surfaces, tools, and hands. Many successful growers work near a Smart Mushroom Grow Chamber that maintains optimal conditions while minimizing contamination risks.
Hand and Tool Sterilization Wash hands thoroughly with soap, then apply 70% isopropyl alcohol. Sterilize all tools by flaming them with a lighter or soaking in alcohol for at least 30 seconds.
Air Quality Management Work in still air or use a laminar flow hood when possible. Avoid working during windy conditions or when household activities might stir up dust and contaminants.
Environmental Controls for Contamination Prevention
Temperature Management Maintain appropriate temperatures for your specific mushroom variety. Most contaminating organisms thrive at higher temperatures than optimal mushroom growing ranges.
Humidity Balance While mushrooms need high humidity, excessive moisture creates ideal conditions for bacterial contamination. The Lykyn Smart Mushroom Grow Kit automatically maintains optimal humidity levels without creating overly wet conditions.
Air Circulation Proper airflow prevents stagnant conditions that encourage contamination. Fresh air exchange dilutes contaminant spores while providing oxygen for healthy mycelium growth.
Substrate and Spawn Quality
Source Material Selection Start with high-quality spawn from reputable suppliers. Poor-quality spawn often carries latent contamination that manifests during cultivation.
Proper Sterilization Ensure complete sterilization of substrates before inoculation. Pressure cooking at 15 PSI for appropriate time periods kills most contaminants while preserving nutrients.
Storage Conditions Store sterilized substrates in clean, dry conditions until use. Contamination often occurs during storage rather than preparation.
Recovery and Salvage Techniques When Contamination Strikes
When contamination appears, quick action sometimes allows partial or complete recovery. The success of salvage operations depends on contamination type, extent, and how quickly you respond.
Immediate Response Protocols
Isolation Procedures Immediately isolate contaminated projects from clean grows. Move contaminated materials to a separate area to prevent spore dispersal.
Assessment and Documentation Photograph contamination for learning purposes and assess the extent of damage. Document conditions that may have contributed to contamination.
Containment Strategies For small, localized contamination, you might attempt surgical removal. Using sterile tools, carefully remove contaminated substrate along with a buffer zone of apparently healthy material.
Advanced Recovery Methods
pH Manipulation Some growers successfully use lime water or other pH adjusters to create conditions unfavorable to common contaminants while allowing mushroom recovery.
Salt Solutions Certain contamination types respond to careful application of salt solutions, though this requires experience to avoid damaging your mushroom mycelium.
Beneficial Microorganism Introduction Advanced growers sometimes introduce beneficial bacteria or fungi that compete with harmful contaminants.
Frequently Asked Questions About Mycelium Contamination
What should I do if I find green mold in my mushroom kit?
Immediately isolate the contaminated kit from other growing projects. Green mold (typically trichoderma) spreads rapidly through airborne spores. If contamination is minimal and localized, you might attempt surgical removal with sterile tools, but often disposal is the safest option. The Turkey Tail Mushroom growing guide emphasizes that prevention is always better than attempting to treat established contamination.
How can I tell the difference between healthy aging and contamination?
Healthy mycelium may develop a slight yellow color as it ages, particularly in areas with accumulated metabolites. This yellowing should be uniform and gradual. Contamination typically appears as distinct colored patches (green, blue, black, or pink) with different textures than surrounding mycelium. When in doubt, smell test—healthy aging mycelium maintains pleasant mushroom scents while contamination produces off-odors.
Is it safe to eat mushrooms that grew near contaminated areas?
Never consume mushrooms from contaminated substrates. Contaminants can produce toxic compounds and may indicate the presence of harmful microorganisms. Even if the mushrooms themselves appear healthy, the risk isn't worth taking. Always discard entire projects when contamination is present.
Can I prevent contamination completely with proper technique?
While perfect sterile technique dramatically reduces contamination rates, completely eliminating risk is nearly impossible in home growing environments. Professional facilities with laminar flow hoods and controlled atmospheres achieve very low contamination rates, but home growers should expect occasional contamination even with excellent technique. Focus on prevention and quick response rather than expecting perfection.
What's the most effective way to dispose of contaminated materials?
Seal contaminated materials in plastic bags before disposal to prevent spore dispersal. Some growers compost contaminated substrates in outdoor compost piles where the contamination poses no threat to indoor growing. Never put contaminated materials in household compost or areas where spores might affect future growing projects.
Key Takeaways for Successful Contamination Management
Preventing mycelium contamination requires consistent application of sterile techniques, proper environmental controls, and quality starting materials. Early detection through visual inspection and smell tests allows for quick response that can save entire projects.
When contamination does occur, immediate isolation and careful assessment determine whether salvage attempts are worthwhile or disposal is necessary. Remember that prevention efforts cost far less in time and materials than dealing with contamination after it appears.
Advanced growing systems like the Smart Mushroom Grow Chamber help maintain optimal conditions while reducing contamination risks through automated environmental controls and HEPA filtration.
Start Your Contamination-Free Growing Journey Today
Don't let fear of contamination prevent you from enjoying the rewarding hobby of mushroom cultivation. With proper knowledge, quality equipment, and consistent technique, you can achieve successful harvests while minimizing contamination risks.
Explore the complete selection of mushroom growing solutions for beginners and discover how modern growing systems make contamination prevention easier than ever. Whether you're interested in growing Lion's Mane at home or exploring the diverse world of edible mushrooms, proper contamination management skills will serve as the foundation for all your future growing success.
Transform your approach to mushroom cultivation by mastering contamination prevention and detection. Your future harvests depend on the sterile techniques and environmental awareness you develop today.












Share:
How to Grow Mushrooms in a Bag: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Home Cultivation
Yellow Oyster Mushroom: The Complete Guide to Growing, Cooking, and Enjoying This Golden Treasure