Venturing into the fascinating world of mushroom identification opens up an extraordinary realm of discovery, culinary exploration, and connection with nature. Whether you're an aspiring forager, culinary enthusiast, or curious naturalist, learning to properly identify mushrooms is the crucial first step in your fungi journey. This comprehensive guide will walk you through essential identification techniques, key features of common edible varieties, and vital safety practices to ensure your mushroom adventures are both rewarding and safe.

Understanding Mushroom Anatomy for Proper Identification
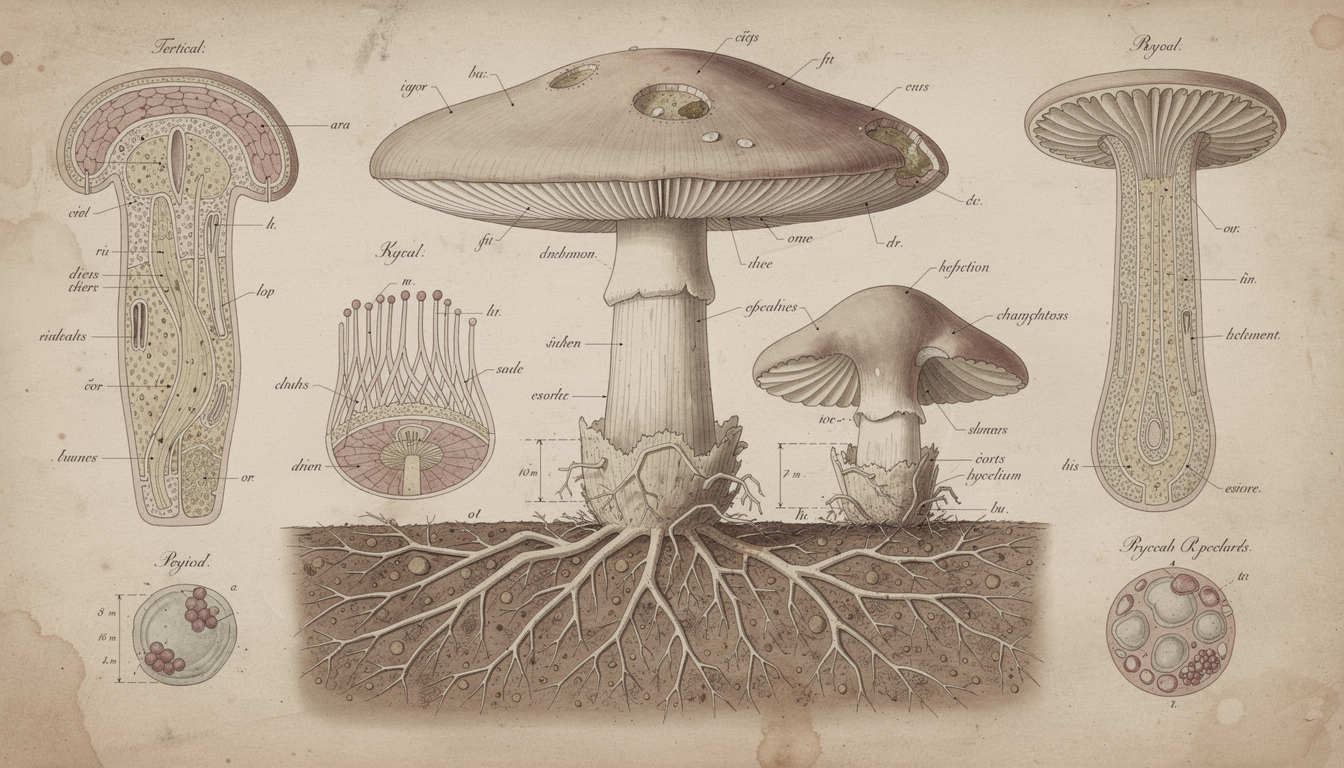
Before heading into the forest with basket in hand, it's essential to understand the basic anatomy of mushrooms and how these features help with identification. Every part of a mushroom provides valuable identification clues.
Key Mushroom Features to Examine
The most reliable mushroom identification begins with a systematic approach to observing specific characteristics. When examining a specimen, always note the following:
- Cap Structure and Color: Observe the shape (convex, flat, funnel-shaped), texture (smooth, scaly, velvety), and color patterns. Cap colors can vary significantly even within the same species depending on age and environmental conditions.
- Gill Arrangement: Check if the mushroom has gills, pores, or teeth under the cap. For gilled mushrooms, note how the gills attach to the stem (free, attached, decurrent) and their spacing, color, and texture.
- Stem Characteristics: Examine the stem's shape, thickness, texture, and whether it has a ring (annulus) or cup (volva) at the base. The presence of a volva is particularly important as many deadly Amanita species have this feature.
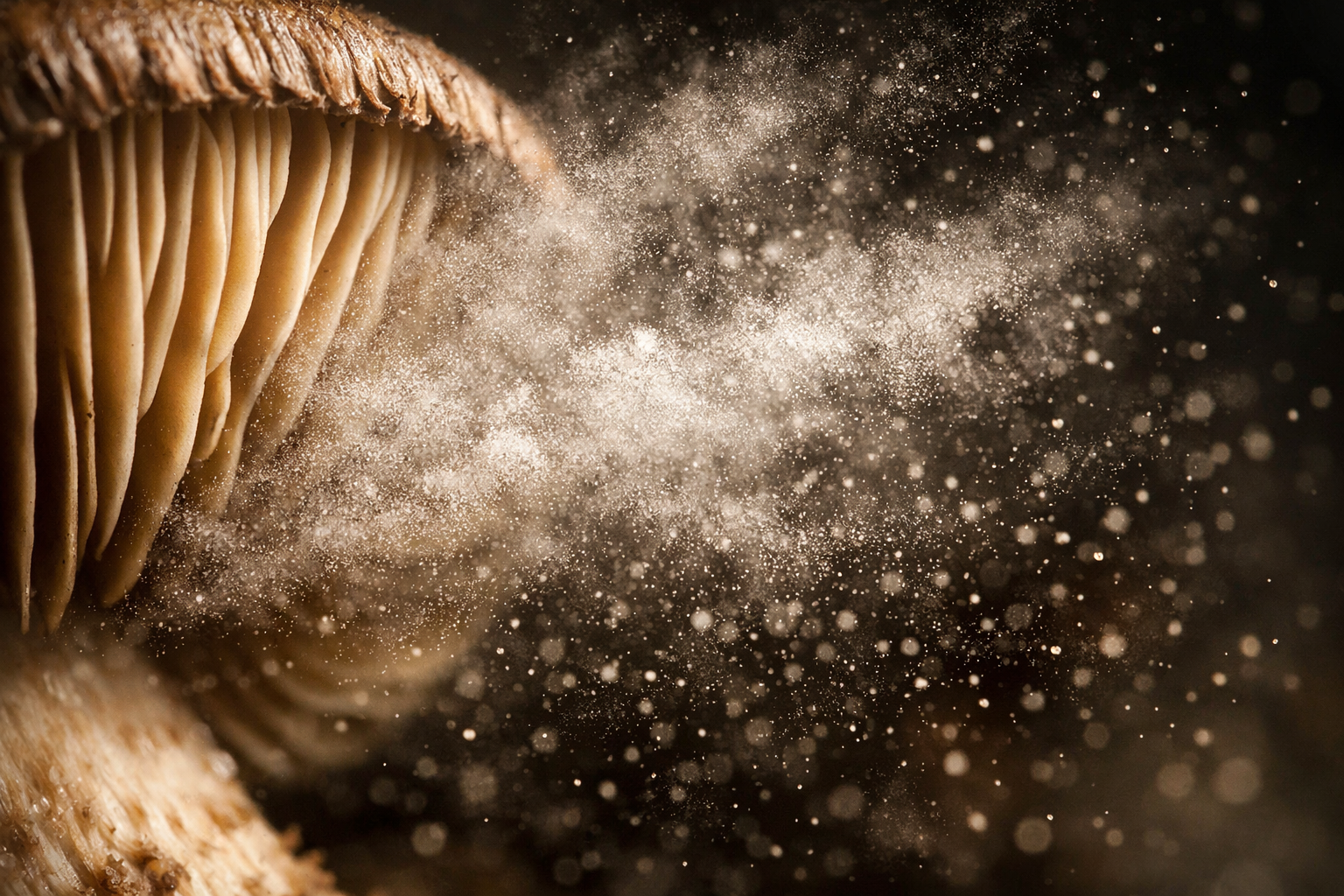
- Spore Print Color: Creating a spore print is one of the most valuable identification techniques. Simply remove the cap, place it gill-side down on paper, cover overnight, and check the resulting color pattern in the morning.

Habitat and Season Considerations
Where and when you find a mushroom provides crucial identification context:
- Growing Medium: Note whether the mushroom grows from soil, wood (living or dead), or other material
- Tree Associations: Many mushrooms form symbiotic relationships with specific trees
- Seasonal Appearance: Different species fruit in specific seasons, with some appearing only after certain weather conditions
"In Colorado, mushrooms mainly appear in mixed conifer forest—spruce and fir—above a certain elevation, usually around 9,000 feet and above," as noted in our Colorado mushroom guide, highlighting how regional knowledge enhances identification accuracy.
Common Edible Mushroom Varieties and Their Identifying Features
Let's explore some popular edible mushroom varieties and their distinctive identification characteristics.
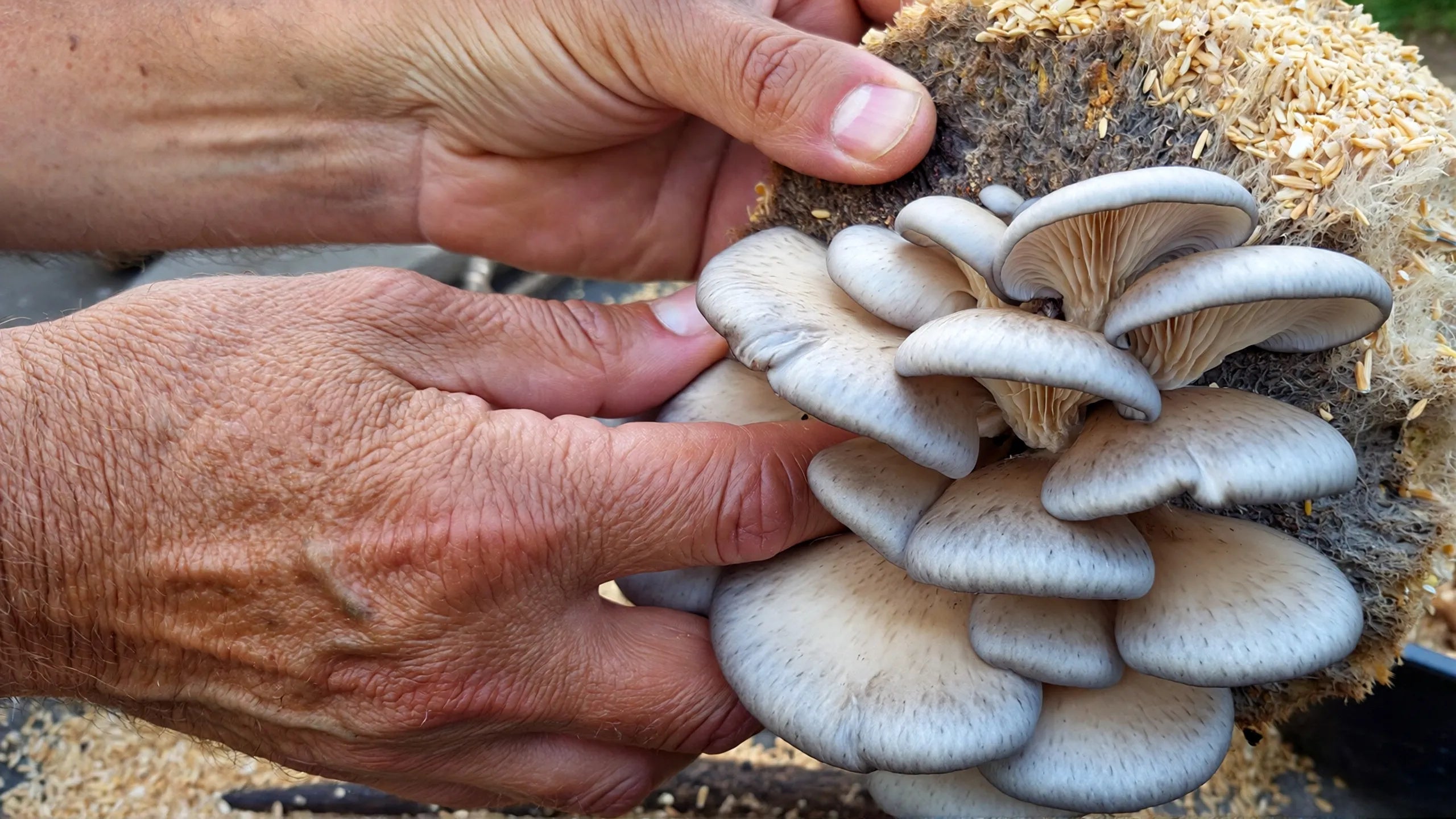
Oyster Mushrooms (Pleurotus species)
Oyster mushrooms rank among the most sought-after edible fungi thanks to their delicious flavor and relative abundance. As detailed in our oyster mushroom identification guide, these fungi have several key identifying features:
- Growth Pattern: They grow in shelf-like clusters directly on dead or dying trees
- Cap Shape: Shell or fan-shaped caps with smooth margins when young
- Stem: Short, stubby, and often off-center or absent entirely
- Gills: Distinctive decurrent gills running down the stem
- Color: Varies by species from white and pale gray to blue, pink, or yellow
Safety Note: While all true oyster mushrooms are edible, beginners should be aware of potential look-alikes. Always verify identification with multiple sources before consuming.

Morel Mushrooms (Morchella species)
Morel mushrooms are prized for their distinctive honeycomb-like caps and exceptional flavor. According to our morel mushrooms guide, all true morels share these key identification features:
- Hollow Interior: When sliced lengthwise, true morels are completely hollow from stem to cap
- Attached Cap: The cap is attached to the stem, either at the base or halfway up
- Pitted Surface: Distinctive honeycomb or sponge-like appearance with pits and ridges
- No True Gills: Unlike many mushrooms, morels don't have gills underneath the cap
Always beware of false morels (Gyromitra species), which can cause severe toxicity. True morels are hollow when cut lengthwise, while false morels typically have a cottony interior.
Lobster Mushrooms (Hypomyces lactifluorum)
The lobster mushroom represents one of nature's most fascinating fungi. As our lobster mushroom guide explains, it's actually a parasitic fungus that transforms other mushroom species:
- Color: Bright orange to red exterior with a bumpy, coral-like texture
- Texture: Firm and dense flesh with no hollow spaces
- Interior: White to pale orange interior that contrasts with the vibrant exterior
- Aroma: Subtle seafood-like smell reminiscent of shellfish
"The parasitic fungus essentially mummifies its host, creating a preserved, transformed organism that can last much longer than typical mushrooms while developing complex flavor compounds," making it one of the more unique edibles in the mushroom world.
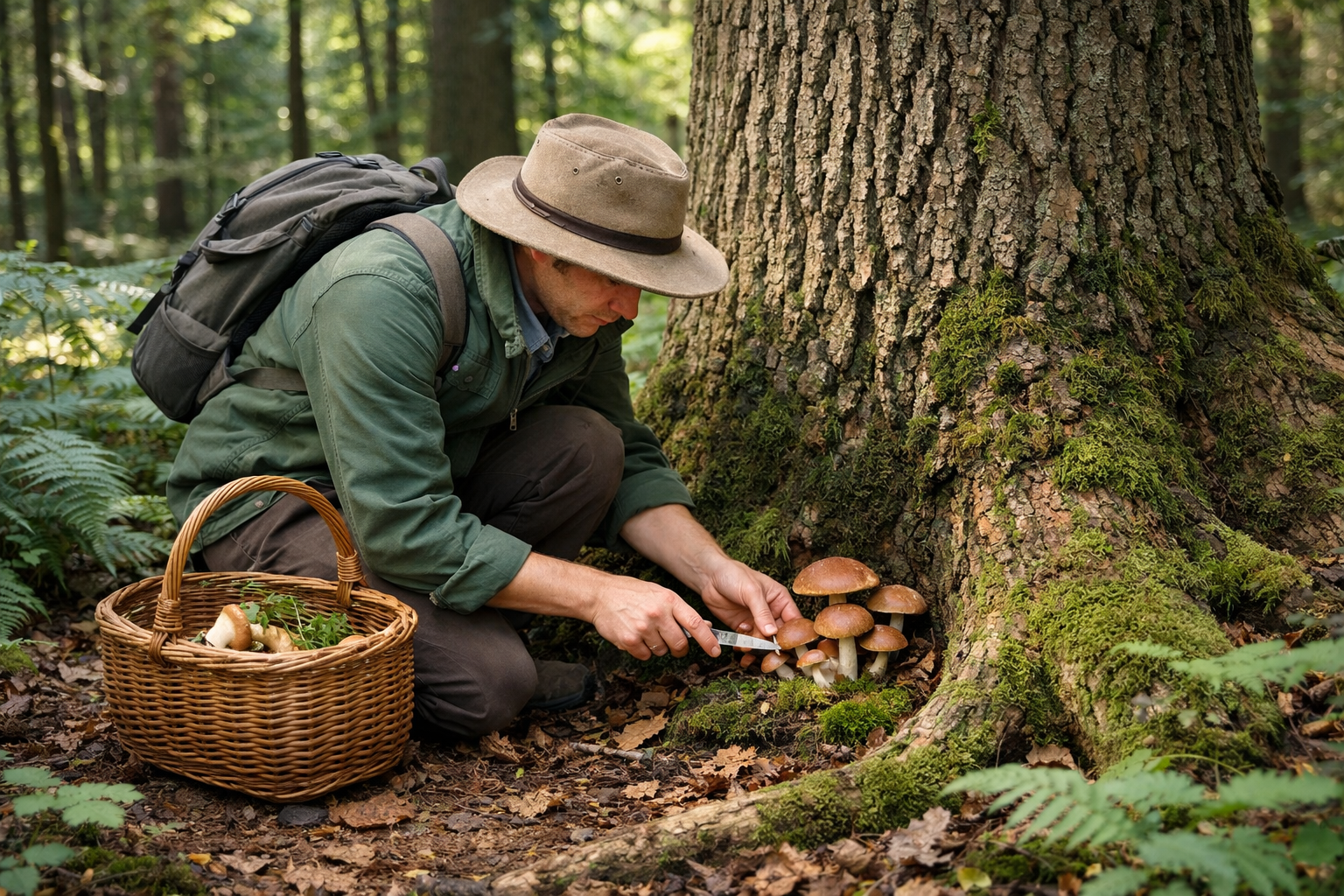
Mushroom Identification Safety Practices
Proper mushroom identification requires a cautious, methodical approach to ensure safety, especially for beginners.
Essential Rules for Safe Mushroom Foraging
- Never consume a mushroom without 100% positive identification
- Learn to recognize dangerous lookalikes in your region
- Start with easily identifiable species with few toxic mimics
- Use multiple reliable field guides and identification resources
- Join local mycological societies or guided forays with experts
- When in doubt, throw it out – no mushroom is worth the risk
Using Technology for Mushroom Identification
While traditional knowledge remains fundamental, modern technology can provide valuable assistance:
- Mushroom Identification Apps: Can offer preliminary suggestions but should never be the sole method for identifying edible species
- Online Mushroom Communities: Platforms where experts can help verify your findings
- Digital Field Guides: Comprehensive databases with detailed photos and descriptions
However, technology should supplement rather than replace traditional identification methods and expert confirmation.

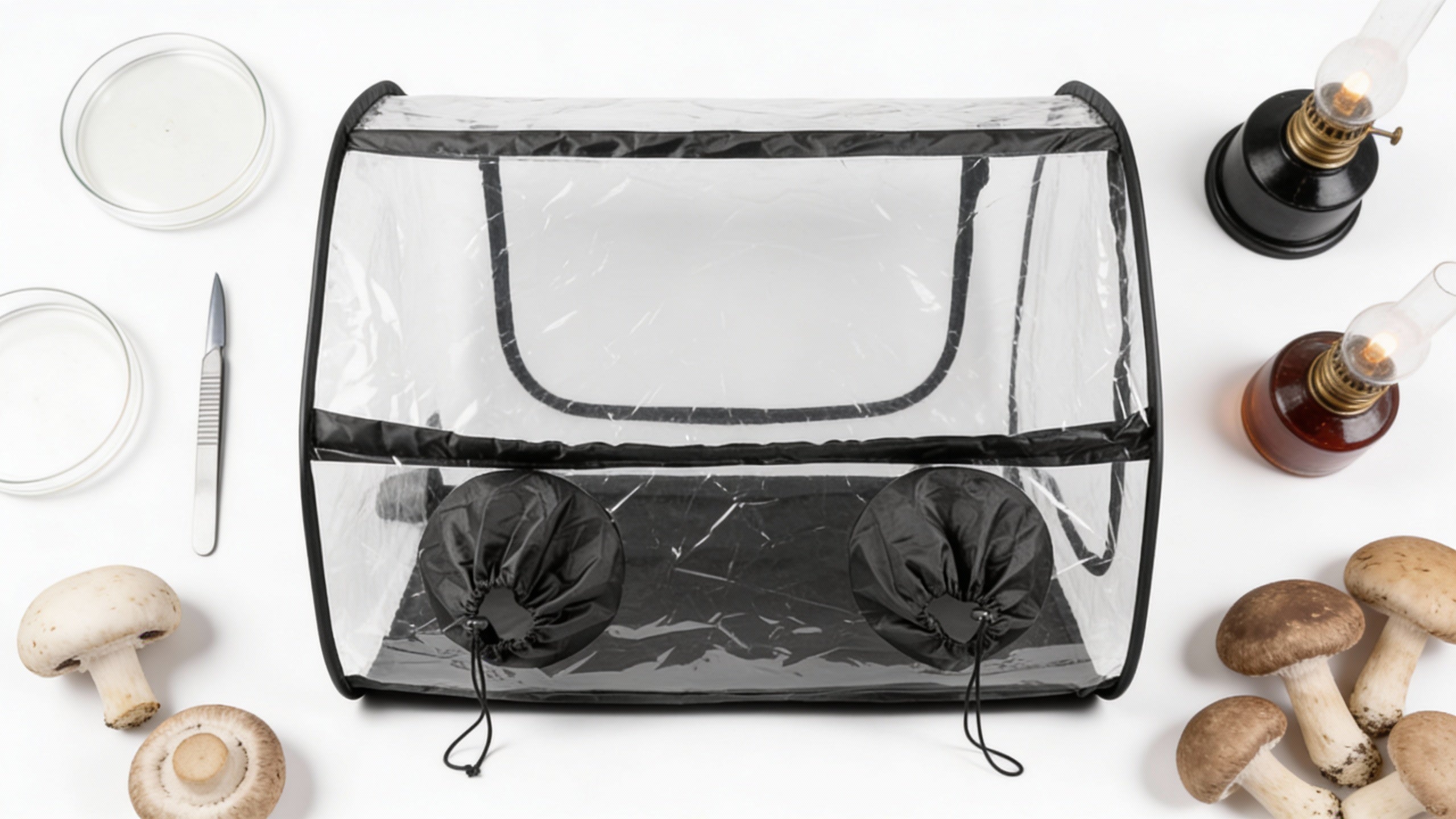
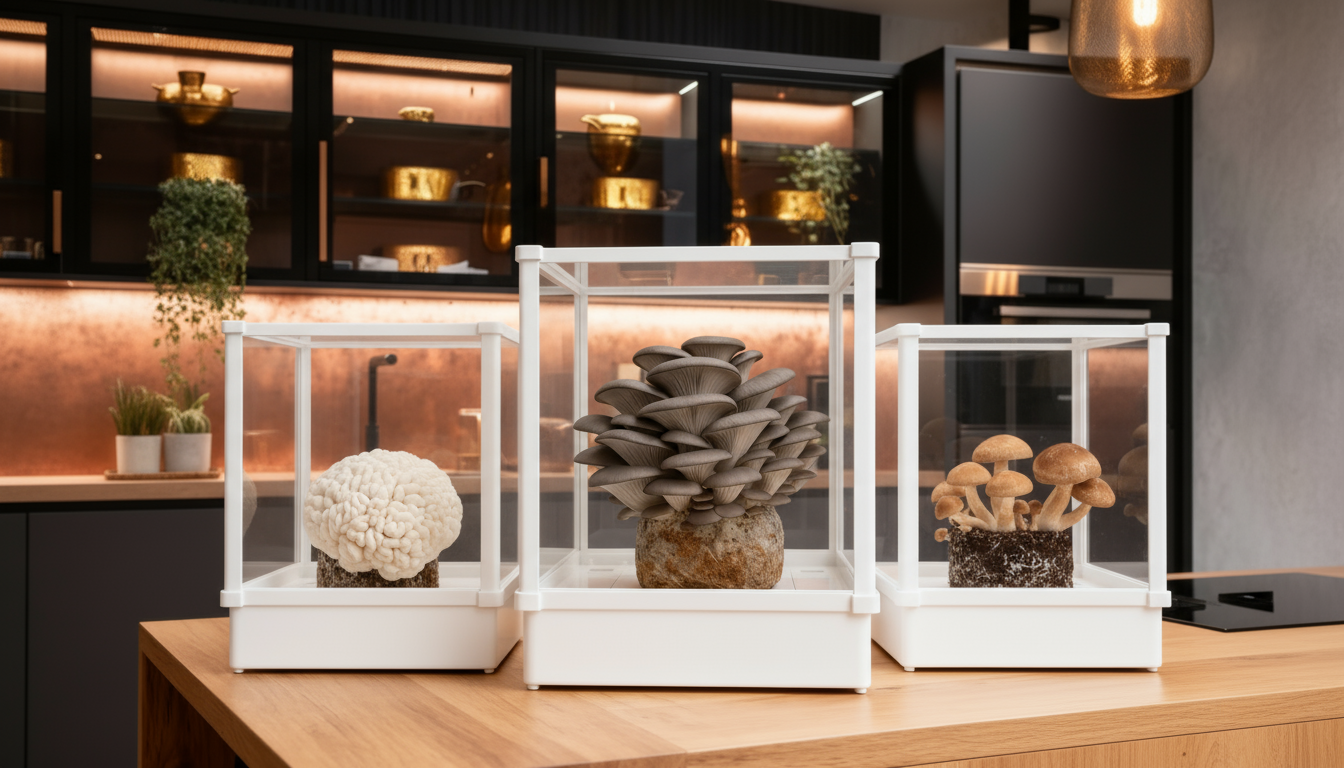
Cultivating Mushrooms at Home: A Safer Alternative
For those fascinated by mushrooms but concerned about the risks of wild foraging, home cultivation offers a safer alternative. With Lykyn's Smart Mushroom Grow Kit, you can grow various gourmet mushrooms with confidence.
This innovative system automatically maintains perfect growing conditions through:
- Smart sensors and app control for ideal humidity and airflow
- Integrated humidifier with 2.8L tank
- HEPA filtration for contaminant-free growing
- Silent operation suitable for any home environment
Home cultivation allows you to:
- Practice identification skills with known species
- Enjoy fresh, organic mushrooms year-round
- Eliminate the risk of misidentification
- Experiment with various gourmet varieties
As noted in our best mushroom grow kit for beginners guide, "Starting with a quality mushroom grow kit eliminates the guesswork that often frustrates new growers," making it an ideal entry point into the world of mushrooms.
Common Mushroom Identification Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced foragers can make mistakes. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
- Relying on a single identification feature: Always use multiple characteristics for confirmation
- Ignoring the mushroom's habitat: Where a mushroom grows is crucial identification information
- Failing to create spore prints: This simple technique can distinguish between similar-looking species
- Assuming bright colors always indicate toxicity: While many colorful mushrooms are toxic, some edible varieties also display vibrant colors
- Using taste or smell as primary identification methods: Never taste an unidentified mushroom as part of the identification process
Frequently Asked Questions About Mushroom Identification
How can beginners start learning mushroom identification safely?
Begin with easily identifiable species that have few dangerous look-alikes. The elm oyster mushroom is excellent for beginners as it "has no poisonous lookalikes, making it ideal for beginning foragers." Join local mycological clubs, attend guided forays, and use multiple identification resources before consuming any wild mushroom.
What equipment should I bring when mushroom hunting?
Essential equipment includes a field guide specific to your region, a knife for harvesting, a brush for cleaning specimens, a basket or mesh bag that allows spores to spread, a magnifying glass for examining detailed features, and a camera to document findings for later verification.
Can I rely on rules of thumb like "all mushrooms with white gills are poisonous"?
No. While certain generalizations can be helpful starting points, there are always exceptions. Many deadly poisonous mushrooms don't follow common "rules of thumb," which is why positive identification based on multiple features is essential for each individual specimen.
How can I tell if white fuzz on mushrooms is normal or contamination?
According to our white fuzzy mushroom guide, "White fuzz on mushrooms is usually harmless mycelium (the mushroom's root system) but can indicate mold contamination." Safe mycelium appears as bright white, hair-like filaments, while dangerous mold typically sits on top, appears slimy, and often has a blue-green tint with foul odors.
Are mushroom identification apps reliable?
While apps can be helpful tools, they should never be your sole identification method for mushrooms you intend to eat. Current technology has limitations in distinguishing subtle differences between edible and toxic species. Always verify with multiple sources and expert consultation.
How do I create a spore print for mushroom identification?
Remove the cap from the stem, place it gill-side down on paper (half white, half dark paper works best), cover with a bowl to prevent air currents, and leave overnight. The pattern and color of spores deposited on the paper provide valuable identification information that can help distinguish between similar-looking species.
Summary: Key Takeaways for Safe Mushroom Identification
Successful mushroom identification combines knowledge, caution, and a methodical approach. Remember these key principles:
- Learn to identify mushrooms by multiple characteristics including cap, gills, stem, spore print, habitat, and season.
- Never consume any wild mushroom unless you are 100% confident in your identification.
- Use multiple reliable resources and expert consultation to verify your findings.
- Start with easily recognizable species that have few dangerous lookalikes.
- Consider home cultivation with the Lykyn Smart Mushroom Grow Kit as a safe alternative to wild foraging.
The world of mushrooms offers endless fascination, culinary delights, and natural wonder. With proper knowledge and respect for these remarkable organisms, you can safely explore their diversity while developing a deeper connection to the natural world.
Ready to Begin Your Mushroom Journey?
Whether you're eager to develop your identification skills for wild foraging or prefer the controlled environment of home cultivation, Lykyn has everything you need to start your mushroom adventure. Explore our comprehensive mushroom guides for more species-specific identification information, or check out our Smart Mushroom Grow Kit to begin growing your own gourmet varieties at home with confidence.
Start your mushroom journey today and discover the remarkable diversity, flavors, and benefits these fascinating fungi have to offer!













Share:
White Button Mushrooms: Your Complete Guide to Nutrition, Benefits, and Culinary Uses
Nootropic Mushrooms: Complete Guide to Lion's Mane, Reishi & Cognitive-Enhancing Fungi