Morel mushrooms are among the most sought-after wild edibles in North America, prized for their uniquely earthy flavor and distinctive honeycomb appearance. Every spring, enthusiasts venture into forests and woodlands in search of these culinary treasures. However, proper identification is crucial, as morels have toxic look-alikes that can cause illness if consumed.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through everything you need to know about identifying morel mushrooms, from their distinctive features to the habitats where they grow, and how to differentiate them from dangerous imposters.
True Morel Characteristics: What to Look For
True morels (genus Morchella) have several distinctive features that make them identifiable in the wild. Here are the key characteristics to look for:
1. The Distinctive Cap
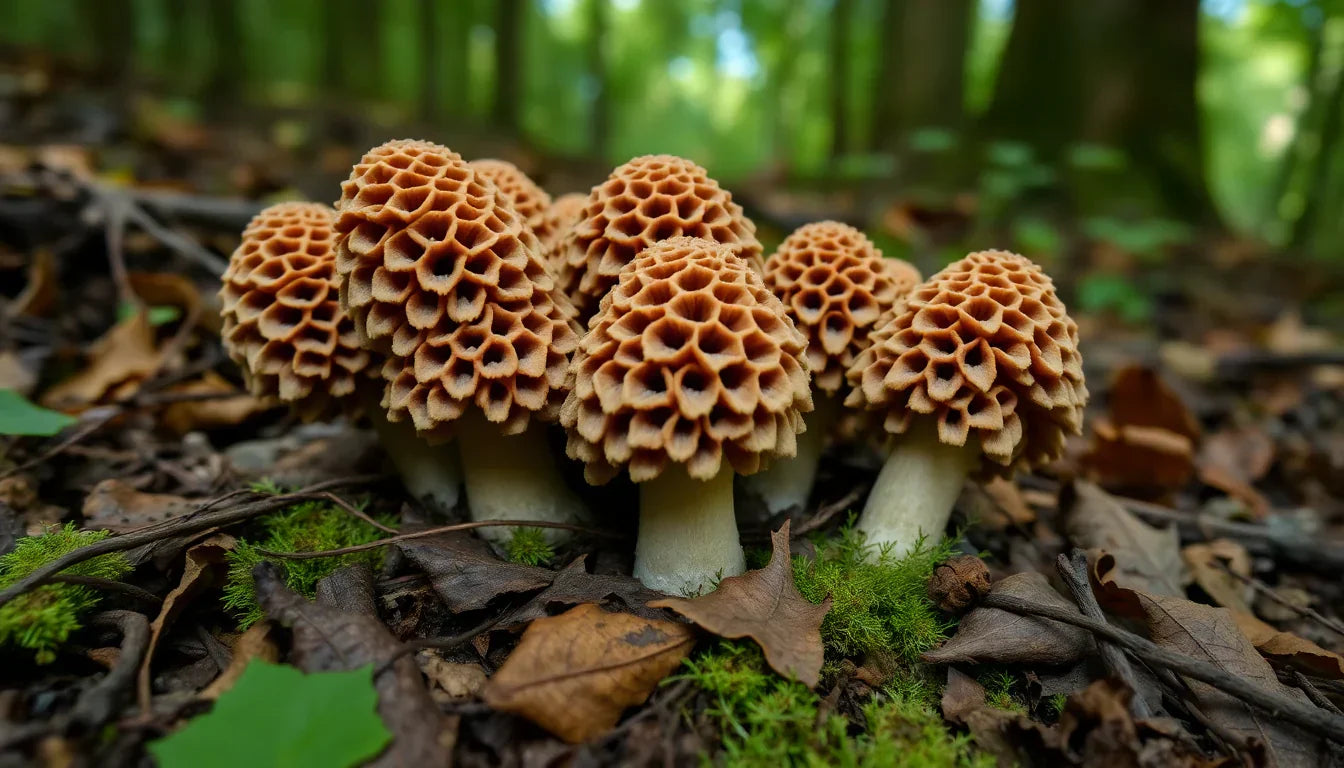
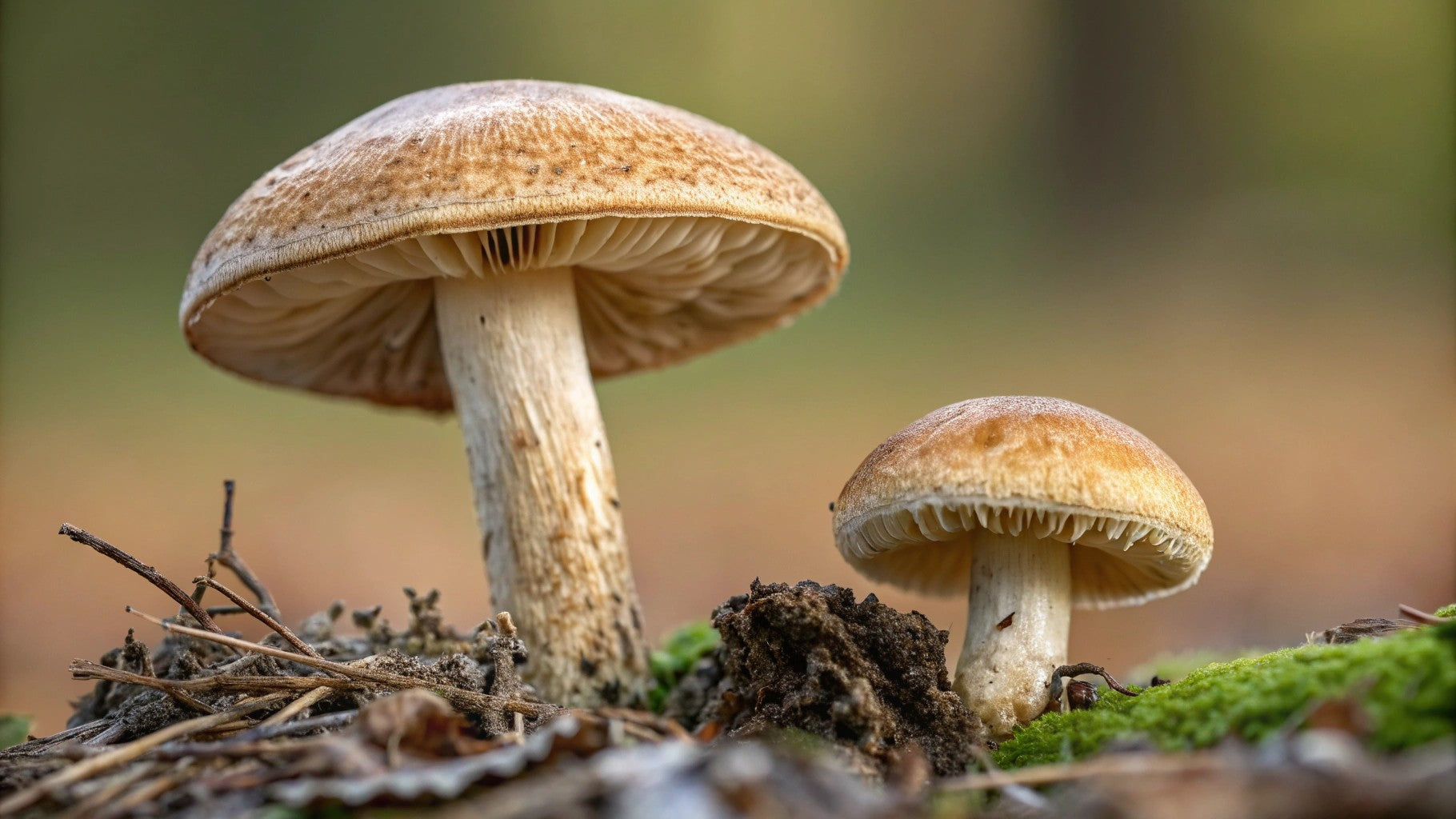
The most recognizable feature of a morel mushroom is its cap, which has a distinctive honeycomb pattern of ridges and pits.
-
Pitted Texture: True morels have caps with deep, defined pits that look like little hollows punched partway through them. These pits are arranged in a somewhat uniform pattern, creating the characteristic honeycomb or sponge-like appearance.
-
Cap Shape: Depending on the species, morel caps can be conical, egg-shaped, elongated with a rounded top, or nearly spherical.
-
Cap Color: Colors vary by species but typically range from light cream to yellowish-brown to almost black. Yellow morels often have pale ridges with darker pits, while black morels typically have dark ridges with paler pits.
2. Cap-to-Stem Attachment
The way the cap attaches to the stem is another crucial identifying feature:
- In true morels, the cap is attached directly to the stem at the base (though in "half-free" morels, the attachment point is roughly halfway up the cap).
- The cap and stem form a continuous structure, not two separate parts.
3. Hollow Interior
When sliced lengthwise, true morels reveal a completely hollow interior from the base of the stem to the top of the cap. This is one of the most reliable identification features and can be summarized by the forager's adage: "If it isn't hollow, don't swallow."
4. Stem Characteristics
- Morel stems are typically unpitted with a smooth or granular texture.
- Stems can range from white to yellowish.
- Like the cap, the stem is completely hollow inside.

True Morel Species
Several species of true morels can be found in North America. While all are edible when properly cooked, knowing the distinctions can help you better target your hunting grounds and seasons.
Yellow Morels (Morchella esculenta and related species)
- Appearance: Typically larger than black morels, with yellowish to tan coloration.
- Cap Pattern: Random honeycomb pattern (not vertically aligned).
- Habitat: Often found in hardwood forests, particularly near dying elm trees and old apple orchards.
- Season: Usually appear later in spring than black morels.
Black Morels (Morchella angusticeps and related species)
- Appearance: Darker coloration, from gray in young specimens to almost black in older ones.
- Cap Pattern: More vertically oriented ridges.
- Habitat: Commonly found near ash, aspen, poplar, and sometimes pine trees.
- Season: Usually the first morels to appear in spring, often when serviceberry bushes are in bloom.
Half-Free Morels (Morchella punctipes and Morchella populiphila)
- Appearance: The cap is attached to the stem only about halfway down, leaving the bottom half of the cap hanging free.
- Size: Typically smaller than other morel species.
- Distribution: M. punctipes is found east of the Rocky Mountains, while M. populiphila is found in Northwestern North America.
Burn Morels
Several morel species appear prolifically in areas recently affected by forest fires:
- Appearance: Similar to black morels but can have grayish tones.
- Habitat: Areas where forest fires occurred in the previous 1-2 years.
- Season: Can appear later than other morels, depending on elevation and moisture conditions.
Dangerous Look-Alikes: False Morels
Several mushroom species resemble morels but are potentially toxic. These are collectively known as "false morels" and include members of the Gyromitra and Verpa genera.
Gyromitra Species (Beefsteak Mushrooms)
- Cap Structure: Rather than a pitted honeycomb pattern, false morels have wavy, lobed, or wrinkled caps that often appear brain-like or folded.
- Interior: When sliced lengthwise, the interior is not hollow but filled with cottony tissue or chambers.
- Cap Attachment: The cap may be irregularly shaped and not uniformly attached to the stem.
- Toxicity: Contains the toxin gyromitrin, which converts to monomethylhydrazine (MMH) in the body. Consumption can cause dizziness, vomiting, and in severe cases, liver damage or death.
Verpa Species (Early Morels or Thimble Morels)
- Cap Attachment: The cap sits on top of the stem like a thimble, attached only at the very top.
- Interior: The stem may contain cottony pith rather than being completely hollow.
- Appearance: While they can look similar to true morels, the caps are often more smooth or wrinkled rather than pitted.
- Toxicity: While some people consume these without issue, they can cause gastrointestinal distress and are generally not recommended.
Key Differentiators Between True and False Morels
-
The Hollow Test: True morels are completely hollow from stem to cap when sliced lengthwise. False morels contain cottony fibers or have chambered interiors.
-
Cap Attachment: In true morels, the cap attaches to the stem at the base (or halfway in half-free morels). In Verpa species, the cap attaches only at the top like a thimble.
-
Surface Texture: True morels have a honeycomb pattern of pits and ridges. False morels have irregular, brain-like wrinkles or folded surfaces that bulge outward rather than being pitted inward.
-
Color and Form: False morels often have more irregular shapes and may be reddish-brown, which is uncommon in true morels.
Remember the forager's rule: "When in doubt, throw it out." Never consume any wild mushroom unless you are 100% confident in its identification.
Where and When to Find Morel Mushrooms
Understanding the preferred habitats and growing seasons of morels can significantly increase your chances of finding these elusive fungi.
Preferred Habitats
Morels grow in a variety of environments, but certain conditions tend to produce better results:
-
Tree Associations: Different morel species prefer different trees:
- Yellow morels: Often found near elm, ash, poplar, and apple trees
- Black morels: Commonly associated with ash, aspen, and occasionally conifers
- Burn morels: Appear in forests recovering from fires, especially coniferous forests
-
Soil Conditions: Morels prefer well-drained, moist soil with ample organic material. They often grow in areas with a mix of sand and loam.
-
Terrain Features:
- Early in the season, south and west-facing slopes warm up faster and may produce morels earlier
- Later in the season, north and east-facing slopes may be more productive
- Riparian areas along streams or rivers can be productive throughout the season
-
Disturbed Ground: Morels often appear in areas where the ground has been disturbed, such as:
- Recently burned areas (particularly for burn morels)
- Around dying or dead trees
- Along edges of trails or logging roads
- Old apple orchards
Seasonal Timing
Morel season varies by region, but is generally governed by soil temperature and moisture conditions:
- Southern United States: March through early May
- Mid-Atlantic & Midwest: April through May
- Northern States & Canada: May through June
- Mountain Regions: Varies by elevation, sometimes extending into July at higher elevations
Morels typically begin to appear when soil temperatures consistently reach 50-55°F (10-13°C) and continue fruiting until temperatures rise above 65°F (18°C) for extended periods.
The progression of the season typically follows this pattern:
- Black morels appear first
- Half-free morels next
- Yellow morels last
Weather Conditions
Optimal conditions for morel fruiting include:
- Daytime temperatures in the 60s-70s°F (15-25°C)
- Nighttime temperatures in the 40s-50s°F (5-15°C)
- Recent rainfall followed by warmer days
- High soil moisture but not waterlogged conditions

Tips for Successful Morel Hunting
-
Start with Known Producers: If you find one morel, stop and carefully scan the surrounding area. Morels often grow in groups, so where there's one, there are likely more nearby.
-
Focus on Tree Species: Learn to identify elm, ash, apple, and other morel-associated trees, even when they don't have leaves. Dead or dying elms with bark starting to slough off are particularly productive.
-
Watch the Ground Temperature: Invest in a soil thermometer and focus your hunting when ground temperatures are consistently in the 50-55°F range.
-
Follow the Season Progression: Start hunting on south-facing slopes early in the season, and as the season progresses, shift to east, then north-facing slopes.
-
Look After Rain: Morels often appear shortly after a good spring rain when followed by warm days.
-
Scan Carefully: Morels can be camouflaged among leaves and dappled light. Move slowly and scan methodically.
-
Return to Productive Spots: Morels often reappear in the same locations year after year, so mark your successful hunting grounds.
-
Check Burn Areas: If there's been a forest fire in your region in the past 1-2 years, these areas can be extremely productive for certain morel species.
Safe Harvesting and Preparation
Once you've confidently identified true morels, follow these guidelines for safe harvesting and consumption:
-
Harvesting Method: Use a knife to cut the mushroom at the base, leaving the bottom portion in the soil. Alternatively, pinch or twist the stem just above soil level.
-
Use a Mesh Bag: Collect morels in a mesh bag, which allows spores to disperse as you walk, potentially seeding new growth.
-
Clean Thoroughly: Before cooking, slice morels lengthwise and rinse them to remove any dirt, debris, or insects. Some foragers prefer to soak them briefly in salt water.
-
Always Cook Thoroughly: Never eat morels raw, as they contain hydrazine compounds that can cause gastrointestinal distress. These compounds are destroyed by proper cooking.
-
First-Time Caution: If it's your first time eating morels, start with a small amount, as some people may have individual sensitivities.
-
Avoid Alcohol: Some people report adverse reactions when consuming morels with alcoholic beverages.
Conclusion
Morel mushroom identification requires attention to detail and a thorough understanding of their distinctive features. By focusing on the honeycomb pattern, hollow interior, cap attachment, and growing habitat, you can confidently distinguish true morels from their toxic look-alikes.
Remember, no morel is worth risking your health over. When in doubt about identification, consult with experienced foragers or mycologists, or simply leave the mushroom where you found it. With practice and patience, you'll develop the skills needed to safely enjoy the springtime treasure hunt that is morel foraging.
Happy hunting, and may your baskets be full of these springtime delicacies!













Share:
Morel Mushroom Trees: A Forager’s Guide to Finding Nature’s Delicacies
Types of Morel Mushrooms: A Complete Guide to Identification and Varieties