Introduction to Morel Mushrooms
Morel mushrooms (Morchella species) are among the most sought-after wild fungi in the world, prized for their distinctive honeycomb-like caps, rich earthy flavor, and impressive nutritional profile. These springtime delicacies have been treasured by foragers, chefs, and food enthusiasts for centuries, not only for their unique taste but also for their remarkable health benefits.
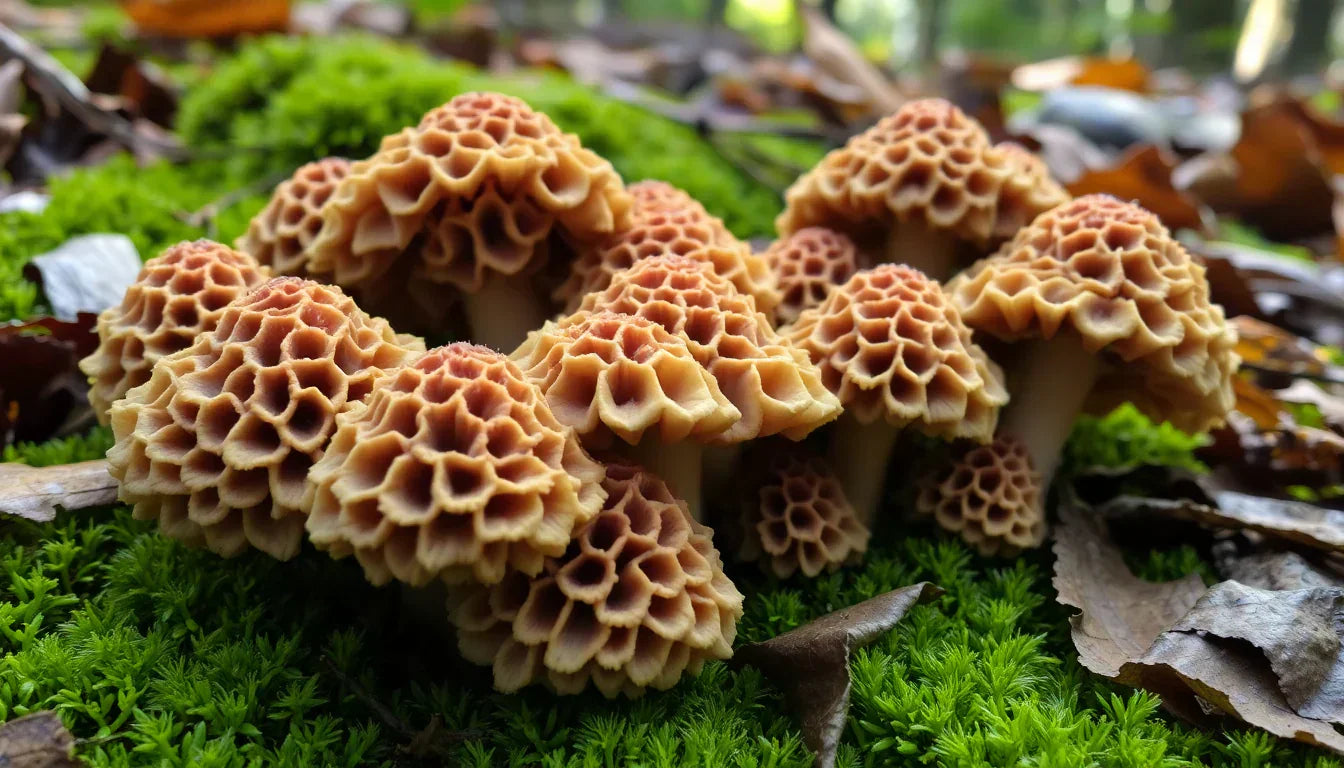
Found primarily in woodland areas during spring, morels have a distinctive appearance: a pale, hollow stem supporting a conical cap covered with a network of ridges and pits resembling a honeycomb or sponge. Their color ranges from yellowish to dark brown, depending on the variety and age.
What truly sets morels apart, however, is their exceptional nutritional value. As we'll explore in this comprehensive guide, morel mushrooms pack an impressive array of nutrients within their distinctive form, making them not just a culinary delight but a nutritional powerhouse as well.
Nutritional Composition of Morel Mushrooms
Macronutrient Profile
Morel mushrooms offer an impressive nutritional balance while remaining remarkably low in calories, making them an excellent addition to health-conscious diets. A typical 100-gram serving of fresh morel mushrooms contains:
- Calories: Approximately 31 calories
- Protein: 3.1 grams
- Carbohydrates: 5.1 grams
- Fat: 0.4 grams
- Fiber: 2.8 grams
This macronutrient composition makes morels particularly valuable for those seeking nutrient-dense foods that support weight management. Their protein content is notably higher than many other vegetables and mushroom varieties, contributing to their satiety value and nutritional impact.
Vitamin Content
Morel mushrooms contain an impressive array of vitamins that contribute to their health-promoting properties:
-
Vitamin D: One of the most noteworthy aspects of morel nutrition is their vitamin D content. Morels are one of the few natural food sources of this essential vitamin, which plays crucial roles in bone health, immune function, and mood regulation.
-
B Vitamins: Morels are rich in several B vitamins, including:
- Niacin (B3): 6.2 mg per 100g, approximately 39% of the Daily Value (DV)
- Riboflavin (B2): Supports energy production and cellular function
- Thiamine (B1): Essential for energy metabolism
- Folate (B9): Important for DNA synthesis and repair
-
Vitamin E: Contains tocopherols that act as antioxidants in the body
The vitamin D content deserves special attention, as dietary sources of this nutrient are relatively rare. Exposure to sunlight during drying can actually increase the vitamin D levels in morels, making properly dried specimens potentially even more nutritious than fresh ones in this respect.
Mineral Content
Morel mushrooms are particularly remarkable for their mineral content, with some minerals present in quantities that significantly contribute to daily requirements:
- Iron: Contains approximately 12.2 mg per 100g, representing about 68% of the DV
- Copper: Significant amounts that support enzyme function and iron metabolism
- Phosphorus: Essential for bone health and cellular function
- Zinc: Supports immune function and wound healing
- Manganese: Important for metabolism and antioxidant function
- Potassium: Helps maintain healthy blood pressure and fluid balance
- Selenium: Acts as an antioxidant protecting cells from damage
The iron content is especially notable, making morels a valuable food for those at risk of iron deficiency, including menstruating women, pregnant women, and individuals following plant-based diets.
Bioactive Compounds
Beyond traditional nutrients, morel mushrooms contain several bioactive compounds that contribute to their health benefits:
- Beta-glucans: Complex carbohydrates that stimulate immune function
- Ergothioneine: A powerful antioxidant amino acid
- Polysaccharides: Complex sugars with potential immune-modulating properties
- Phenolic compounds: Plant chemicals with antioxidant properties
These compounds work synergistically with the vitamins and minerals in morels to provide health benefits that exceed what might be expected from their basic nutritional profile.
Health Benefits of Morel Mushrooms
Immune System Support
The combination of vitamin D, selenium, zinc, and beta-glucans in morel mushrooms creates a powerful support system for immune function:
- Vitamin D regulates immune responses and may enhance protection against respiratory infections
- Beta-glucans stimulate macrophages and natural killer cells, key components of the immune system
- Zinc supports the development and function of immune cells
- Selenium helps regulate immune responses and reduce inflammation
Together, these nutrients and compounds may help strengthen the body's natural defenses against pathogens and support overall immune resilience.
Antioxidant Protection
Morel mushrooms contain several potent antioxidants that help combat oxidative stress in the body:
- Ergothioneine: A unique amino acid with powerful antioxidant properties that concentrates in tissues undergoing oxidative stress
- Phenolic compounds: Plant chemicals that neutralize free radicals
- Selenium: Works as part of antioxidant enzymes
- Vitamin E: Protects cell membranes from oxidative damage
Regular consumption of foods rich in varied antioxidants, like morel mushrooms, is associated with reduced risk of chronic conditions and slower cellular aging.
Cardiovascular Health Support
Several components of morel mushrooms support heart health:
- Potassium: Helps regulate blood pressure by balancing sodium effects
- Fiber: May help manage cholesterol levels
- B vitamins: Support heart function and help reduce homocysteine, a risk factor for heart disease
- Low sodium content: Makes them heart-friendly for those monitoring sodium intake
These heart-healthy attributes make morels a valuable addition to dietary patterns focused on cardiovascular wellness.
Bone Health Promotion
Morel mushrooms contribute to bone health through several nutrients:
- Vitamin D: Essential for calcium absorption and bone mineralization
- Phosphorus: A major component of bone tissue
- Calcium: Present in modest amounts but contributes to daily needs
- Copper: Necessary for collagen formation in bones
These nutrients work together to support bone density and strength, potentially helping to reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures as we age.
Weight Management Support
With their low calorie count, high fiber content, and satisfying umami flavor, morel mushrooms make an excellent addition to weight management diets:
- Low energy density: Provides volume and nutrition with minimal calories
- Dietary fiber: Promotes feelings of fullness and satiety
- Protein content: Higher than many vegetables, contributing to meal satisfaction
- Flavor impact: Adds richness to dishes without requiring additional fats
These properties make morels a valuable ingredient for those seeking to maintain a healthy weight while enjoying flavorful, satisfying meals.
Culinary Aspects of Morel Mushrooms
Proper Preparation Techniques
Before enjoying the nutritional benefits of morel mushrooms, proper preparation is essential:
-
Cleaning: Due to their honeycomb structure, morels can trap dirt, debris, and small insects. Slice them lengthwise and rinse gently under cold water, or soak briefly in lightly salted water to remove any inhabitants.
-
Never Eat Raw: It's crucial to thoroughly cook morel mushrooms before consumption. Raw morels contain hydrazine toxins that are destroyed through cooking at proper temperatures (above 140°F/60°C) for at least 15 minutes.
-
Drying: Properly dried morels can maintain their nutritional value for months and often develop a more intense flavor profile. Reconstitute by soaking in warm water before using in recipes.
Cooking Methods That Preserve Nutrition
Different cooking methods can affect the nutritional content of morel mushrooms:
- Sautéing: A quick sauté in a small amount of healthy fat helps preserve nutrients while developing flavor.
- Braising: Gentle cooking in liquid helps retain water-soluble vitamins.
- Roasting: Can intensify flavor while maintaining much of the nutritional value.
- Adding to soups and stews: Allows nutrients that leach into cooking liquid to remain in the dish.
Regardless of method, minimizing cooking time once the mushrooms have reached a safe temperature helps preserve heat-sensitive nutrients.
Flavor Pairings to Enhance Nutritional Impact
Certain ingredient pairings can enhance both the flavor and nutritional benefits of morel mushrooms:
- Vitamin C-rich foods: Pairing morels with foods high in vitamin C (like bell peppers or lemon) can enhance iron absorption from the mushrooms.
- Healthy fats: Combining morels with olive oil or avocado increases absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin D and E.
- Allium family: Garlic, shallots, and leeks provide complementary flavors and additional health benefits.
- Fresh herbs: Herbs like thyme, parsley, and chives add flavor along with additional micronutrients.
Classic Morel Recipes
Simple Sautéed Morels
- Clean and slice morels lengthwise
- Heat a small amount of olive oil or butter in a pan over medium heat
- Add morels and sauté until they release their moisture and begin to brown
- Season with salt, pepper, and fresh thyme
- Finish with a splash of white wine or sherry
Morel and Spring Vegetable Risotto Combine morels with other seasonal spring vegetables like asparagus and peas in a creamy risotto for a nutritionally balanced main dish.
Morel Mushroom Soup Create a nourishing soup by combining morels with a good-quality broth, aromatic vegetables, and herbs for a concentrated dose of morel nutrition.
Seasonal Availability and Storage
Wild Harvesting Season
Morel mushrooms typically appear in spring, with the exact timing depending on geographic location and weather conditions:
- In warmer regions, they may begin appearing in March
- In cooler areas, the season might start in April or May
- The season is typically brief, lasting only 2-4 weeks in any given area
This limited seasonal availability contributes to their prized status among culinary enthusiasts and makes understanding proper storage particularly important.
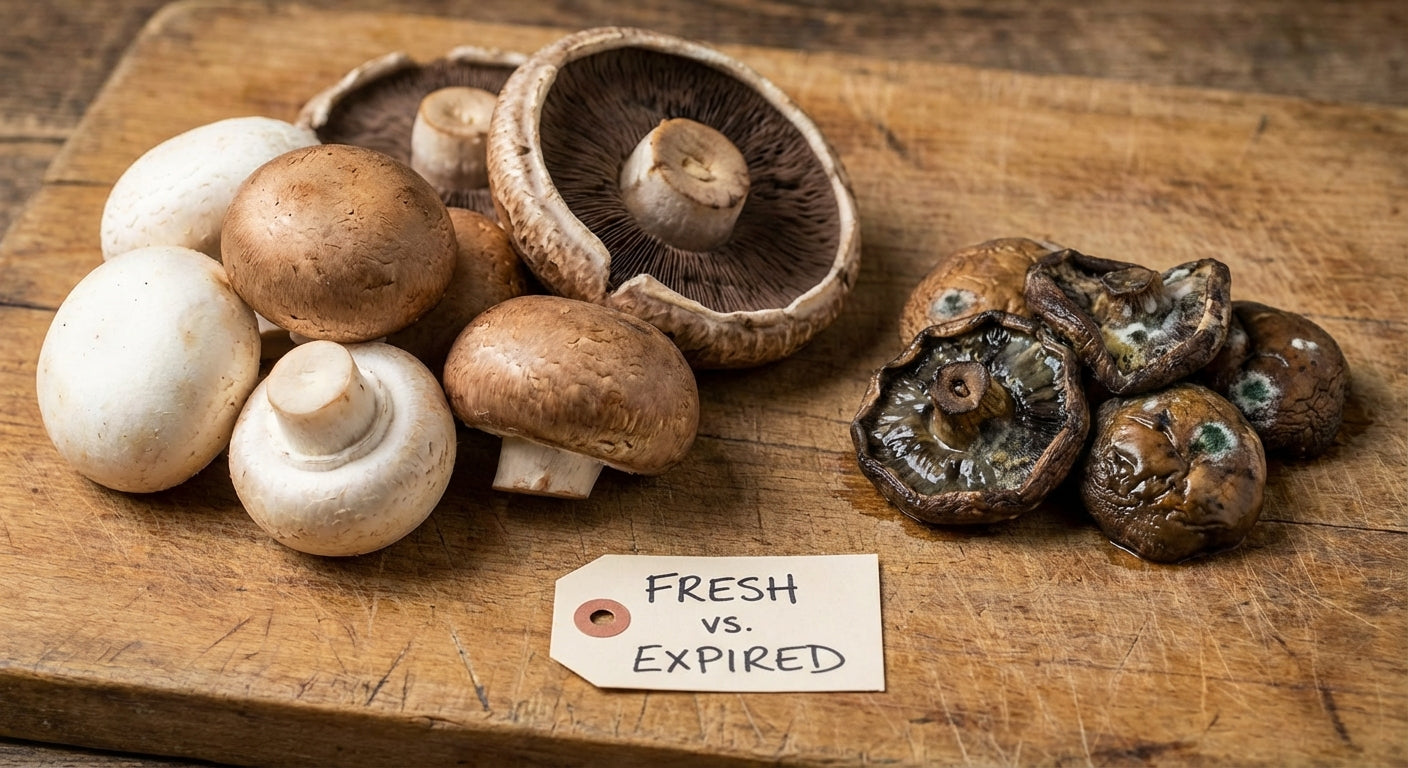
Storage Methods to Preserve Nutritional Value
To maintain the nutritional benefits of morel mushrooms beyond their brief season:
-
Fresh storage: Keep unwashed morels in a paper bag in the refrigerator for up to 5 days. Avoid plastic bags which can trap moisture and accelerate spoilage.
-
Drying: Properly dried morels can retain most of their nutritional value for up to a year when stored in airtight containers in a cool, dark place.
-
Freezing: For longer storage, morels can be sautéed briefly and frozen. This helps preserve their texture better than freezing them raw.
Nutritional Comparisons
How Morels Compare to Common Mushrooms
When compared to commonly consumed button mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus), morels offer:
- Higher protein content: 3.1g vs 2.2g per 100g
- More iron: 12.2mg vs 0.5mg per 100g
- Higher vitamin D levels: Significantly more than button mushrooms
- Greater concentration of antioxidants: Including unique compounds not found in cultivated varieties
Comparison with Other Wild Mushrooms
Among wild mushrooms, morels have a nutritional profile that stands out for its:
- Balanced nutrition: Good amounts of protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals
- Higher vitamin D: More than many other wild varieties
- Exceptional iron levels: Among the highest in edible mushrooms
- Lower toxicity concerns: When properly prepared, fewer concerns than some other wild species
Special Considerations
Potential Allergies and Sensitivities
While relatively uncommon, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to morel mushrooms. It's advisable to try a small amount initially if you've never consumed morels before. Watch for symptoms such as:
- Gastrointestinal discomfort
- Skin reactions
- Respiratory issues
False Morels and Look-alikes
An important safety consideration is proper identification. False morels (Gyromitra species) can resemble true morels but contain the toxin gyromitrin, which can cause illness or, in rare cases, be fatal. Key differences include:
- True morels have caps attached to the stem at the base
- True morels are completely hollow inside when cut lengthwise
- False morels often have wrinkled caps rather than distinct pits and ridges
Always purchase morels from reputable sources or consult with experienced foragers if harvesting wild specimens.
Sustainable Consumption
As wild foods, morels are subject to environmental pressures. Sustainable practices include:
- Purchasing from suppliers who follow responsible harvesting guidelines
- If foraging, cutting mushrooms at the stem rather than pulling them out
- Using mesh bags during collection to allow spore dispersal
- Never over-harvesting from any single area
Practical Tips for Incorporating Morels into Your Diet
Beginner-Friendly Approaches
For those new to morel mushrooms:
- Start with simple preparations that highlight their natural flavor
- Begin with smaller portions to ensure tolerance
- Use dried morels when fresh aren't available
- Add to familiar dishes like pasta, risotto, or omelets
Creating Nutritionally Balanced Meals with Morels
To maximize the nutritional impact:
- Combine with vitamin C-rich foods to enhance iron absorption
- Pair with whole grains for complementary proteins
- Add to vegetable medleys for increased nutrient diversity
- Include healthy fats to improve absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
Cost-Effective Ways to Enjoy Morels
Given their premium price, especially when fresh:
- Use dried morels and save the soaking liquid for stocks and sauces
- Blend with more affordable mushroom varieties in recipes
- Focus on morels as a flavor accent rather than the main ingredient
- Consider growing kits as a long-term investment
Latest Research on Morel Mushroom Nutrition
Emerging Studies on Health Benefits
Recent scientific interest in morel mushrooms has focused on:
- Potential prebiotic effects on gut microbiome composition
- Anti-inflammatory properties of their bioactive compounds
- Detailed analysis of antioxidant capacity compared to other foods
- Effects of different drying methods on nutrient retention
Future Directions in Morel Research
Ongoing and planned research areas include:
- Cultivation techniques to make morels more widely available
- Extraction methods for bioactive compounds
- Potential applications in functional foods and supplements
- Effects on specific health conditions like immune disorders
Conclusion: Embracing Morel Mushroom Nutrition
The impressive nutritional profile of morel mushrooms makes them much more than just a gourmet delicacy. From their protein content to their vitamin D levels, essential minerals, and beneficial compounds, morels offer a wide array of health benefits that support overall wellness.
Whether enjoyed fresh during their spring season or utilized in dried form year-round, these unique fungi deserve a place in your culinary repertoire not just for their distinctive flavor, but for their remarkable nutritional benefits as well.
By understanding morel mushroom nutrition as outlined in this guide, you can make informed decisions about including these fantastic fungi in your diet, supporting your health while enjoying their delectable taste. Their seasonal nature reminds us to appreciate nature's rhythms and the special nutritional gifts that come with each turning of the seasons.













Share:
How to Keep Morel Mushrooms Fresh and Flavorful
Morel Mushroom Benefits: Discover Nature’s Hidden Superfood