Oak trees create the perfect ecosystem for numerous mushroom species, offering rich nutrients and ideal growing conditions that mushroom enthusiasts treasure. Whether you're a forager, cultivator, or simply curious about these fascinating fungi, understanding which mushrooms thrive on oak trees opens up a world of culinary and medicinal possibilities.
From the prized shiitake to the abundant oyster mushrooms, oak-dwelling fungi represent some of nature's most valuable and delicious species. This comprehensive guide explores the most common mushrooms that grow on oak trees, helping you identify, harvest, and even cultivate these remarkable organisms safely and sustainably.
Most Common Mushrooms That Grow on Oak Trees
Oyster Mushrooms (Pleurotus ostreatus)
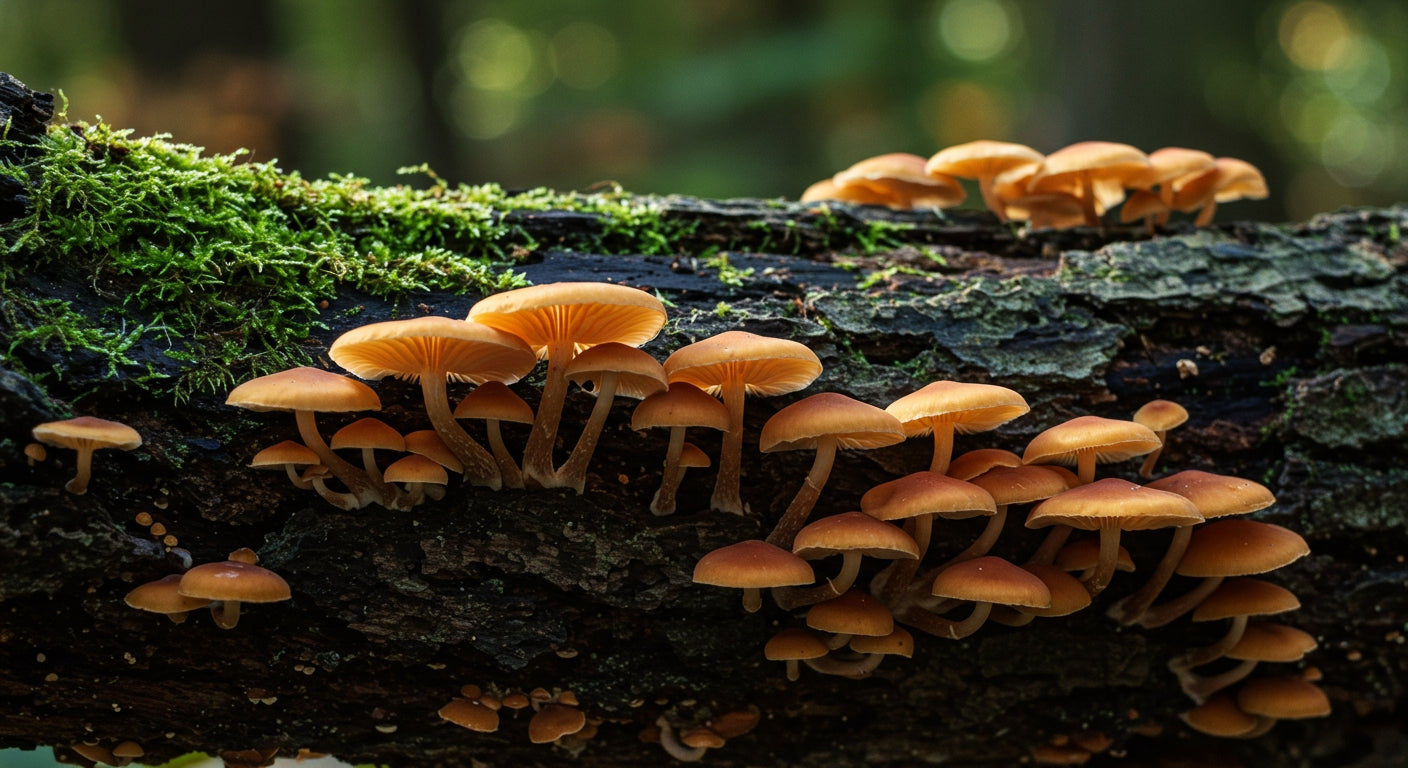
Oyster mushrooms rank among the most recognizable and abundant mushrooms found on oak trees. These fan-shaped fungi typically appear in overlapping clusters, displaying colors ranging from white to gray-brown. Their gills run down the stem, and they possess a subtle, pleasant aroma reminiscent of anise.

Oak trees provide ideal conditions for oyster mushrooms because the dense, nutrient-rich wood breaks down slowly, creating sustained food sources. These mushrooms typically fruit in cooler months, from fall through early spring, making them excellent for year-round foraging.
Shiitake Mushrooms (Lentinula edodes)
Shiitake mushrooms naturally grow on oak trees in their native Asian habitats and have become increasingly popular in North American cultivation. These brown-capped mushrooms feature distinctive white gills and a rich, umami flavor that makes them highly sought after by chefs and home cooks alike.
Unlike oyster mushrooms, shiitake prefer freshly fallen oak logs and branches rather than living trees. They typically fruit in spring and fall when moisture levels are optimal, producing flushes of mushrooms that can be harvested over several weeks.
Maitake Mushrooms (Grifola frondosa)
Also known as "hen of the woods," maitake mushrooms form large, ruffled clusters at the base of oak trees. These distinctive fungi can grow quite large, sometimes reaching 20 pounds or more, and are prized for both their culinary value and potential health benefits.
Maitake mushrooms prefer mature oak trees and typically fruit in late summer through fall. Their complex, layered structure and rich flavor make them a favorite among gourmet mushroom enthusiasts.
Safety Guidelines for Foraging Oak Tree Mushrooms
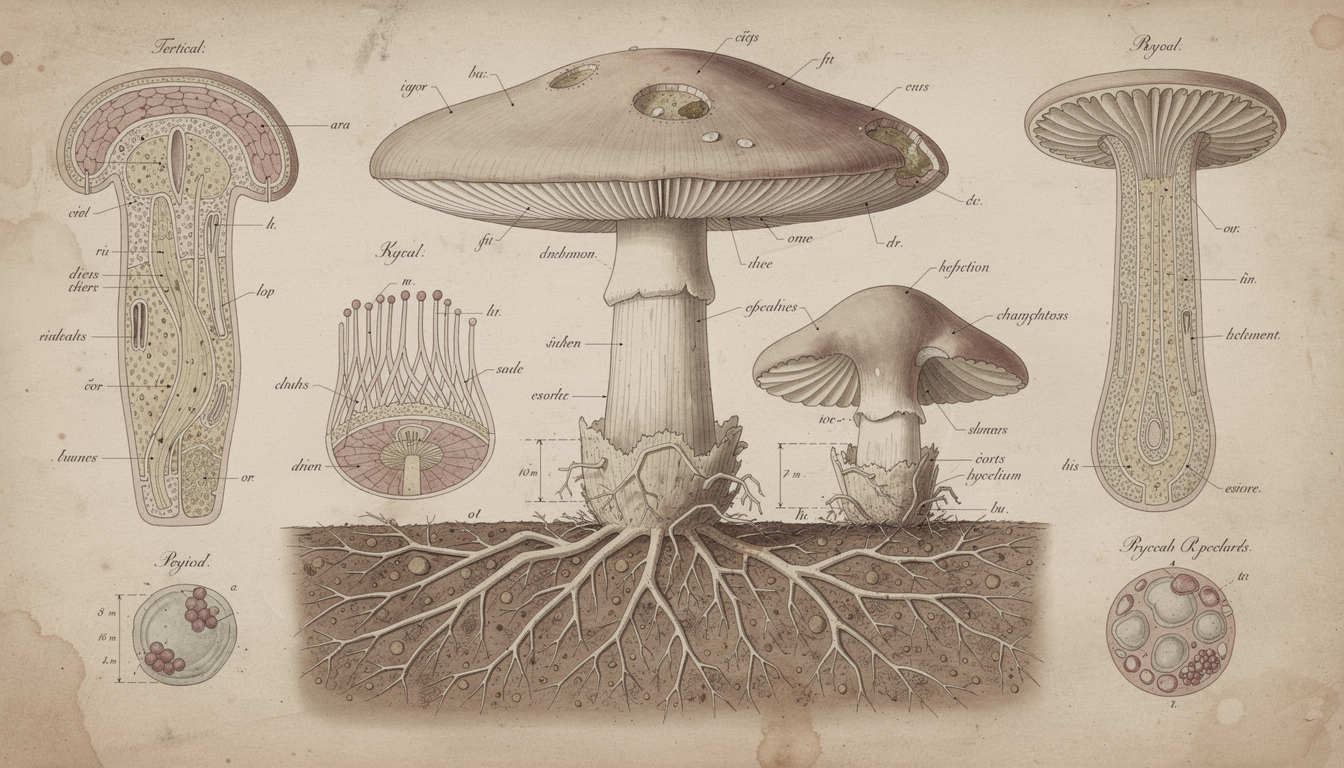
Proper Identification Techniques
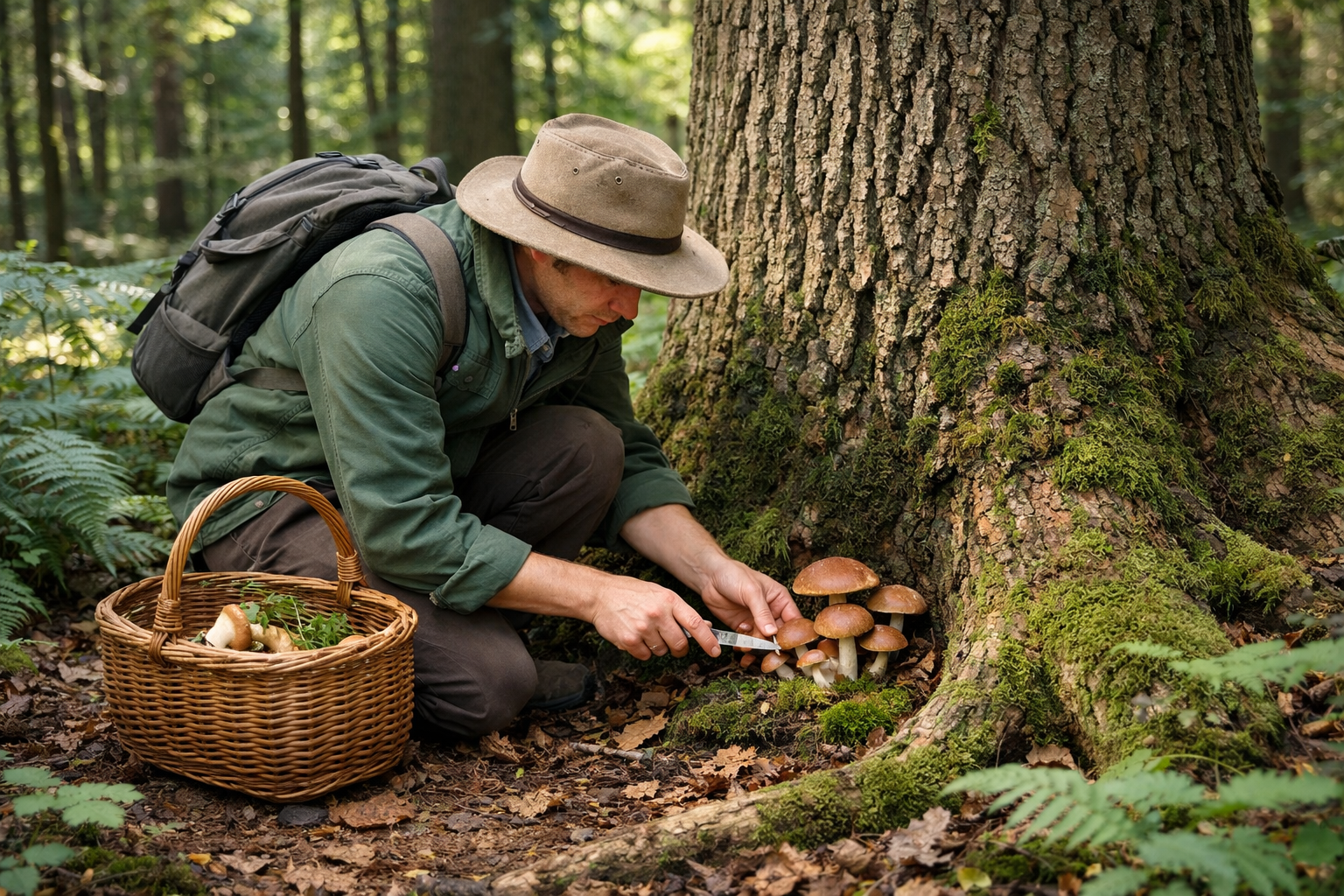
Never consume any wild mushroom without 100% positive identification. Oak tree mushrooms can sometimes resemble toxic species, making careful observation crucial for safe foraging. Always consult multiple field guides and consider joining local mycological societies for hands-on learning experiences.
Key identification features to examine include cap shape, gill structure, spore print color, and growth patterns. Take photographs from multiple angles and note the specific type of oak tree and surrounding environment when documenting your finds.
Sustainable Harvesting Practices
When harvesting mushrooms from oak trees, always leave the root system (mycelium) intact to ensure future fruiting. Cut mushrooms cleanly at the base rather than pulling them out, and never harvest more than you can use within a few days.
Respect private property and obtain proper permissions before foraging. Many public lands have specific regulations regarding mushroom collection, so research local laws and guidelines before heading out.
Cultivation Methods for Oak-Loving Mushrooms
Log Cultivation Techniques
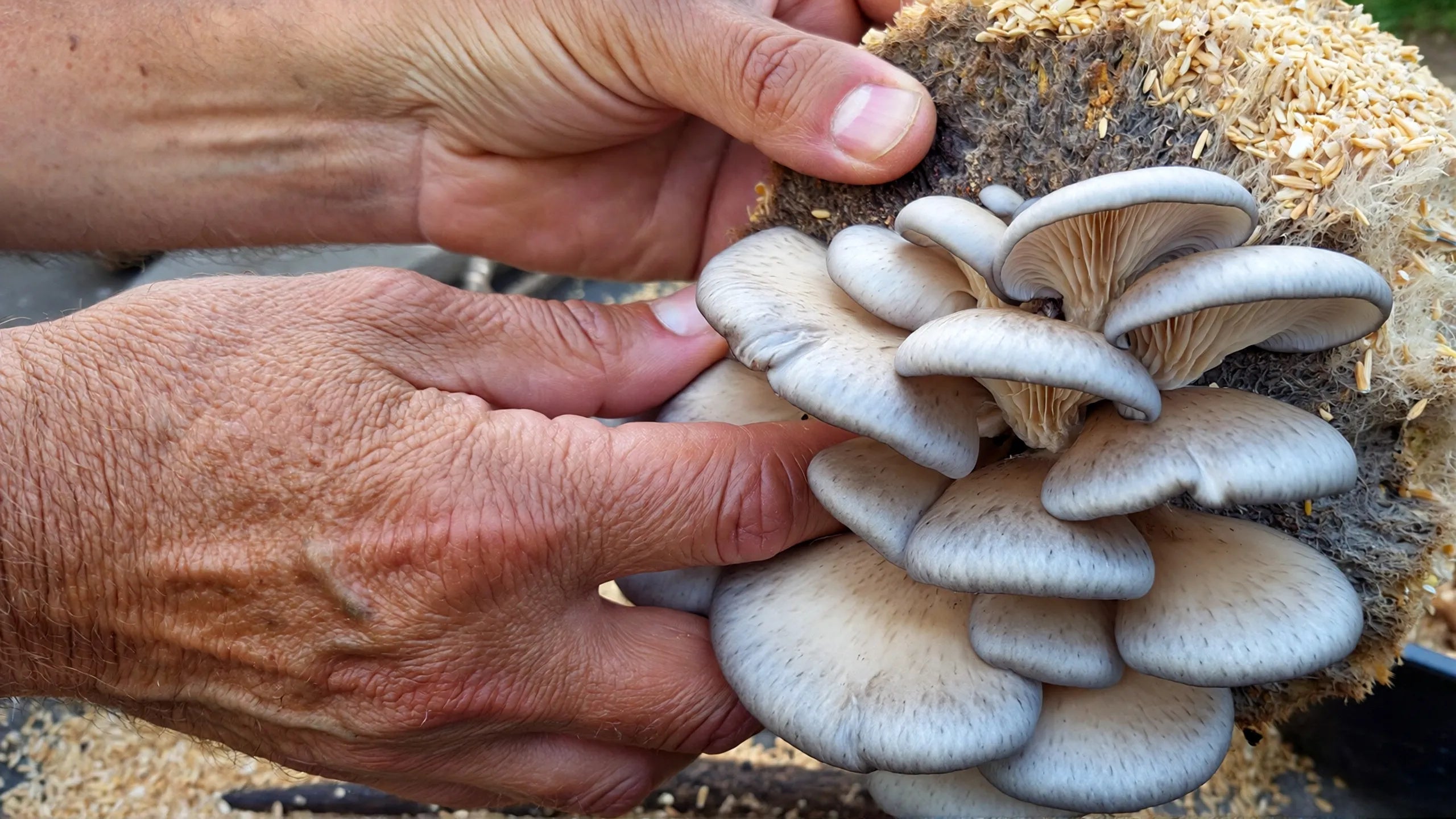
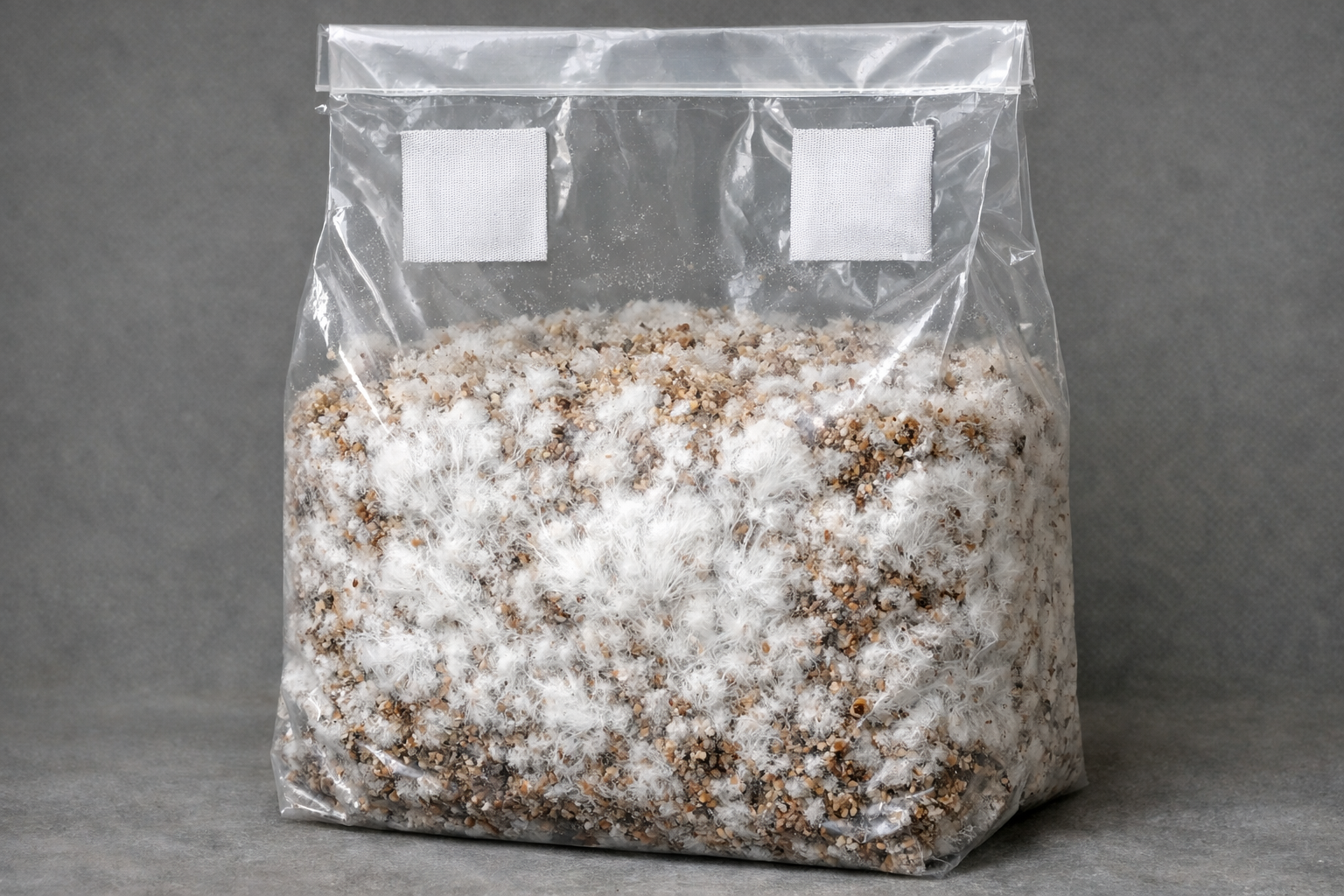
Growing mushrooms on oak logs represents the most natural cultivation method that mimics wild conditions. Fresh oak logs, cut within 2-4 weeks, provide the ideal substrate for species like shiitake and oyster mushrooms.
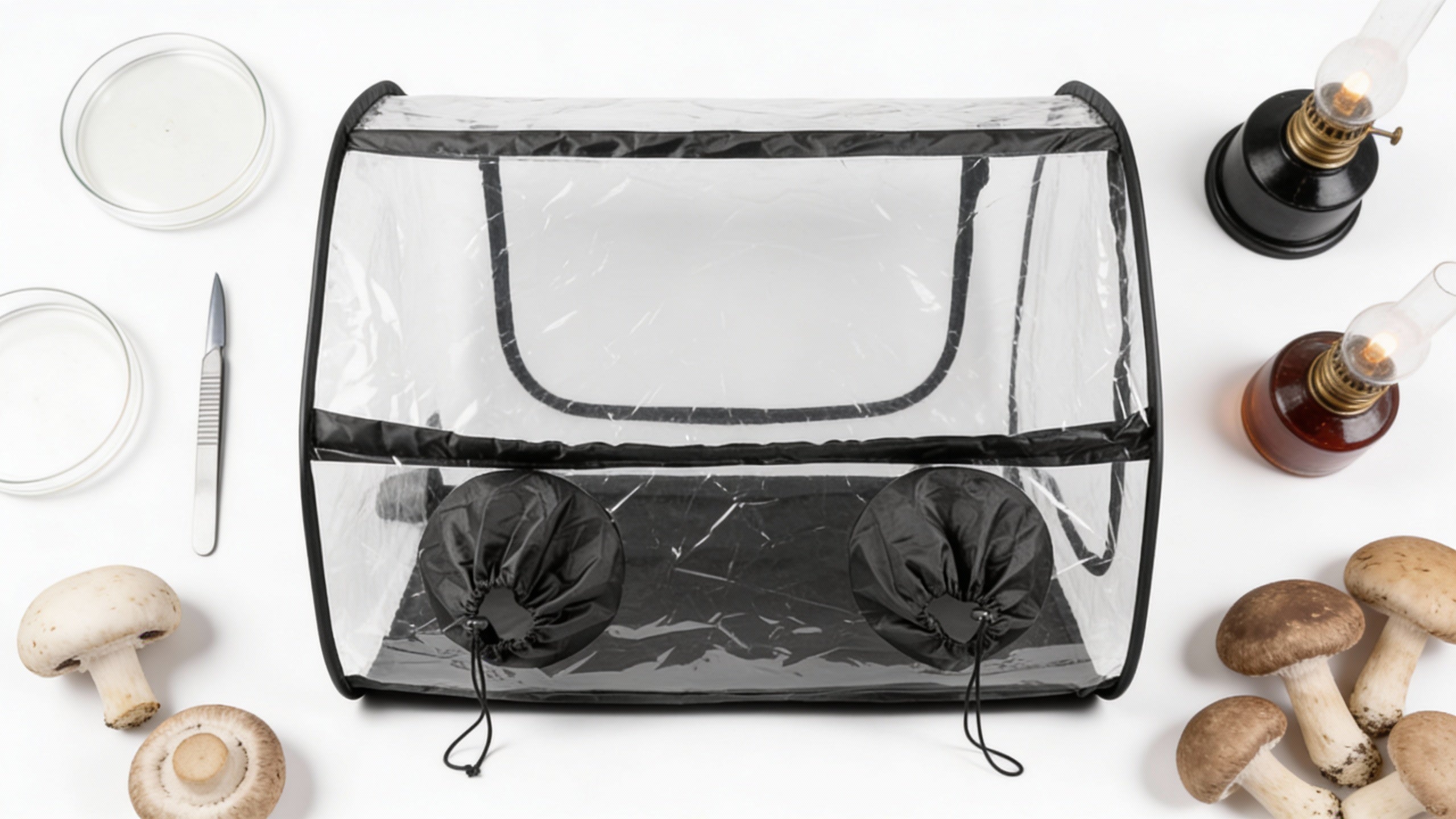
The process involves inoculating logs with mushroom spawn, then maintaining proper moisture and temperature conditions. Lykyn's Mushroom Grow Kit offers beginners an excellent starting point for understanding mushroom cultivation principles before advancing to log-based growing.
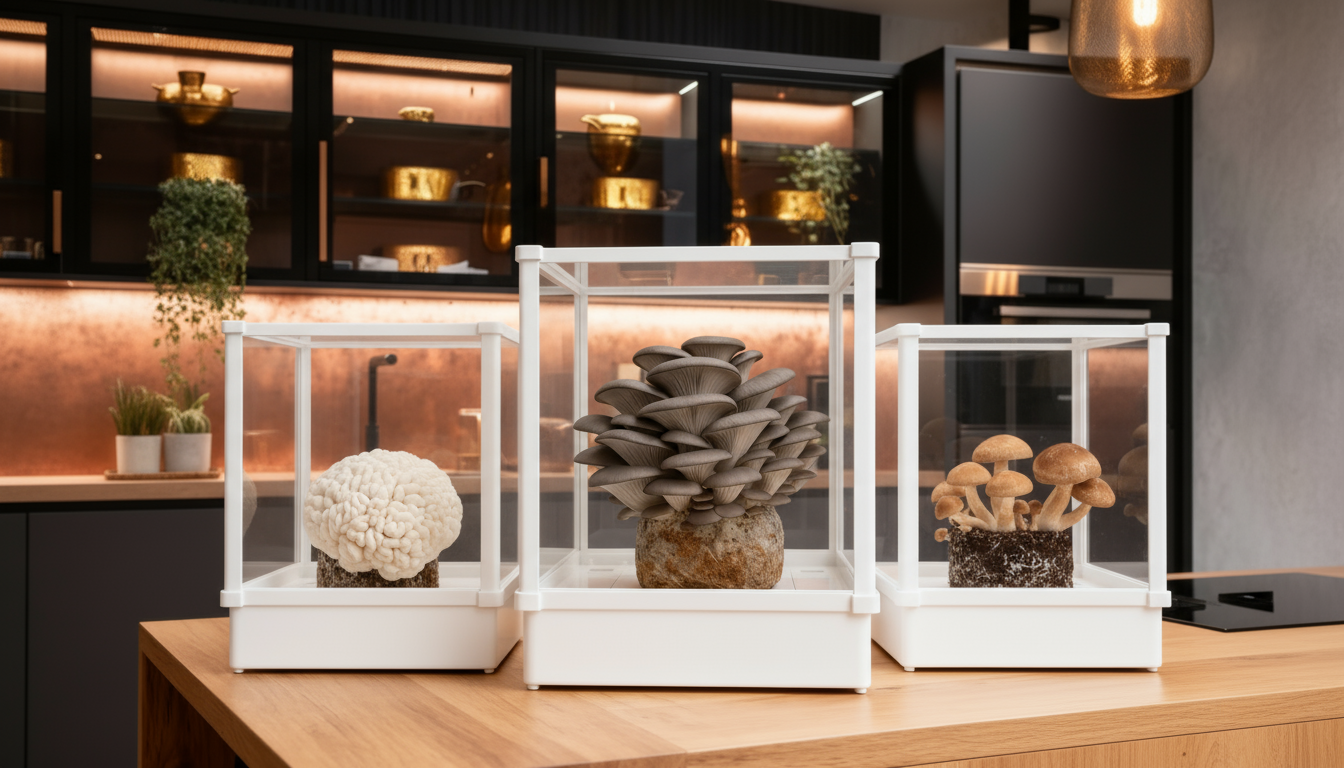
Indoor Growing Systems
Advanced growers can simulate oak tree conditions using specialized growing systems. These controlled environments allow for year-round production and consistent harvests, regardless of outdoor weather conditions.
Modern cultivation technology, such as the Smart Mushroom Grow Kit, incorporates sensors and automated controls that maintain optimal humidity, temperature, and airflow conditions. This technology makes growing oak-loving mushrooms accessible to urban gardeners and indoor farming enthusiasts.
Substrate Preparation
Creating the right growing medium is crucial for successful oak mushroom cultivation. Oak sawdust, wood chips, and shredded oak bark provide excellent substrates when properly prepared and sterilized.
The substrate must be pasteurized to eliminate competing microorganisms while preserving beneficial nutrients. This process typically involves heating the material to specific temperatures for predetermined periods, ensuring optimal conditions for mushroom growth.
Health Benefits and Culinary Applications
Nutritional Value
Mushrooms that grow on oak trees offer exceptional nutritional profiles, containing high levels of protein, B vitamins, and essential minerals. These fungi also provide unique compounds like beta-glucans, which support immune system function.
Oyster mushrooms contain significant amounts of potassium, iron, and vitamin C, while shiitake mushrooms are rich in selenium and contain compounds that may support cardiovascular health. For detailed information about specific mushroom benefits, explore our comprehensive guide on edible mushrooms.
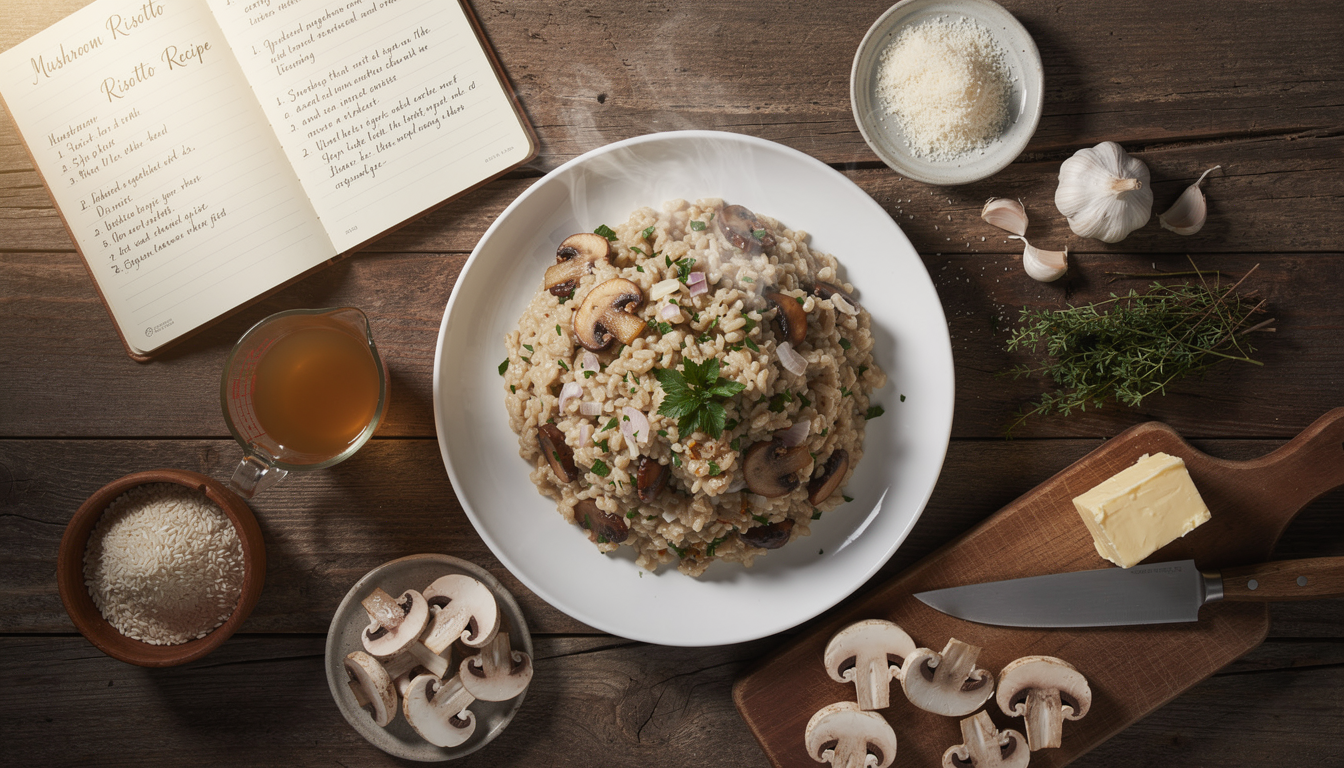
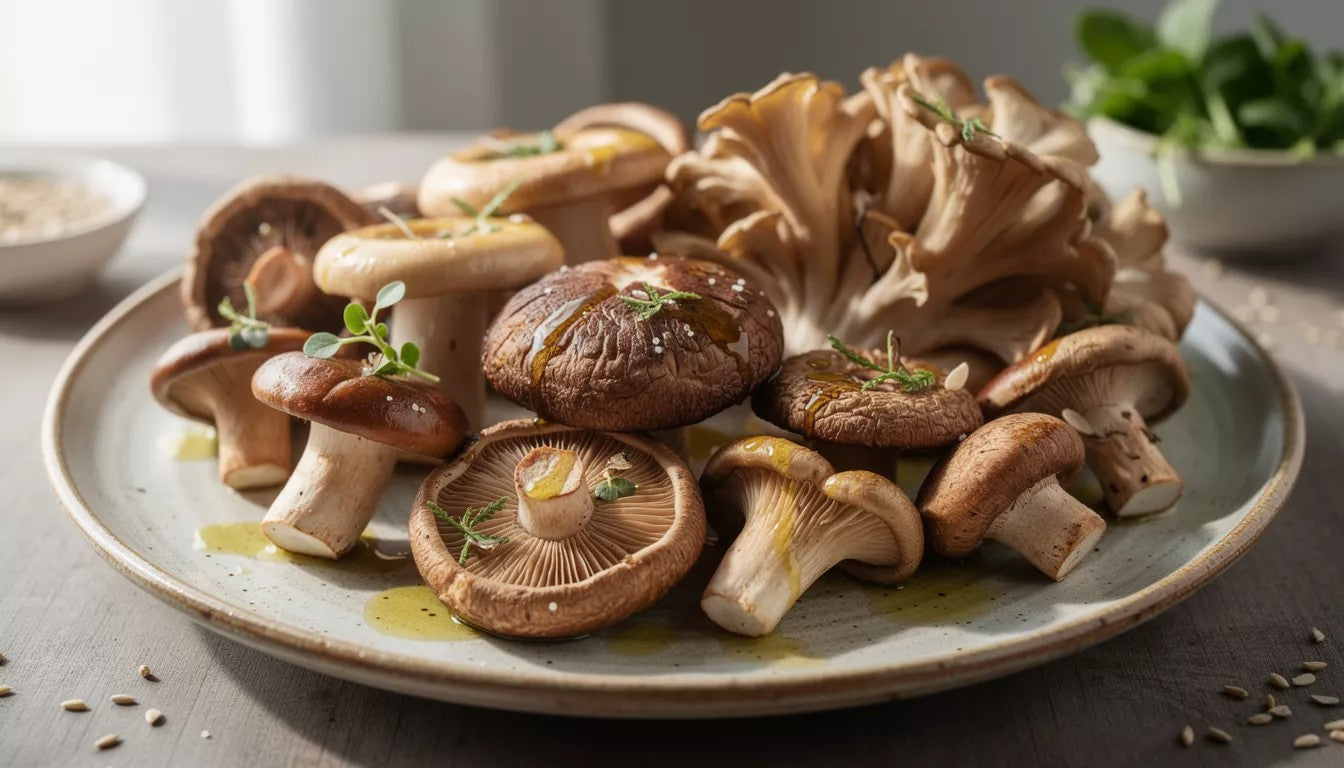
Cooking and Preservation
Oak tree mushrooms offer versatile culinary applications, from simple sautéing to complex gourmet preparations. Their robust flavors complement both vegetarian and meat-based dishes, making them valuable ingredients for diverse cooking styles.
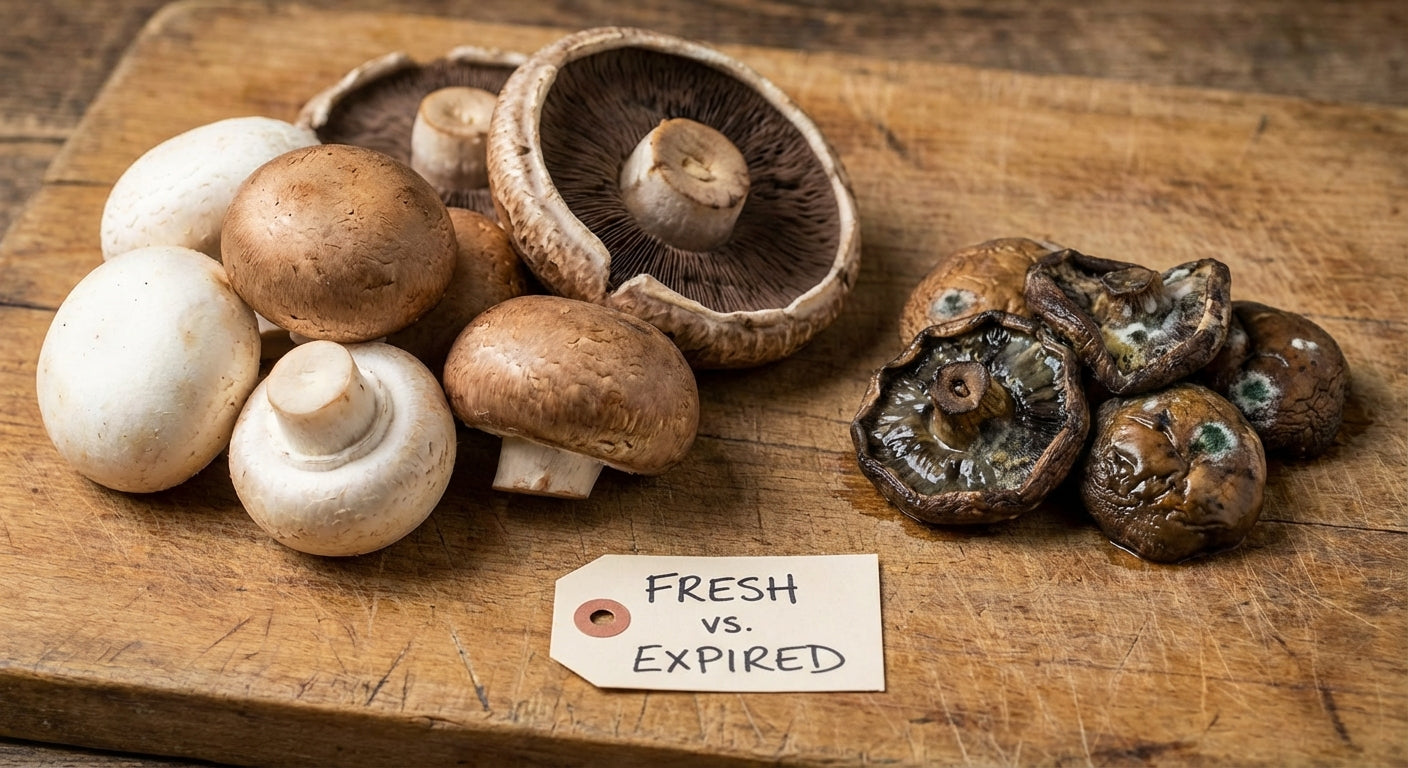
Fresh mushrooms should be used within 3-5 days of harvesting, but they can be preserved through drying, freezing, or pickling methods. Proper storage maintains their nutritional value and extends their usability for months.
Seasonal Patterns and Timing
Spring Fruiting Cycles
Many oak tree mushrooms begin their fruiting cycles in late spring when temperatures warm and moisture levels increase. Shiitake mushrooms particularly thrive during this period, producing abundant flushes that can continue for several weeks.
Spring foraging requires attention to weather patterns, as consistent rainfall followed by warm temperatures typically triggers mushroom development. Monitor your favorite oak tree locations during these conditions for optimal harvesting opportunities.
Fall Abundance
Fall represents the peak season for most oak tree mushrooms, with multiple species often fruiting simultaneously. Oyster mushrooms, maitake, and various bracket fungi typically produce their largest harvests during autumn months.
This seasonal abundance coincides with oak trees' natural cycles, as falling leaves and increased moisture create perfect conditions for fungal growth. Plan your foraging activities around these natural patterns for the best results.
FAQ Section
Q: Are all mushrooms that grow on oak trees safe to eat? A: No, not all mushrooms found on oak trees are edible. Some species can be toxic or cause digestive upset. Always ensure 100% positive identification before consuming any wild mushroom, and consult multiple reliable field guides or experts.
Q: How do I know if an oak tree mushroom is fresh and safe to harvest? A: Fresh mushrooms should be firm, have bright colors, and show no signs of decay or insect damage. Avoid mushrooms that are slimy, have dark spots, or emit unpleasant odors. Harvest only young, healthy specimens for the best quality and safety.
Q: Can I grow oak tree mushrooms indoors without actual oak logs? A: Yes, many oak-loving mushrooms can be grown indoors using oak-based substrates like sawdust or wood chips. Commercial growing systems and grow kits provide controlled environments that simulate natural oak tree conditions.
Q: What's the best time of year to start looking for mushrooms on oak trees? A: The best times are typically late spring through early summer and fall through early winter. Specific timing depends on your location, local weather patterns, and the mushroom species you're seeking.
Q: How long do oak tree mushrooms typically take to mature after initial formation? A: Most oak tree mushrooms mature within 7-14 days after initial pin formation, though this varies by species and environmental conditions. Oyster mushrooms tend to develop quickly, while shiitake may take longer to reach full maturity.
Summary
Oak trees support diverse mushroom ecosystems, hosting valuable species like oyster, shiitake, and maitake mushrooms. These fungi offer excellent nutritional benefits and culinary versatility when properly identified and harvested. Successful cultivation requires understanding seasonal patterns, proper substrate preparation, and maintaining optimal growing conditions.
Whether you're interested in foraging wild specimens or cultivating your own oak-loving mushrooms, start with proper identification skills and safety practices. The rewarding experience of growing and harvesting these remarkable fungi connects you with nature's incredible biodiversity while providing delicious, nutritious food for your table.
Ready to begin your mushroom growing journey? Explore our beginner-friendly mushroom grow kits and discover how easy it can be to cultivate gourmet mushrooms at home. With the right tools and knowledge, you'll soon be enjoying fresh, homegrown mushrooms that rival the best oak tree specimens found in nature.













Share:
Edible Mushrooms in Massachusetts: Your Complete Foraging Guide for 2025
How to Store Lion's Mane Mushrooms: Your Complete Preservation Guide