The black winter truffle (Tuber melanosporum) stands as the crown jewel in the world of fungi—a mysterious, aromatic delicacy that has captivated chefs, gourmands, and foragers for centuries. Often called the "Black Diamond of the Kitchen," these subterranean treasures command extraordinary prices and inspire passionate devotion from those who fall under their spell. Unlike most cultivated mushrooms, truffles represent a unique intersection of luxury, ecology, and gastronomic tradition that sets them apart in both culinary and mycological worlds. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about black winter truffles—from their fascinating biology to their unparalleled culinary applications.
The Mystique of Black Winter Truffles
What exactly makes black winter truffles so special, and why have they maintained their status as one of the world's most expensive foods for centuries?
History and Cultural Significance
Truffles have a rich historical legacy dating back thousands of years:
- Ancient Appreciation: Records of truffle consumption date to Sumerian civilizations around 4000 BCE
- Roman Luxury: Prized by Roman nobility who believed truffles were created when lightning struck damp earth
- Renaissance Revival: Gained renewed prominence in European royal courts during the Renaissance
- French Elevation: Achieved gastronomic prestige in 18th and 19th century French haute cuisine
- Modern Globalization: Now appreciated worldwide, though traditional European harvesting regions maintain their prominence
Throughout history, black winter truffles have been attributed with properties ranging from aphrodisiac powers to medicinal benefits. Their rarity and difficulty in procurement have consistently positioned them as status symbols across cultures and eras.
Geographical Distribution
Black winter truffles have specific native regions and introduced territories:
- Traditional Regions: Primarily southern France (Périgord), northern Spain, and central Italy
- Expanding Territories: Successful cultivation now established in Australia, New Zealand, Chile, and the United States
- Microclimate Requirements: Require specific soil conditions, climate patterns, and host tree relationships
- Seasonal Availability: Peak season runs December through March in the northern hemisphere, June through September in the southern hemisphere
Climate change and habitat loss have impacted traditional truffle territories, while cultivation efforts have expanded their global footprint—though production volumes remain limited compared to demand.
Biology and Ecology of Black Winter Truffles
Understanding the unique lifecycle and ecological relationships of black winter truffles reveals why they're so difficult to cultivate compared to other fungi.
Taxonomy and Physical Characteristics
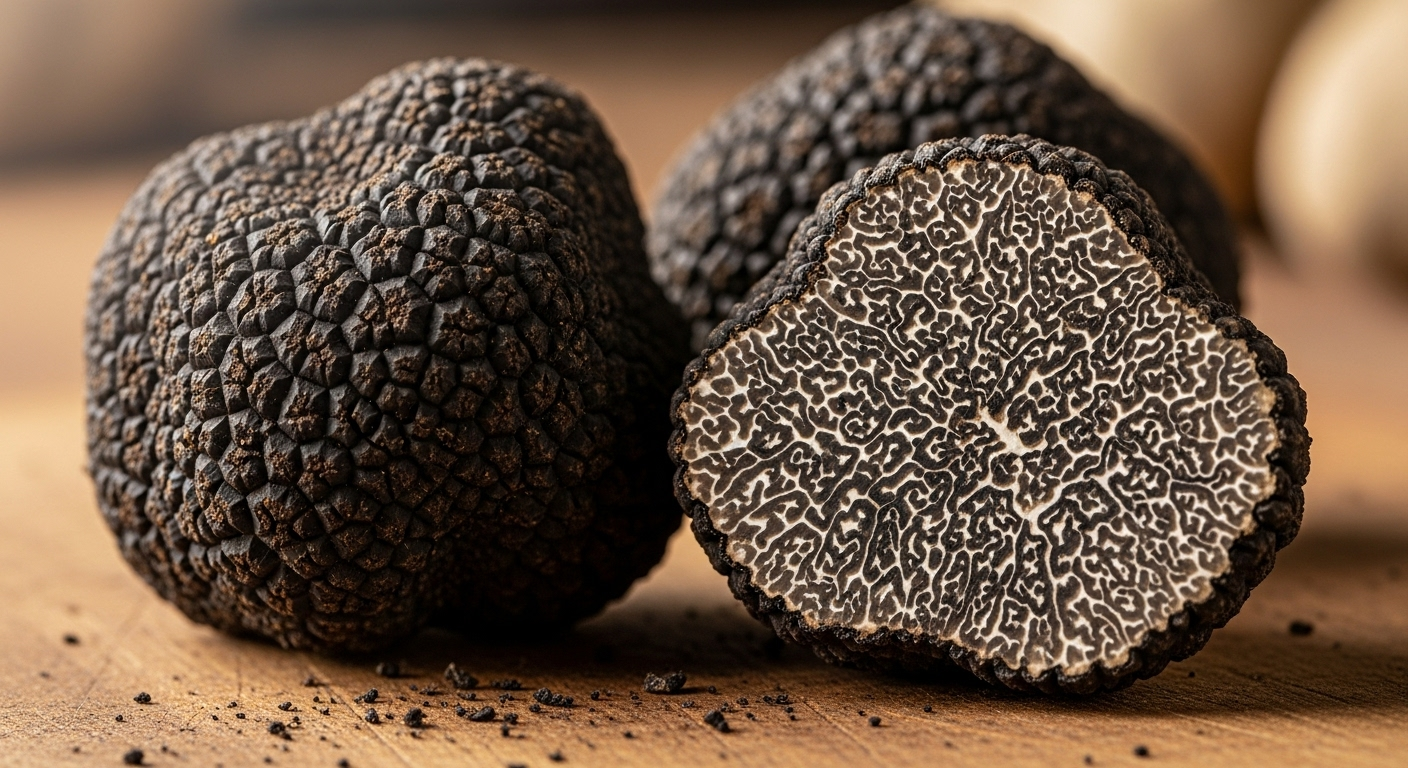
Black winter truffles possess distinctive features that set them apart from other truffle species:
- Scientific Classification: Kingdom Fungi, Phylum Ascomycota, Family Tuberaceae, Species Tuber melanosporum
- Appearance: Irregular, rounded shape with a rough, warty exterior
- Size: Typically 3-10 cm in diameter, weighing 30-300 grams
- External Color: Blackish-brown to deep black exterior
- Interior: Marbled interior with white veining against a black/purple-brown background
- Aroma: Complex scent described as musky, earthy, and encompassing notes of chocolate, forest floor, garlic, and fermented cheese
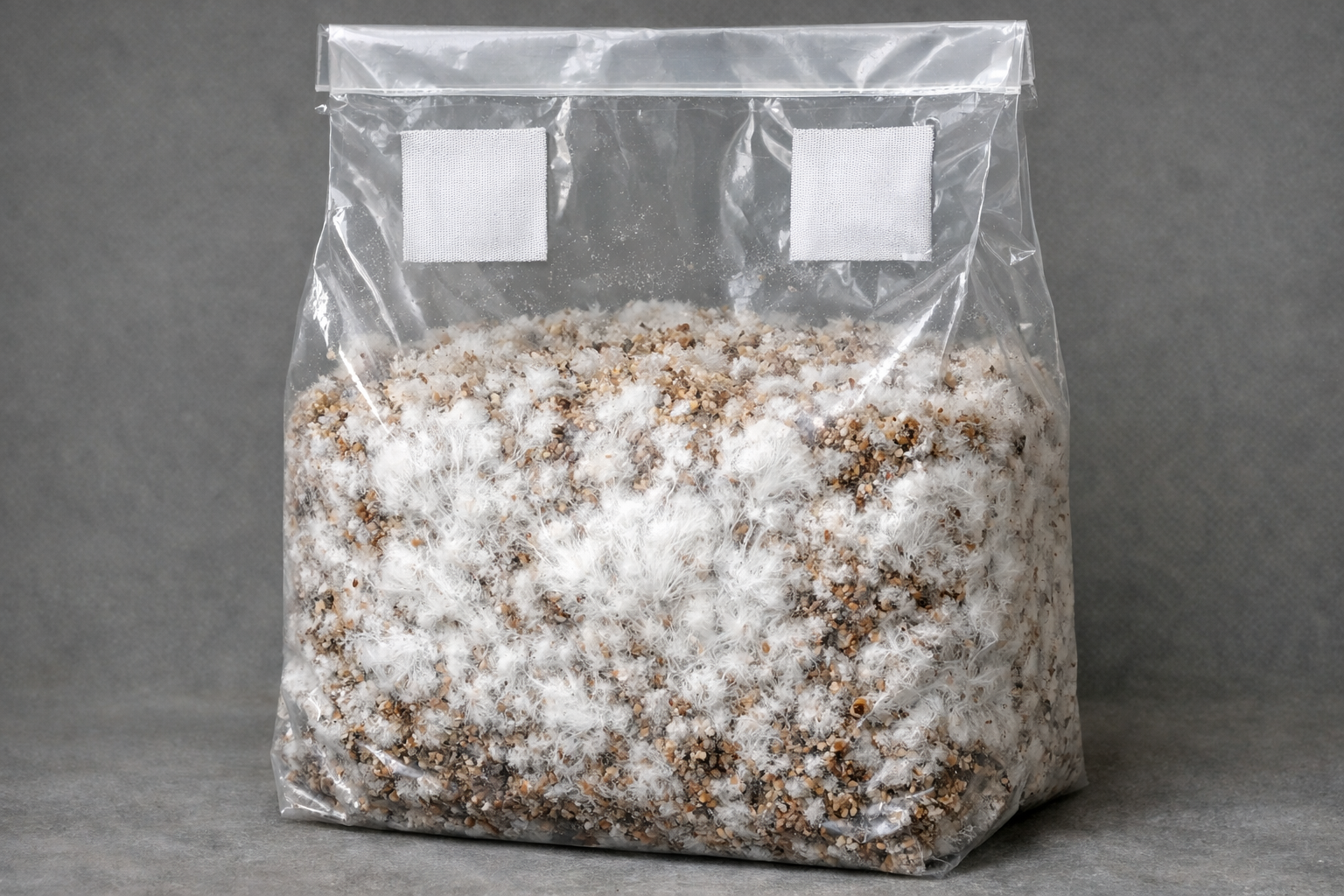
Unlike the mushrooms that can be grown in controlled environments such as the Lykyn Smart Mushroom Grow Kit, truffles develop entirely underground and require completely different growing conditions.
Lifecycle and Symbiotic Relationships
Black winter truffles engage in complex ecological partnerships:
- Mycorrhizal Relationship: Form symbiotic connections with the root systems of specific host trees
- Preferred Host Trees: Primarily oak (Quercus) and hazelnut (Corylus), occasionally beech, poplar, and hornbeam
- Mutual Exchange: Truffle provides minerals and water to the tree; tree provides carbohydrates to the truffle
- Reproductive Strategy: Produces aromatic compounds that attract animals (particularly wild boars and specialized dogs) which dig up and consume the truffles, dispersing spores
- Growth Cycle: Requires 5-7 years from spore to first truffle production; productive trees can yield truffles for decades
This obligate symbiotic relationship with tree roots makes truffles fundamentally different from saprotrophic mushrooms (like shiitake, oyster, or lion's mane) that feed on dead organic matter and can be cultivated on substrates in controlled environments.
Soil and Climate Requirements
The exacting environmental needs of black winter truffles include:
- Soil Composition: Calcareous (limestone-rich) soil with pH between 7.5-8.5
- Soil Structure: Well-draining with good aeration
- Climate: Mediterranean-type climate with mild, wet winters and warm, dry summers
- Rainfall Pattern: Requires significant summer rainfall or irrigation
- Temperature Range: Cannot tolerate extreme cold; prefers moderate winter temperatures
These specific requirements explain why natural truffle habitats remain limited to particular regions despite centuries of attempts to expand production areas.

Cultivation Challenges vs. Traditional Mushroom Growing
While many gourmet mushrooms can be reliably grown in controlled indoor environments, black winter truffles present unique cultivation challenges that explain their limited production and high market value.
Why Truffles Cannot Be Grown in Traditional Mushroom Systems
Unlike the mushroom varieties optimized for the Lykyn Smart Mushroom Grow Kit, black winter truffles cannot be cultivated in controlled indoor environments due to several fundamental differences:
- Obligate Symbiosis: Require living host trees rather than sterilized growing substrates
- Extended Timeline: Need 5-7 years from inoculation to first harvest (compared to weeks for most cultivated mushrooms)
- Spatial Requirements: Develop in expansive underground networks around tree roots, requiring significant land area
- Environmental Complexity: Need natural seasonal variations and complex soil ecology that cannot be fully replicated indoors
- Microbial Community: Rely on diverse soil microorganisms that form part of their growing environment
These factors make truffles unsuitable for the controlled, rapid-cycle cultivation systems that work well for saprotrophic mushroom species.
Modern Truffle Orchard Approaches
Despite these challenges, advances in truffle cultivation have made plantation production increasingly successful:
- Inoculated Seedlings: Young host trees are inoculated with truffle spores in their root systems
- Soil Preparation: Ground is carefully tested and amended to achieve ideal pH and mineral content
- Irrigation Systems: Precise water management systems counter rainfall variability
- Orchard Management: Regular pruning and maintenance of host trees to optimize growing conditions
- Patience: Investors must wait years before seeing any return on investment
Even with these modern approaches, truffle cultivation remains inherently uncertain. Many planted orchards never achieve commercial production levels, while others exceed expectations. This unpredictability contributes to the mystique and premium pricing of cultivated truffles.
Contrasting with Controlled Indoor Cultivation
To understand why truffles command such high prices, consider how their production differs from controlled indoor mushroom cultivation:
| Cultivation Aspect | Black Winter Truffles | Indoor-Grown Mushrooms |
|---|---|---|
| Growing Medium | Living tree roots in natural soil | Sterilized substrates |
| Time to Harvest | 5-7 years | 2-8 weeks |
| Space Required | Acres of orchard | Compact growing chambers |
| Yield Predictability | Highly variable and weather-dependent | Consistent and reliable |
| Harvest Method | Manual detection and digging | Simple collection |
| Cultivation Control | Limited management options | Precise environmental control |
For those interested in reliable home mushroom cultivation, focusing on species well-suited to controlled environments makes more sense. The Lykyn Smart Mushroom Grow Kit optimizes growing conditions for varieties like shiitake, oyster, and lion's mane mushrooms, which offer excellent culinary and nutritional value with much more predictable results.
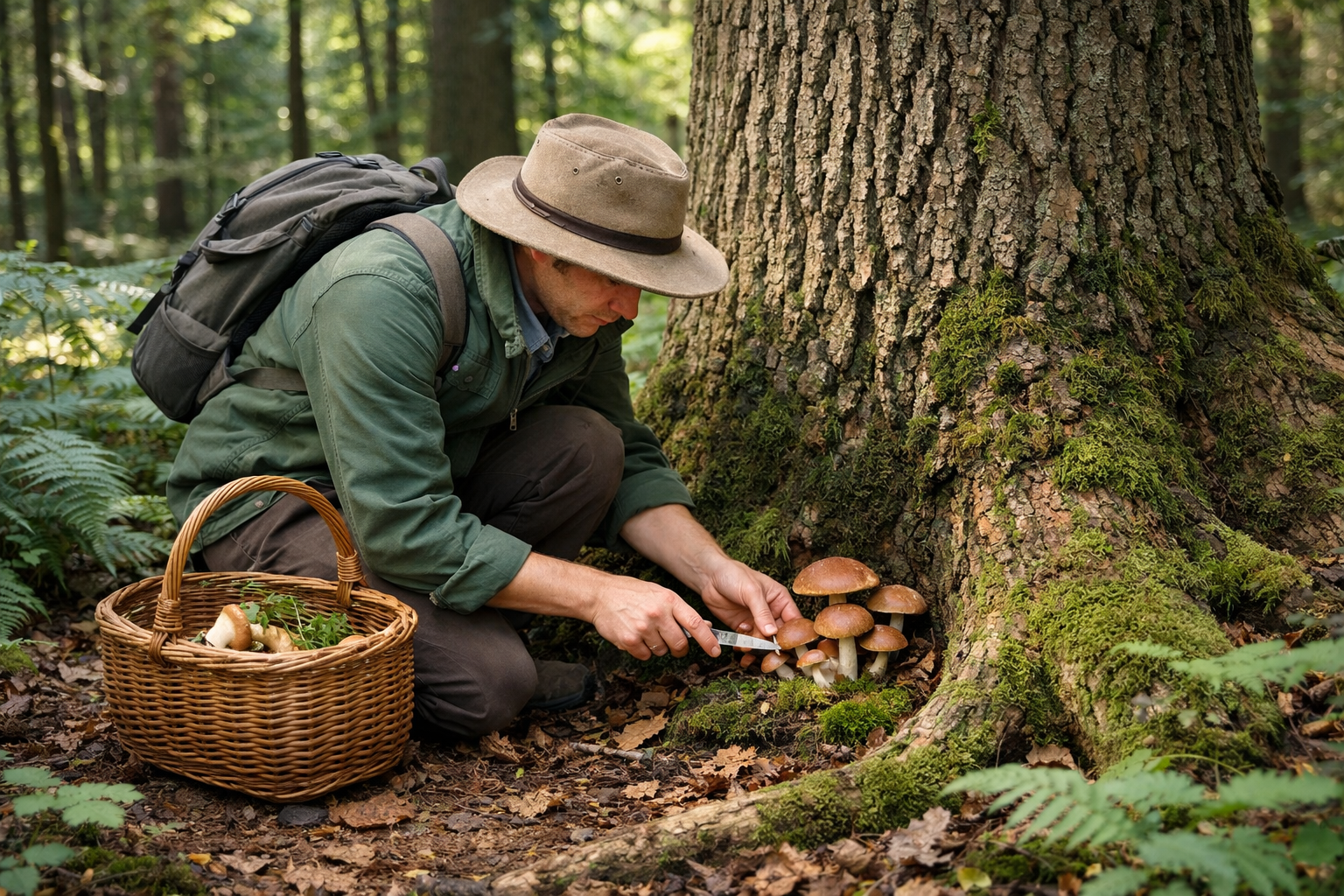
Truffle Hunting: The Art of Harvest
The traditional methods of locating and harvesting black winter truffles add another layer to their mystique and value.
Traditional Hunting Methods
Truffle hunting has evolved distinctive approaches over centuries:
Trained Animals
- Dogs: Currently the preferred method, using breeds like the Lagotto Romagnolo with specific truffle-hunting training
- Pigs: Historically used (especially female pigs naturally attracted to truffle compounds resembling boar pheromones)
- Training Process: Animals are conditioned to associate truffle scent with rewards through careful positive reinforcement
- Advantages: Animals can detect mature truffles up to 30cm underground through scent alone
Human Indicators
- Fly Spotting: Expert hunters observe certain flies that lay eggs on soil above truffles
- Plant Associations: Identifying "brûlé" (burnt areas) where vegetation is suppressed around truffle-producing trees
- Soil Cracks: Recognizing specific soil formations that may indicate truffle growth
- Limitations: Generally less reliable than trained animals and requires years of experience
Harvest Timing and Technique
Proper harvesting requires precision and expertise:
- Optimal Ripeness: Harvesting only fully mature truffles with developed aroma
- Careful Extraction: Using specialized tools (truffle picks and digging knives) to avoid damaging the fungi
- Soil Preservation: Replacing soil and mycelial networks to protect future production
- Site Marking: Experienced hunters often map productive areas for future seasons
- Season Timing: Harvesting during peak season (December-March) when aroma and flavor reach maximum development
The expertise required for successful truffle hunting represents yet another factor in the high market value of quality specimens.
Post-Harvest Handling
Immediate post-harvest treatment significantly impacts truffle quality:
- Gentle Cleaning: Light brushing to remove soil without damaging the exterior
- Inspection: Checking for ripeness, insect damage, and quality characteristics
- Grading: Sorting by size, aroma intensity, and visual appearance
- Careful Wrapping: Individually wrapping premium specimens in absorbent paper
- Temperature Control: Immediate refrigeration at specific humidity levels
From forest to kitchen, each truffle may pass through multiple hands, with each step potentially affecting its final value and quality.

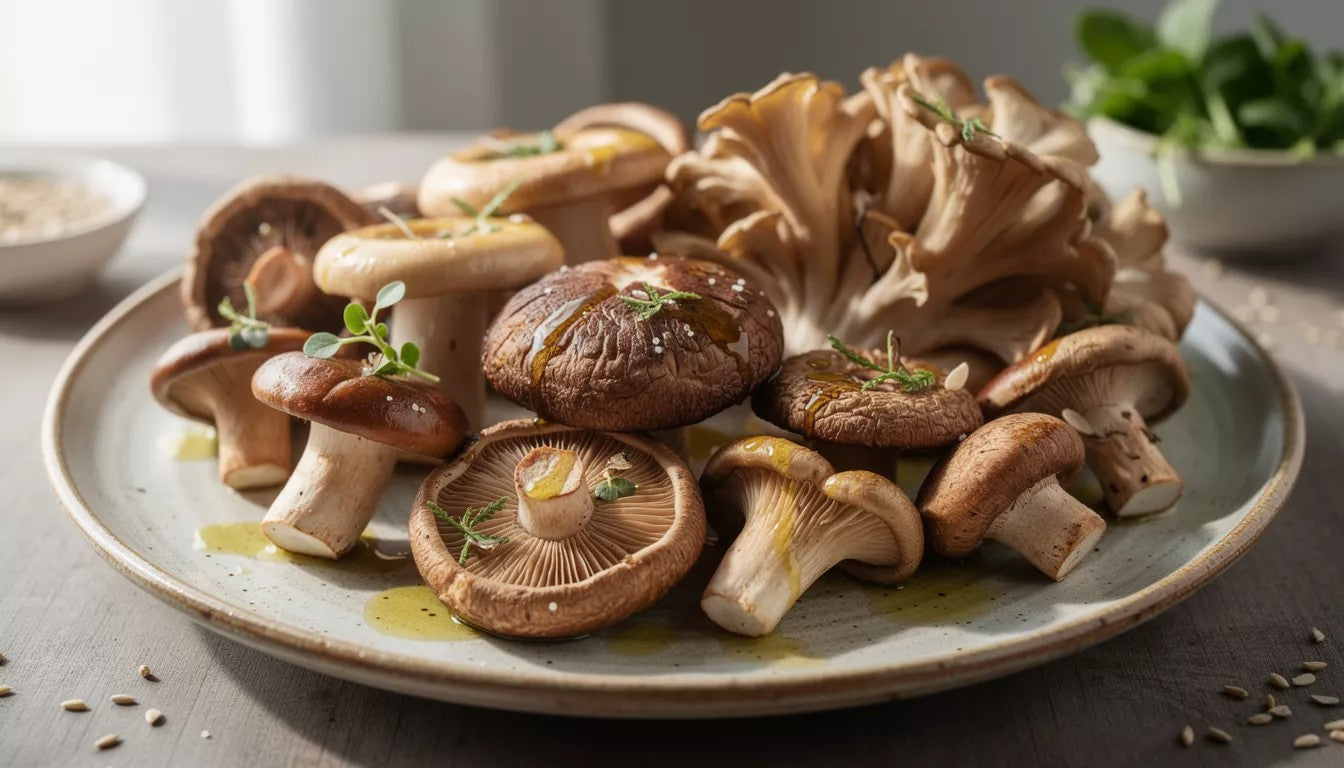
Culinary Applications and Flavor Profile
The extraordinary culinary status of black winter truffles stems from their unique sensory characteristics and versatility in fine dining.
Understanding Truffle Aroma and Flavor
Black winter truffles possess a complex sensory profile:
- Aroma Compounds: Contains over 120 volatile compounds contributing to its scent
- Primary Notes: Earthy, musky, and chocolate-like base notes
- Secondary Elements: Hints of garlic, nuts, hay, and fermented cheese
- Tertiary Complexity: Subtle notes of petroleum, spice, and forest floor
- Taste Experience: Rich umami foundation with subtle sweetness and distinctive pungency
- Flavor Development: Aroma intensifies when gently warmed, releasing volatile compounds
This extraordinary aromatic complexity explains why even small amounts can transform dishes dramatically.
Classic Culinary Applications
Traditional preparations showcase black winter truffles in specific ways:
Simple Presentations
- Truffle Butter: Infusing high-quality butter with truffle shavings
- Eggs: Scrambled eggs, omelets, and fried eggs with truffle shavings
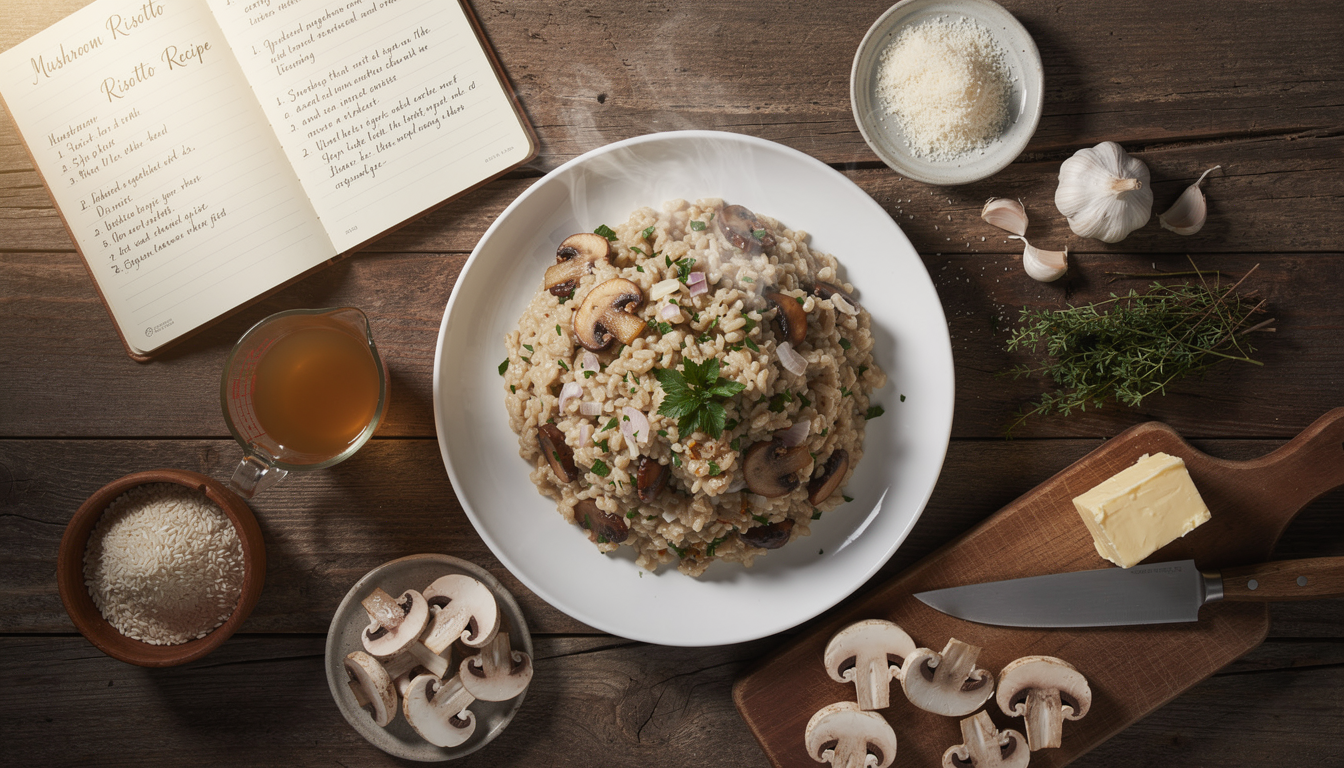
- Risotto: Traditional risotto finished with fresh truffle
- Pasta: Simple pasta dressed with butter or light cream and fresh truffle
- Potatoes: Mashed or roasted potatoes topped with truffle
Advanced Preparations
- Sous Vide Infusions: Vacuum-sealing ingredients with truffle to intensify flavor transfer
- Truffle-Centered Terrines: Layered preparations highlighting truffle aroma
- Slow-Cooked Meats: Rich braises and roasts complemented with truffle
- Aged Cheese Pairings: Serving alongside specific aged cheeses that complement truffle notes
Traditional wisdom holds that simpler preparations often better showcase the truffle's inherent quality, allowing its aroma to take center stage rather than competing with complex flavors.
Chef's Guidelines for Optimal Use
Professional chefs follow several principles to maximize black winter truffle impact:
- Temperature Sensitivity: Serve truffles warm (never hot) to release volatile compounds
- Minimal Cooking: Add at the end of preparation or serve raw; extended cooking diminishes aroma
- Fat Affinity: Pair with fat-rich ingredients (butter, cream, cheese, egg yolks) that capture and carry aromatic compounds
- Shaving Technique: Use dedicated truffle slicers for paper-thin, uniform slices
- Immediate Service: Serve promptly after shaving to capture peak aroma
- Complementary Ingredients: Choose mild, creamy base ingredients that won't overwhelm truffle notes
These techniques explain why seemingly simple dishes like truffle pasta or eggs with truffle can command premium prices at fine restaurants—when executed correctly, they perfectly showcase the truffle's extraordinary qualities.
Storage, Preservation, and Market Considerations
The perishable nature of fresh black winter truffles creates significant challenges for distribution and storage, contributing further to their luxury status.
Fresh Truffle Storage Best Practices
To maintain maximum quality of fresh black winter truffles:
- Temperature: Store at 34-36°F (1-2°C)—slightly warmer than standard refrigeration
- Humidity: Maintain 85-90% humidity to prevent drying
- Wrapping Method: Wrap individually in clean, absorbent paper (changed daily)
- Container: Store in sealed glass containers with absorbent material
- Isolation: Keep separate from other foods to prevent aroma transfer
- Usage Timeline: Consume within 5-7 days of harvest for optimal quality
- Quality Check: Inspect daily for moisture or softening, which indicates spoilage
Even with perfect storage, fresh truffles lose approximately 3-5% of their mass daily and experience aroma degradation, creating a literal countdown clock from harvest to consumption.
Preservation Methods and Their Limitations
Various preservation techniques extend usability but alter the truffle experience:
Freezing
- Process: Flash-freezing at ultra-low temperatures
- Effectiveness: Maintains some aroma but alters texture significantly
- Applications: Best used in cooked preparations after thawing
Canning
- Process: Heat-sterilized in oil or brine
- Effectiveness: Significantly diminishes fresh aroma but maintains shelf stability
- Applications: Usable in cooked dishes where visual presentation matters more than peak aroma
Infusion
- Process: Steeping truffles in neutral oil, butter, or honey
- Effectiveness: Transfers some aromatic compounds while sacrificing the original truffle
- Applications: Creates versatile flavored ingredients with extended usability
Dehydration
- Process: Carefully drying sliced truffles at low temperatures
- Effectiveness: Concentrates certain flavors while losing volatile compounds
- Applications: Can be powdered for use as seasoning
While these methods extend availability, they represent significant compromises compared to fresh specimens. For those interested in preservation techniques for other mushroom varieties, our guide on creating mushroom powders offers applicable insights.
Market Value and Economic Impact
The black winter truffle market represents a fascinating economic ecosystem:
- Price Range: Premium specimens typically sell for $800-$1,200 per pound retail
- Grading Factors: Size, aroma intensity, visual perfection, and harvest timing
- Regional Variations: French Périgord truffles often command higher prices than those from other regions
- Market Volatility: Prices fluctuate dramatically based on seasonal yields and quality
- Economic Impact: Supports specialized rural economies in traditional growing regions
- Industry Size: Global market estimated at $200-300 million annually
- Future Outlook: Cultivation expansion likely to stabilize but not dramatically reduce prices
The combination of limited supply, high demand, and the inherent unpredictability of production ensures that black winter truffles remain a luxury commodity for the foreseeable future.

Nutritional Profile and Potential Health Benefits
Beyond their culinary applications, black winter truffles offer interesting nutritional properties and potential health benefits.
Nutritional Composition
Black winter truffles provide a unique nutritional profile:
- Macronutrients: Low in calories, fat, and carbohydrates; moderate protein content
- Fiber Content: Good source of dietary fiber relative to volume
- Mineral Composition: Rich in potassium, phosphorus, and magnesium
- Vitamin Profile: Contains B vitamins, particularly riboflavin and niacin
- Antioxidants: Provides various phenolic compounds with antioxidant properties
- Unique Compounds: Contains ergosterol (precursor to vitamin D) and various terpenes
While truffles wouldn't be consumed in quantities sufficient to serve as primary nutrient sources, their distinctive compound profile contributes to their potential functional benefits.
Traditional Medicinal Uses
Throughout history, truffles have been attributed with various health properties:
- Aphrodisiac Effects: Historically believed to stimulate romantic desire
- Longevity Promotion: Traditional European medicine considered truffles life-extending
- Digestive Support: Used to stimulate appetite and aid digestion
- Energy Enhancement: Believed to provide vital energy and stamina
- Immune Function: Traditional use for supporting general immunity
These traditional applications, while not scientifically validated in their original context, have inspired modern research into potential health properties.
Contemporary Research Areas
Modern scientific investigation has identified several promising areas regarding truffle bioactivity:
- Antimicrobial Properties: Studies suggest compounds in truffles may have antimicrobial effects
- Antioxidant Activity: Various extracts demonstrate free radical scavenging capabilities
- Anti-inflammatory Potential: Certain compounds show promise in reducing inflammatory markers
- Prebiotic Effects: Fiber components may support beneficial gut bacteria
- Immunomodulation: Some truffle extracts appear to influence immune response in preliminary studies
While this research remains preliminary and primarily conducted in laboratory settings rather than human clinical trials, it suggests that the historical appreciation for truffles may have had some basis beyond their extraordinary flavor.
For those interested in fungi with more established health benefits, our guides on lion's mane mushrooms and shiitake mushrooms explore species with substantial research behind their functional properties.
FAQ About Black Winter Truffles
How can I tell if a black winter truffle is fresh and high quality?
Why are black winter truffles so expensive compared to other mushrooms?
Can I grow black winter truffles at home using mushroom growing kits?
What's the difference between black winter truffles and other truffle varieties?
How should I cook with black winter truffles to get the most value?
The Future of Black Winter Truffles
As technology advances and climate conditions shift, the world of black winter truffles continues to evolve in interesting ways.
Cultivation Innovation
Modern approaches are gradually increasing production reliability:
- DNA Testing: Advanced genetic techniques help verify truffle species in inoculated seedlings
- Soil Microbiome Analysis: Better understanding of beneficial bacterial communities that support truffle growth
- Climate Modeling: Sophisticated predictions of suitable growing regions under changing conditions
- Irrigation Technology: Precision water management systems that mimic ideal natural conditions
- Root Imaging: Non-invasive techniques to monitor underground mycorrhizal development
While these advances improve success rates, they don't fundamentally change the lengthy timeline or specialized conditions required for truffle production.
Climate Change Implications
Shifting climate patterns are affecting traditional and emerging truffle territories:
- Traditional Regions: Historic European growing areas experiencing challenges from altered rainfall patterns and temperature increases
- New Opportunities: Previously unsuitable regions becoming viable as climate zones shift
- Seasonal Shifts: Harvesting seasons changing in timing and duration
- Quality Concerns: Potential impacts on aroma development and truffle size
- Adaptation Strategies: Producers implementing water management and shade systems to counter climate effects
These changes represent both challenges and opportunities for the global truffle industry, potentially reshaping production geography over coming decades.
Market Evolution
The black winter truffle market continues to develop in response to various forces:
- Cultivation Expansion: Increasing production from new regions like Australia, Chile, and North America
- Consumer Education: Growing awareness of truffle characteristics and quality factors
- Authenticity Concerns: Development of verification methods to combat fraudulent products
- Processing Innovation: New preservation techniques aiming to capture more fresh-like qualities
- Market Access: Digital platforms connecting producers directly with global buyers
While production increases may moderately improve availability, the fundamental limitations of truffle biology ensure they will remain a luxury item for the foreseeable future.

Experiencing Black Winter Truffles: Practical Advice
For those intrigued by black winter truffles, here are practical recommendations for meaningful experiences with these extraordinary fungi.
Finding and Selecting Quality Truffles
When seeking to purchase black winter truffles:
- Timing: Shop during peak season (December-March) when quality is highest
- Sources: Seek specialty purveyors with direct relationships to truffle hunters/farmers
- Selection Criteria: Look for firm texture, intense aroma, and uniform appearance
- Price Expectations: Quality specimens typically sell for $50-100 per ounce retail
- Quantity Guidance: Even small amounts (10-15 grams) can significantly impact multiple dishes
Developing a relationship with a reputable truffle supplier often leads to better selection opportunities and occasionally preferential access to exceptional specimens.
Truffle-Focused Culinary Experiences
Beyond purchasing truffles, consider these alternative experiences:
- Truffle-Hunting Tours: Participate in guided truffle hunts in producing regions
- Dedicated Restaurants: Visit establishments known for truffle expertise during season
- Cooking Classes: Take specialized courses focused on truffle preparation
- Regional Festivals: Attend celebrations in traditional producing areas
- Truffle Markets: Visit specialty markets during peak season for immersive experiences
These experiences often provide deeper understanding and appreciation than simply purchasing truffles for home use.
Alternatives for Mushroom Enthusiasts
For those fascinated by truffles but seeking more accessible fungi experiences:
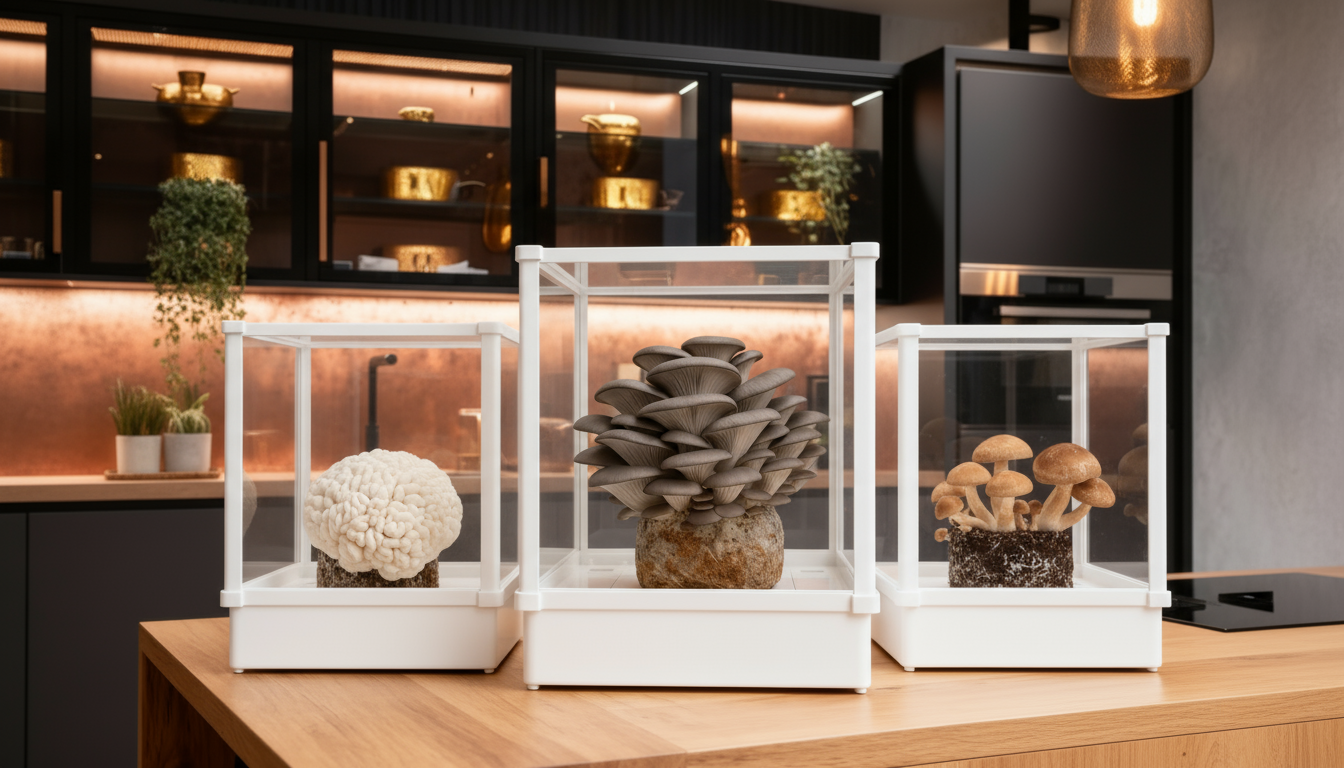
- Home Cultivation: Grow gourmet mushrooms using the Lykyn Smart Mushroom Grow Kit, which creates ideal conditions for varieties like shiitake, oyster, and lion's mane
- Mushroom Foraging: Learn to identify wild mushroom species in your region through guided tours
- Specialty Mushroom Exploration: Experiment with other gourmet varieties that offer unique flavors and textures
- Preservation Techniques: Master methods for drying and powdering mushrooms to extend their usability
While these alternatives don't replicate the specific truffle experience, they provide rewarding connections to the fascinating world of fungi through more accessible avenues.
Conclusion: The Enduring Allure of Black Winter Truffles
Black winter truffles represent a fascinating intersection of biology, gastronomy, tradition, and luxury. Their unique growth requirements—forming symbiotic relationships with tree roots in specific soil conditions over many years—create natural limitations that cultivation technology has only partially addressed. This inherent scarcity, combined with their extraordinary aromatic properties and cultural cachet, ensures they remain one of the world's most prized culinary ingredients.
For most mushroom enthusiasts, direct experience with black winter truffles may be occasional and special—perhaps a restaurant splurge during truffle season or a small purchase for a significant celebration. Meanwhile, the broader world of fungi offers many more accessible pleasures, from the satisfaction of growing your own gourmet mushrooms to exploring the diverse flavors and potential health benefits of various species.
Whether your interest lies in someday experiencing the unique sensory pleasure of fresh black winter truffles or in the more immediately accessible joy of cultivating mushrooms at home, the kingdom of fungi offers endless fascination and reward. The contrasts between the mysterious underground world of truffles and the controlled precision of modern mushroom cultivation highlight the remarkable diversity within this extraordinary biological kingdom.
Ready to begin your own mushroom growing journey? While black winter truffles remain beyond home cultivation capabilities, many exceptional gourmet mushroom varieties thrive in controlled environments. The Lykyn Smart Mushroom Grow Kit makes growing delicious and nutritious mushrooms at home simple and rewarding, providing a fascinating window into the world of fungi cultivation.













Share:
Mushroom Powders: Ultimate Guide to Benefits, Uses, and DIY Methods 2025
Candy Cap Mushrooms: Complete Guide to Nature's Maple Syrup Fungi