Truffle mushrooms represent the pinnacle of culinary luxury in the fungal world, commanding extraordinary prices and captivating food enthusiasts with their distinctive aromas and flavors. Unlike their above-ground mushroom cousins, these subterranean delicacies grow in symbiotic relationships with tree roots, developing entirely underground and relying on specialized harvesting techniques. This comprehensive guide explores the fascinating world of truffle mushrooms, from their biological characteristics and varieties to cultivation methods and culinary applications.

Understanding Truffle Mushrooms: Nature's Buried Treasure
Truffle mushrooms are the fruiting bodies of fungi belonging to the genus Tuber, growing underground in a symbiotic relationship with the roots of specific trees. Unlike typical mushrooms that release their spores to the wind, truffles rely on animals to find and consume them, dispersing their spores through excretion.
The Biology of Truffles
Truffles form a unique relationship with trees called mycorrhizal symbiosis. In this relationship:
- The truffle mycelium (fungal network) connects with the tree's root system
- The fungi help the tree absorb nutrients and water more efficiently
- In exchange, the tree provides the truffle with carbohydrates and other organic compounds
- When conditions are right, the truffle forms its fruiting body underground
This specialized relationship explains why truffles cannot simply be cultivated like other mushrooms using organic material as a substrate. The living tree roots are essential to the truffle's lifecycle.
Key Characteristics of Truffle Mushrooms
Truffles share several distinctive features that set them apart from other fungi:
- Underground growth: Develop completely beneath the soil surface
- Appearance: Typically round or irregularly shaped with rough exteriors
- Size: Range from marble to fist-sized, depending on the variety
- Interior: Solid flesh with marbled veining patterns
- Aroma: Intense, complex scents that are highly valued in gastronomy
- Tree association: Each variety forms relationships with specific tree species
- Seasonality: Different varieties have distinct harvesting seasons throughout the year
Major Truffle Varieties and Their Characteristics
Several truffle varieties hold particular importance in both culinary applications and cultivation efforts, each with unique characteristics and growing requirements.
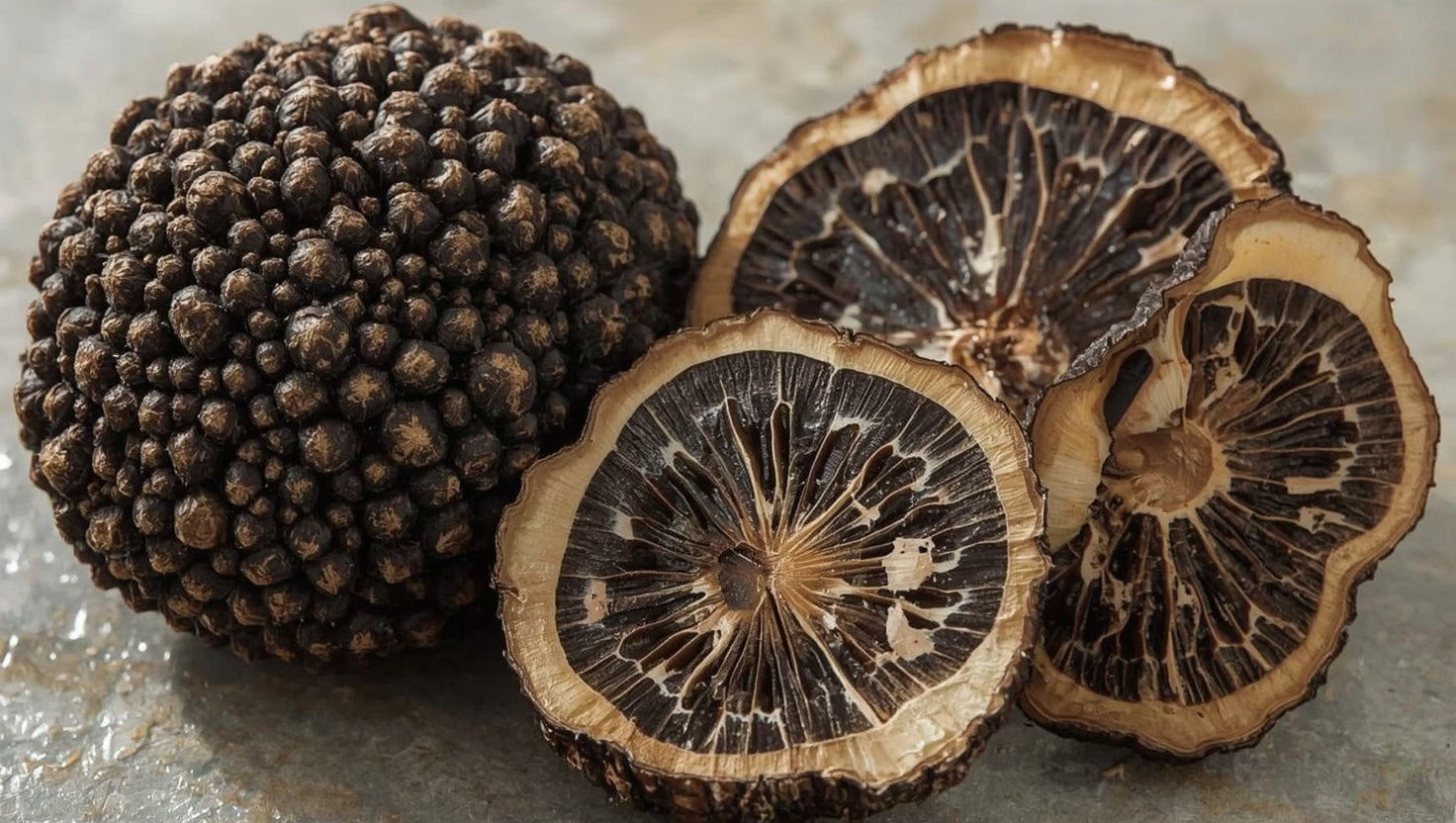
Black Périgord Truffle (Tuber melanosporum)
The black Périgord truffle, often called the "black diamond," is one of the most commercially valuable truffle species:
- Appearance: Dark black exterior with distinctive black-brown interior marbling
- Size: Typically 3-10 cm in diameter
- Aroma: Strong earthy, musky aroma with chocolate and red wine notes
- Season: Harvested from late autumn to winter (November-March in the Northern Hemisphere)
- Tree associations: Primarily oak and hazelnut trees
- Cultivation: Successfully cultivated in France, Spain, Italy, Australia, and the United States
- Culinary uses: Excellent for cooking, retains flavor when heated
White Truffle (Tuber magnatum)
The white truffle, primarily from the Piedmont region in Italy, is often considered the most prestigious:
- Appearance: Smooth, light-colored exterior with pale beige to yellow-brown interior
- Size: Usually 2-8 cm in diameter
- Aroma: Intense, garlicky aroma with notes of honey and hay
- Season: October-December
- Tree associations: Poplar, oak, hazel, and beech trees
- Cultivation: Resists cultivation efforts; primarily harvested from wild sources
- Culinary uses: Best served raw, shaved over dishes to preserve the delicate aroma
Summer Truffle (Tuber aestivum)
The summer truffle offers a more affordable option while still providing excellent flavor:
- Appearance: Black exterior with large pyramid-shaped warts, light brown interior
- Size: 2-10 cm in diameter
- Aroma: Milder nutty, earthy aroma compared to other varieties
- Season: May-August
- Tree associations: Oak, hazelnut, and other hardwoods
- Cultivation: More adaptable to different soil conditions; successfully cultivated in multiple countries
- Culinary uses: Versatile in cooking due to its more subtle flavor profile
Burgundy Truffle (Tuber uncinatum)
Though technically the same species as the summer truffle, the Burgundy truffle is considered a distinct variety due to its different growth season and stronger aroma:
- Appearance: Similar to summer truffle but with darker interior
- Season: September-December
- Aroma: More intense than summer truffle, with hazelnut and woodland notes
- Cultivation: Successfully grown in North America; well-suited to cooler climates

Traditional Truffle Harvesting Methods
The harvesting of truffles has evolved from traditional methods into a specialized skill that combines animal assistance with human expertise.
Truffle Hunting Animals
Historically, female pigs were used for truffle hunting due to their keen sense of smell and natural attraction to compounds in truffles similar to boar pheromones. Today, specially trained dogs have largely replaced pigs for several reasons:
- Control: Dogs are easier to control and less likely to eat the valuable truffles
- Training versatility: Dogs can be trained to find multiple truffle species
- Discretion: Dogs attract less attention in competitive hunting regions
- Handling ease: More manageable in various terrain and weather conditions
The Hunting Process
A typical truffle hunt involves:
- Early morning or evening outings when scents are strongest
- The trained animal detecting the scent of mature truffles beneath the soil
- Careful digging by the hunter to extract the truffle without damage
- Immediate assessment of quality and maturity
- Gentle cleaning and proper storage to maintain freshness
Truffle Cultivation: Challenges and Approaches
Truffle cultivation represents one of the most challenging and lengthy agricultural endeavors, requiring precise conditions, specialized knowledge, and considerable patience.
Traditional Orchard Cultivation
The most established method of truffle cultivation involves creating a truffle orchard or "truffière":
- Site selection: Choosing land with appropriate soil pH (7.5-8.3), good drainage, and suitable climate
- Soil preparation: Adjusting soil composition and pH if necessary, often by adding limestone
- Inoculated saplings: Planting tree seedlings whose roots have been inoculated with truffle spores
- Orchard management: Maintaining proper irrigation, weed control, and tree care
- Patience: Waiting 5-10 years for the first truffle production
- Harvesting: Using trained dogs to locate mature truffles once production begins
This method has proven successful for certain truffle varieties, particularly the black Périgord truffle and Burgundy truffle, in regions with suitable conditions.
Modern Cultivation Innovations
Research continues to improve truffle cultivation success rates and explore alternative approaches:
- Scientific inoculation methods: More reliable techniques for introducing truffle spores to tree roots
- Soil microbiome management: Better understanding of the soil ecosystem needed for truffle development
- Climate control systems: In some experimental settings, attempts to manage microclimates for truffle production
- Geographic expansion: Successful cultivation in non-traditional regions like Australia, New Zealand, and the United States
Indoor Cultivation Limitations
True culinary truffles (Tuber species) require the living root systems of their host trees to form properly, making traditional indoor cultivation extremely difficult. While some experimental approaches exist, commercial production of true truffles generally requires the orchard approach.
It's important to note that certain products marketed as "truffle grow kits" often contain different fungi species that produce sclerotia (hardened masses of mycelium) rather than true Tuber species truffles. These are sometimes called "magic truffles" but are biologically distinct from culinary truffles.
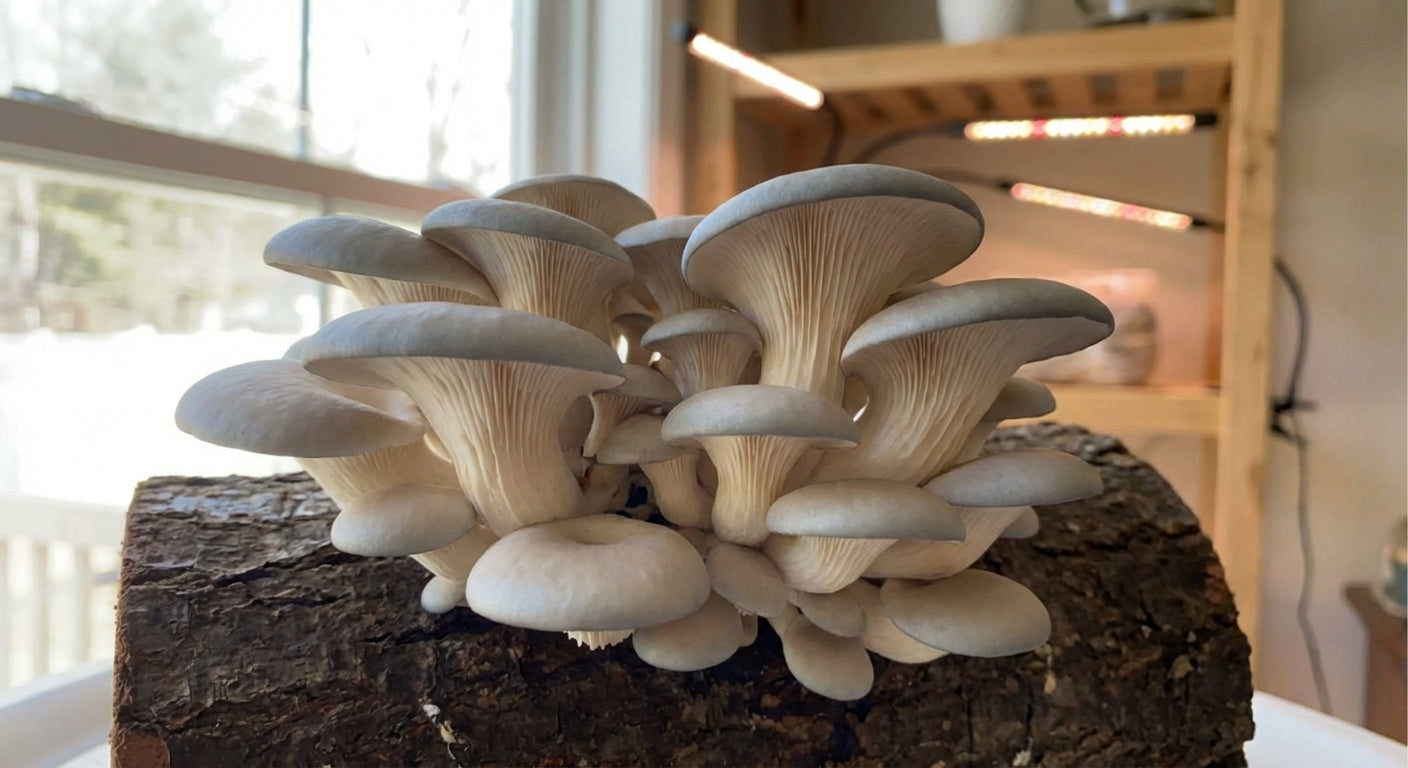
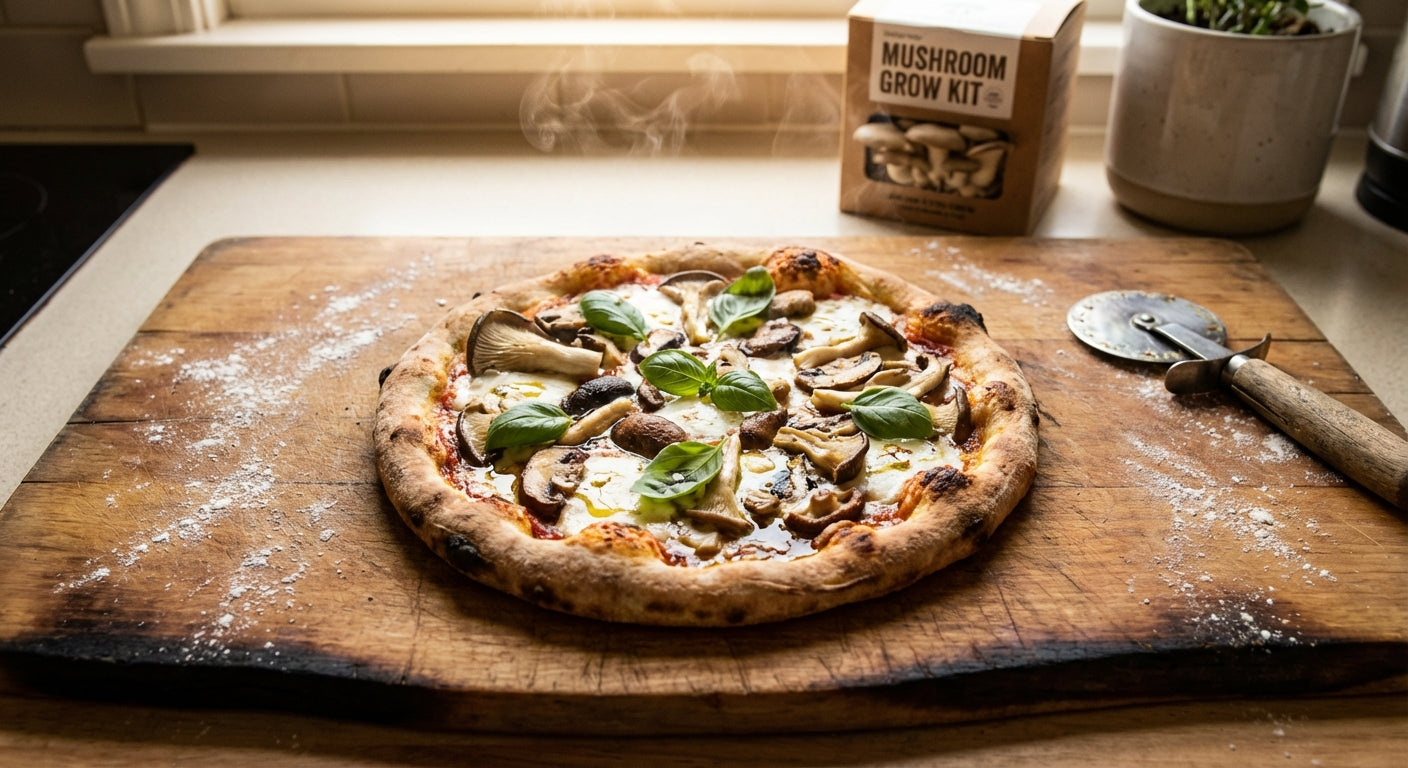
The Smart Mushroom Grow Kit and Truffle Cultivation
The Smart Mushroom Grow Kit from Lykyn represents cutting-edge technology for home mushroom cultivation. While true Tuber species truffles require outdoor orchards and tree symbiosis for production, the kit offers excellent functionality for growing a wide variety of gourmet mushrooms.
Limitations for True Truffle Cultivation
True culinary truffles (Tuber species) present specific challenges that make them unsuitable for indoor grow kit cultivation:
- Symbiotic requirements: True truffles need living tree roots to form properly
- Development timeframe: Truffles typically take years rather than weeks or months to develop
- Soil ecosystem: Truffles require a complex soil environment difficult to replicate in contained settings
- Spatial needs: The expanding mycelial network needs considerable space to form truffle bodies
Alternative Mushroom Opportunities
While true truffles may not be suitable for indoor cultivation, the Smart Mushroom Grow Kit offers excellent opportunities for growing many valuable mushroom species:
- Gourmet mushrooms: Varieties like oyster, lion's mane, and shiitake thrive in the controlled environment
- Medicinal mushrooms: Species like reishi and turkey tail with health-supporting properties
- Culinary delights: Flavor-rich varieties that command premium prices at markets
- Educational value: Observing the fascinating life cycle of various fungi species
For those interested in exploring the world of mushroom cultivation, focusing on these adaptable species provides a rewarding experience while developing foundational knowledge about fungal biology.
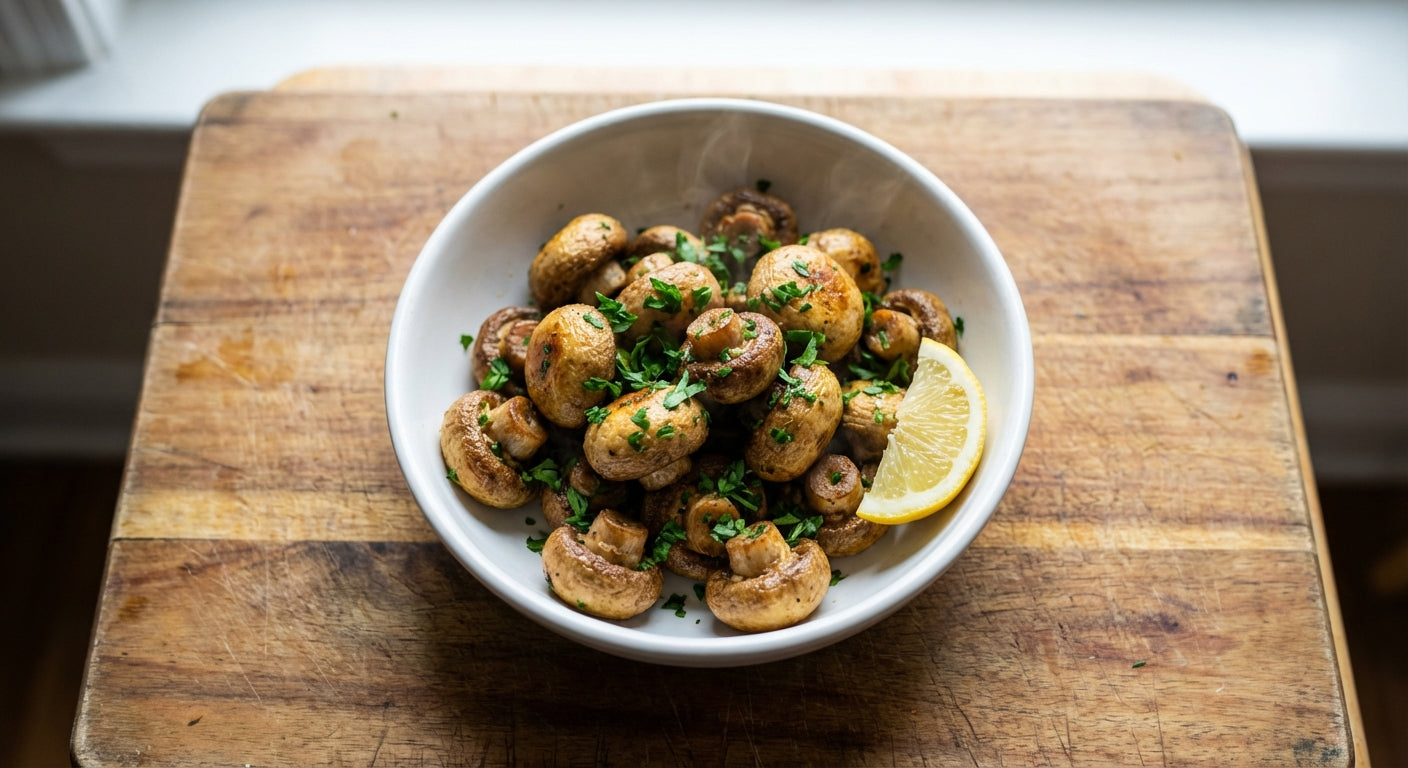
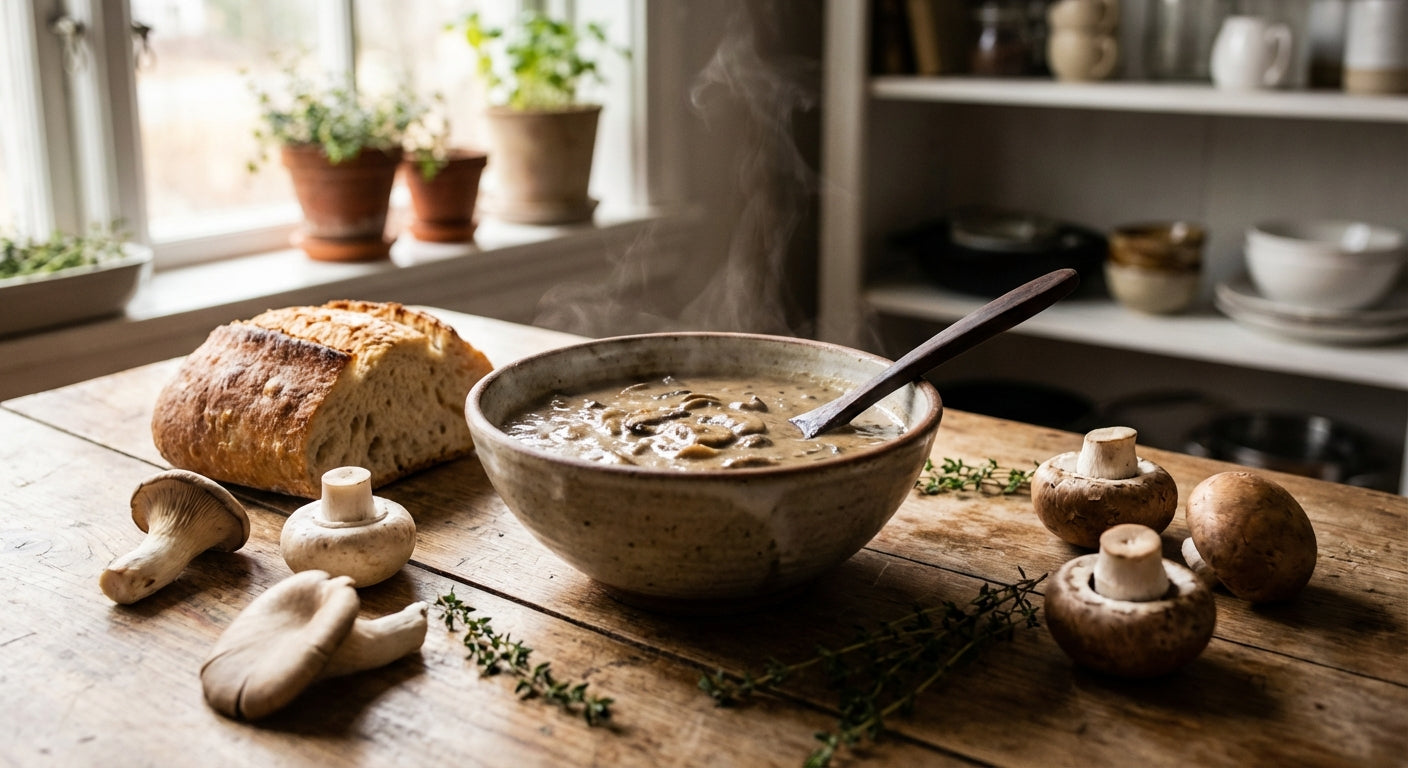
Culinary Uses and Preservation
The exceptional flavor and aroma of truffles have earned them a revered place in fine cuisine worldwide, with various techniques developed to maximize their culinary potential.
Fresh Truffle Applications
Fresh truffles deliver the most intense flavor experience and are used in several ways:
- Shaving: Thin slices added just before serving to dishes like pasta, risotto, eggs, or mashed potatoes
- Infusion: Storing truffles with eggs, rice, or cheese to impart their aroma
- Butter and oils: Incorporating freshly minced truffle into butter for immediate use
- Simple preparations: Minimalist approaches that highlight the truffle's natural flavor
The heat-sensitive compounds in white truffles make them best suited for raw applications, while black truffles can withstand some cooking while retaining their flavor.
Preservation Methods
Given the seasonal nature and high cost of truffles, various preservation methods have been developed:
- Refrigeration: Fresh truffles wrapped in paper towels and stored in airtight containers (5-7 days)
- Freezing: Quick-freezing whole or sliced truffles (diminishes aroma but preserves some flavor)
- Canning: Commercial preservation in jars (significant flavor reduction but extended shelf life)
- Dehydration: Dried and powdered for seasoning (substantially altered flavor profile)
- Truffle products: Commercial items like truffle salt, honey, or oil that capture some essence of the truffle
The Truth About Truffle Oil
Many commercial truffle oils contain synthetic compounds (particularly 2,4-dithiapentane) rather than actual truffles. While these products can impart truffle-like aromas, they typically lack the complexity and subtlety of products made with real truffles.
Authentic truffle oil is made by infusing oil with real truffles, but the heat-sensitive volatile compounds dissipate relatively quickly, giving these products a short shelf life compared to synthetic alternatives.

Frequently Asked Questions About Truffle Mushrooms
Why are truffles so expensive?
Truffles command extraordinary prices due to several factors: their limited growing seasons, difficulty in cultivation, the specialized skills and animals required for harvesting, their perishable nature requiring rapid transportation, and the simple economics of high demand meeting limited supply. White truffles, which have resisted cultivation efforts, remain among the most expensive food ingredients in the world, sometimes fetching thousands of dollars per pound.
Can truffles be grown at home?
True culinary truffles (Tuber species) cannot be effectively grown in home settings as they require living tree roots, specific soil conditions, and years of development. Home cultivation would necessitate suitable outdoor space for planting inoculated trees and a 5-10 year wait for potential production. Products marketed as indoor "truffle kits" typically contain different fungi species that aren't true culinary truffles.
What's the difference between white and black truffles?
Beyond their visual differences, white truffles (predominantly from Italy) have more intense, garlicky aromas and are almost always served raw as their flavor compounds are extremely heat-sensitive. Black truffles have a more earthy, robust flavor that can withstand some cooking. White truffles command higher prices due to their more limited growing regions and resistance to cultivation efforts.
How long do fresh truffles last?
Fresh truffles have a remarkably short shelf life, typically maintaining peak quality for only 5-7 days when properly stored in a refrigerator. They should be wrapped in clean paper towels and kept in an airtight container, with the paper changed daily to absorb moisture. The intense aroma begins diminishing immediately after harvest, which explains the premium price for the freshest specimens.
What trees do truffles grow with?
Different truffle species form symbiotic relationships with specific tree types. Black truffles primarily associate with oak and hazelnut trees, while white truffles form relationships with poplar, oak, hazel, and beech trees. The Burgundy truffle is more adaptable, forming associations with various hardwood trees including oak and hazelnut. These relationships are essential to the truffle's lifecycle and cannot be replaced by artificial growing mediums.
Summary: The Remarkable World of Truffles
Truffle mushrooms represent a fascinating convergence of biology, gastronomy, and tradition. These underground treasures have captivated human interest for centuries, evolving from foraged delicacies into carefully cultivated luxury ingredients in some cases. Their unique growth requirements, distinctive aromas, and culinary versatility ensure they remain among the most sought-after ingredients in fine dining worldwide.
While true Tuber species truffles require specialized growing conditions that make them unsuitable for indoor cultivation, mushroom enthusiasts can explore the fascinating world of fungi cultivation with many other varieties. The Smart Mushroom Grow Kit from Lykyn provides an excellent introduction to mushroom cultivation, offering the opportunity to grow gourmet and medicinal mushroom varieties that thrive in controlled indoor environments.
Whether you're fascinated by the biology of these underground fungi, interested in their culinary applications, or curious about mushroom cultivation in general, the world of truffles offers endless opportunities for exploration and appreciation.
Explore the World of Mushroom Cultivation
While true truffles may require specialized outdoor conditions, you can begin your mushroom cultivation journey today with the Lykyn Smart Mushroom Grow Kit. This innovative system provides ideal growing conditions for a wide variety of gourmet and medicinal mushrooms, allowing you to experience the satisfaction of growing your own fungi at home.
Discover the fascinating lifecycle of mushrooms, enjoy the culinary delights of fresh homegrown varieties, and develop your knowledge of fungi cultivation with this state-of-the-art growing solution. Visit our blog to learn more about different mushroom species and cultivation techniques to enhance your growing experience.















Share:
Hen of the Woods Mushroom: Ultimate Guide to Finding, Growing & Cooking This Gourmet Fungi
Beech Mushrooms: Complete Guide to Growing, Cooking, and Enjoying Shimeji