Introduction to Morel Mushrooms: Nature's Nutrient Treasure
Morel mushrooms (Morchella spp.) represent one of nature's most prized culinary and nutritional treasures. These distinctive, honeycomb-patterned fungi have captivated food enthusiasts and health-conscious consumers alike for centuries. Beyond their exquisite flavor profile, morels harbor an impressive array of nutrients that contribute to their status as a functional food with exceptional health benefits.
What makes morel mushrooms particularly fascinating from a nutritional standpoint is their remarkable nutrient density despite their low calorie content. These wild-growing delicacies manage to pack a significant nutritional punch in each serving, making them a valuable addition to any health-conscious diet.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll uncover the complete nutritional profile of morel mushrooms, exploring their macronutrient composition, vitamin and mineral content, amino acid profile, and bioactive compounds. By revealing these nutritional facts, we aim to provide a deeper understanding of why morel mushrooms deserve a place in your culinary repertoire and nutritional strategy.

Basic Nutritional Composition of Morel Mushrooms
Before diving into the specific nutrients, let's examine the fundamental nutritional makeup of morel mushrooms to understand their basic composition.
Caloric Content and Macronutrients
Morel mushrooms are notably low in calories while providing essential macronutrients:
-
Calories: 100 grams of raw morel mushrooms contain approximately 31 calories, making them an excellent low-calorie food option for those monitoring their energy intake .
-
Macronutrient Distribution: The caloric breakdown of morels shows a balanced profile:
- 54% of calories from carbohydrates
- 32% of calories from protein
- 14% of calories from fat
Carbohydrate Profile
The carbohydrate content in morel mushrooms contributes to both their nutritional value and their potential health benefits:
-
Total Carbohydrates: 100 grams of morels contain approximately 5.1 grams of carbohydrates
-
Dietary Fiber: Morels provide about 2.8 grams of dietary fiber per 100 grams, supporting digestive health and promoting satiety
-
Sugars: With only 0.6 grams of total sugars per 100 grams, morels have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. In fact, a cup of morels contains less than 0.4 grams of glucose, making them suitable for those monitoring their sugar intake
Protein Content and Quality
Despite their low caloric content, morels offer an impressive protein profile:
-
Total Protein: 100 grams of morels provide about 3.1 grams of protein, representing approximately 4% of the recommended daily protein intake
-
Essential Amino Acids: Morels contain all essential amino acids, with threonine and lysine being particularly abundant. This makes them a valuable protein source, especially for those following plant-based diets
Fat Content and Composition
While low in total fat, the fat composition of morels contributes to their nutritional value:
-
Total Fat: 100 grams of morels contain approximately 0.6 grams of fat
-
Fatty Acid Profile: The fat in morels consists primarily of beneficial unsaturated fatty acids, including:
- Oleic acid (a monounsaturated fatty acid)
- Linoleic acid (an omega-6 fatty acid)
- Alpha-linolenic acid (an omega-3 fatty acid)
Vitamin Content in Morel Mushrooms
Morel mushrooms are particularly noteworthy for their vitamin content, especially their exceptional levels of vitamin D compared to other food sources.
Vitamin D: The Sunshine Vitamin
One of the most remarkable nutritional attributes of morel mushrooms is their impressive vitamin D content:
-
Vitamin D Content: 100 grams of raw morels provide approximately 206 IU (5.15 mcg) of vitamin D, which represents about 34% of the daily recommended intake
-
Form of Vitamin D: The vitamin D in morels is primarily in the form of ergocalciferol (vitamin D2), which effectively helps maintain and raise plasma vitamin D levels
-
Significance: Morels are among the few plant-based foods that provide significant amounts of vitamin D, making them especially valuable for those with limited sun exposure or those following vegetarian or vegan diets
B Vitamins: Energy and Metabolism Support
Morel mushrooms offer an impressive array of B vitamins that support energy metabolism and cellular health:
-
Niacin (B3): Morels provide about 24% of the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of niacin per 100 grams, supporting energy production and nervous system function
-
Riboflavin (B2): Present in significant amounts, riboflavin contributes to energy metabolism and cellular growth
-
Pantothenic Acid (B5): This vitamin supports fatty acid synthesis and is found in appreciable quantities in morels
-
Pyridoxine (B6): Morels contain vitamin B6, which is essential for protein metabolism and neurotransmitter synthesis

Mineral Composition of Morel Mushrooms
The mineral profile of morel mushrooms is perhaps their most impressive nutritional attribute, with extraordinarily high levels of several essential minerals.
Iron: Outstanding Source
Morel mushrooms are exceptional sources of iron, a mineral often lacking in many diets:
-
Iron Content: 100 grams of raw morels provide approximately 12.2 mg of iron, which represents about 152% of the daily recommended intake for men and over half of the requirement for women
-
Significance: This high iron content makes morels particularly valuable for preventing iron deficiency anemia and supporting oxygen transport throughout the body
Copper: Essential Trace Mineral
Morels are remarkably rich in copper, which serves numerous essential functions in the body:
-
Copper Content: 100 grams of raw morels provide about 69% of the daily required intake of copper
-
Functions: Copper functions as a co-factor for many oxidative enzymes involved in cellular metabolism, blood cell production, and neurotransmission
Phosphorus and Calcium: Bone Health Support
The combination of phosphorus, calcium, and vitamin D in morels creates a synergistic effect for bone health:
-
Phosphorus Content: 100 grams of morel mushrooms contain 194 mg of phosphorus, representing 28% of the recommended daily intake
-
Calcium Content: Morels provide 43 mg of calcium per 100 grams
-
Bone Health: The presence of both phosphorus and calcium, along with the high vitamin D content, makes morels particularly beneficial for bone development and maintenance
Other Valuable Minerals
Morels contain significant amounts of several other essential minerals:
-
Manganese: 100 grams of morels provide about 26% of the daily required intake
-
Zinc: Morels contain approximately 18% of the daily required zinc intake per 100 grams, supporting immune function, cell growth, and reproductive health
-
Potassium: Present in appreciable quantities, potassium helps regulate blood pressure and fluid balance
Bioactive Compounds in Morel Mushrooms
Beyond their impressive vitamin and mineral content, morel mushrooms contain various bioactive compounds that contribute to their health-promoting properties.
Polysaccharides: Immune Support
Morel mushrooms contain complex polysaccharides with significant health-promoting properties:
-
Beta-Glucans: These compounds interact with immune receptors to enhance the body's natural defense mechanisms
-
Immunomodulatory Effects: Research suggests that polysaccharides from morels may enhance immune function and reduce inflammation
Antioxidant Compounds
Morels are rich in various antioxidants that help protect cells from oxidative damage:
-
Phenolic Compounds: Including gallic acid and tannic acid, these compounds help neutralize free radicals
-
Tocopherols: These vitamin E-related compounds provide additional antioxidant protection
-
Ergosterols: These compounds may contribute to the mushroom's health-promoting effects
Organic Acids
Morel mushrooms contain several organic acids that contribute to both their flavor profile and potential health benefits:
-
Succinic Acid: The most abundant organic acid in morels, succinic acid acts as an antioxidant and may help fight diseases and prolong preservation
-
Other Organic Acids: Morels also contain fumaric acid, citric acid, and malic acid, which contribute to their distinctive flavor
Nutritional Comparison: Morels vs. Other Mushrooms
To fully appreciate the nutritional value of morel mushrooms, it's helpful to compare them with other commonly consumed mushroom varieties.
Vitamin D Content Comparison
When it comes to vitamin D, morels stand out among mushroom varieties:
- Morels: 206 IU per 100 grams
- Maitake: Similar high levels of vitamin D
- Button Mushrooms: Significantly lower vitamin D content unless exposed to UV light
- Shiitake: Lower natural vitamin D content
Mineral Content Comparison
The mineral profile of morels is generally superior to that of other common mushroom varieties:
- Iron Content: Morels contain substantially more iron than button, shiitake, or portobello mushrooms
- Copper Content: The copper content in morels exceeds that of most other mushroom varieties
- Overall Mineral Density: Morels are recognized for their exceptionally rich mineral content compared to other wild edible mushrooms
Protein Quality Comparison
While all mushrooms are good sources of plant protein, morels offer distinct advantages:
- Amino Acid Profile: Morels contain all essential amino acids, with a particularly favorable balance of lysine and threonine
- Protein Digestibility: The protein in morels is highly digestible, enhancing its nutritional value
Health Benefits Based on Nutritional Profile
The impressive nutritional composition of morel mushrooms translates into numerous potential health benefits when incorporated into a balanced diet.
Immune System Support
The combination of vitamin D, zinc, and bioactive polysaccharides in morels contributes to immune system enhancement:
- Vitamin D: Supports immune cell function and helps regulate immune responses
- Zinc: Essential for immune cell development and function
- Beta-Glucans: May stimulate and modulate immune responses
Bone Health Promotion
The synergistic combination of nutrients in morels supports optimal bone health:
- Vitamin D: Essential for calcium absorption and bone mineralization
- Calcium and Phosphorus: Primary structural components of bone tissue
- Copper and Manganese: Required for the formation of bone collagen and bone mineral density
Antioxidant Protection
The various antioxidant compounds in morels help protect cells from oxidative damage:
- Phenolic Compounds: Neutralize free radicals that can damage cells
- Tocopherols: Protect cell membranes from oxidative damage
- Organic Acids: Contribute additional antioxidant properties
Blood Health Maintenance
The high iron content of morels, along with other nutrients, supports optimal blood health:
- Iron: Essential for hemoglobin production and oxygen transport
- Copper: Required for red blood cell maturation
- B Vitamins: Support various aspects of blood cell formation and function
Gut Health Support
Research suggests that components in morels may support a healthy gut microbiome:
- Dietary Fiber: Acts as a prebiotic to nourish beneficial gut bacteria
- Polysaccharides: May enhance gut health by influencing microbial composition
Incorporating Morel Mushrooms into a Nutritious Diet
To maximize the nutritional benefits of morel mushrooms, consider these practical recommendations for incorporating them into your diet.
Optimal Preparation Methods
Proper preparation is essential to preserve the nutritional value of morel mushrooms:
-
Thorough Cleaning: Soak morels briefly in salt water to remove any debris, then rinse gently under cold water.
-
Complete Cooking: Always cook morels thoroughly. Raw or undercooked morels can cause digestive upset and may contain compounds that are inactivated by heat .
-
Minimal Processing: Simple cooking methods like sautéing in a small amount of healthy fat help preserve nutrients while enhancing flavor.
Nutritional Synergies
Pairing morels with certain foods can enhance their nutritional benefits:
-
Vitamin C-Rich Foods: Consuming morels with vitamin C-rich foods enhances iron absorption from the mushrooms.
-
Healthy Fats: Pairing morels with a source of healthy fat improves the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, including vitamin D.
-
Complementary Proteins: Combining morels with whole grains creates complementary protein profiles for those following plant-based diets.
Seasonal Availability and Alternatives
Fresh morels are typically available in spring, but there are options for year-round enjoyment:
-
Fresh Morels: Optimal for nutrition, available from late April through June in the United States .
-
Dried Morels: Retain much of their nutritional value and can be reconstituted for use throughout the year.
-
Morel Powder: Concentrated form that can be added to soups, sauces, and other dishes for a nutritional boost.

Nutritional Considerations and Precautions
While morel mushrooms offer impressive nutritional benefits, there are several important considerations to keep in mind.
Safe Identification
Given the nutritional benefits of morels, it's tempting to forage for them, but proper identification is crucial:
-
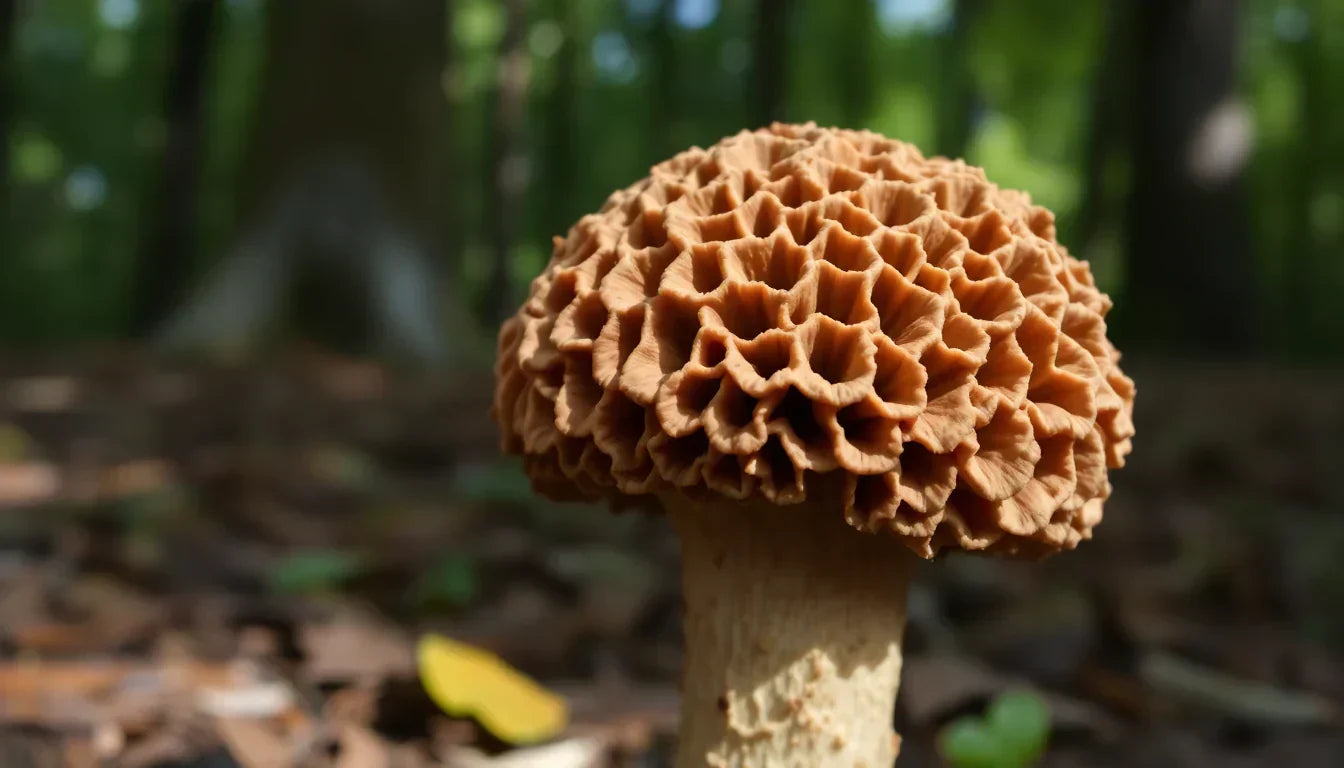
True Morels: Feature a honeycomb-patterned cap that's completely attached to the stem, with both cap and stem being hollow when cut lengthwise.
-
False Morels: Toxic lookalikes (like Gyromitra esculenta) have brain-like caps rather than honeycomb structures and are not completely hollow .
-
Expert Guidance: First-time foragers should always consult with experienced mushroom hunters or mycologists.
Allergies and Sensitivities
As with any food, individual reactions can vary:
-
Allergic Reactions: While rare, allergic reactions to morel mushrooms can occur in some individuals .
-
Initial Testing: If trying morels for the first time, consume a small amount and monitor for any adverse reactions.
Cooking Requirements
Proper cooking is non-negotiable when it comes to morel mushrooms:
-
Thorough Cooking: Even true morels must be cooked thoroughly to eliminate potential toxins and improve digestibility .
-
No Raw Consumption: Never consume morels raw, as they contain compounds that can cause gastrointestinal distress unless properly cooked.
The Future of Morel Mushroom Nutrition Research
As interest in functional foods continues to grow, research into the nutritional properties and health benefits of morel mushrooms is expanding.
Emerging Research Areas
Current and future research is focusing on several promising areas:
-
Bioactive Compound Isolation: Identifying and isolating specific compounds responsible for health benefits .
-
Gut Microbiome Effects: Understanding how morel components influence gut microbial composition and function .
-
Nutrigenomic Interactions: Exploring how compounds in morels may influence gene expression related to health and disease.
Cultivation Advancements
Traditionally difficult to cultivate, recent advances are making morels more accessible:
-
Commercial Cultivation: Development of methods for reliable commercial production .
-
Nutritional Optimization: Research into how growing conditions affect the nutritional profile of cultivated morels.
Conclusion: Embracing the Nutritional Treasure of Morel Mushrooms
Morel mushrooms truly represent a nutritional treasure trove, offering an impressive array of vitamins, minerals, protein, and bioactive compounds in a low-calorie package. Their exceptional content of vitamin D, iron, copper, and various antioxidants makes them stand out among both mushroom varieties and plant foods in general.
The revealed nutrition facts underscore why morels have been valued for centuries not only for their culinary appeal but also for their health-promoting properties. From supporting immune function and bone health to providing antioxidant protection and contributing to blood health, the nutritional profile of morels translates into numerous potential benefits.
Whether enjoyed fresh during their spring season or utilized in dried form throughout the year, incorporating morel mushrooms into a balanced diet can be a delicious way to enhance nutritional intake and support overall well-being. With ongoing research continuing to uncover the full spectrum of their nutritional attributes and health benefits, the appreciation for these remarkable fungi is likely to continue growing.
By understanding and embracing the complete nutritional profile of morel mushrooms, you can make informed dietary choices that leverage these natural treasures for optimal health and culinary enjoyment.













Share:
Morel Mushroom Farm: How to Grow Your Own Gourmet Delicacies
Health Benefits of Morel Mushrooms: Nature’s Hidden Treasure Uncovered