Porcini mushrooms (Boletus edulis) represent the absolute pinnacle of wild mushroom cuisine, earning their reputation as the "king of mushrooms" through centuries of culinary tradition and an unmatched combination of rich, nutty flavor, substantial meaty texture, and remarkable versatility in gourmet cooking applications. These magnificent fungi have captured the hearts of chefs, foragers, and food enthusiasts worldwide, commanding premium prices and inspiring countless culinary creations that showcase their exceptional qualities.
The distinctive characteristics of porcini mushrooms—from their robust, bulbous stems and spongy pore surfaces to their incredible ability to enhance virtually any dish with deep, complex flavors—make them among the most sought-after ingredients in fine dining establishments and home kitchens alike. Their seasonal availability and the skill required to locate them in the wild have only added to their mystique and desirability.
Understanding porcini mushrooms involves more than just recognizing their culinary value; it requires appreciation for their ecological role, proper identification techniques, optimal harvesting practices, and the myriad ways they can be prepared, preserved, and enjoyed. Whether you're a seasoned forager, an aspiring chef, or simply a food lover eager to explore one of nature's most prized ingredients, mastering porcini mushrooms opens doors to extraordinary culinary experiences.
Understanding Porcini Mushroom Characteristics and Identification
Distinctive Physical Features
Porcini mushrooms possess unmistakable characteristics that make them relatively easy to identify for experienced foragers:
Cap Characteristics:
- Color variations ranging from light tan to rich reddish-brown depending on age and conditions
- Smooth, dry surface with a slightly sticky texture when young or wet
- Substantial size caps typically 4-12 inches in diameter when fully mature
- Convex to flat shape starting dome-like and flattening with age
- No gills underneath distinguishing them from many other mushroom varieties
Stem Features:
- Bulbous, swollen base characteristic thick, club-shaped stem structure
- White to light brown coloration often with a network of fine white lines
- Solid, dense texture firm throughout without hollow centers
- Proportional size stems typically 3-8 inches tall and 1-4 inches wide
- Distinctive netting reticulated pattern on upper stem portions
Pore Surface Identification:
- Spongy pore layer instead of gills, with tiny round openings
- Color progression starting white when young, progressing to yellow, then olive-green
- Easy separation pore layer easily separates from cap flesh
- Bruising characteristics may bruise blue-green when cut or damaged
- Spore print brown to olive-brown spore prints for positive identification
Habitat and Growing Conditions
Understanding where porcini mushrooms grow naturally helps foragers locate prime hunting grounds:
Preferred Ecosystems:
- Coniferous forests particularly under pine, spruce, and fir trees
- Mixed woodlands areas combining deciduous and coniferous species
- Mycorrhizal relationships forming beneficial partnerships with tree roots
- Well-drained soils preferring areas with good drainage and organic matter
- Elevation preferences often found at higher elevations in mountainous regions
Seasonal Availability:
- Late summer through fall prime season typically August through November
- Temperature dependence requiring cool nights and warm days for optimal growth
- Moisture requirements needing adequate rainfall but not waterlogged conditions
- Regional variations timing varies significantly based on geographic location
- Climate factors drought or excessive rain can significantly impact availability
Geographic Distribution:
- Northern hemisphere primarily found in temperate regions of North America and Europe
- Western United States abundant in Pacific Northwest and Rocky Mountain regions
- European prevalence particularly common in Italy, France, and Eastern European countries
- Elevation zones typically found between 3,000-10,000 feet in mountainous areas
- Microclimate preferences seeking specific combinations of temperature, humidity, and soil conditions

Nutritional Profile and Health Benefits
Comprehensive Nutritional Analysis
Porcini mushrooms provide exceptional nutritional value with impressive macro and micronutrient profiles:
Macronutrient Composition:
- High-quality protein containing 4-5 grams per 100 grams fresh weight
- Complete amino acid profile including all essential amino acids for optimal nutrition
- Low calorie content approximately 26 calories per 100 grams fresh mushrooms
- Complex carbohydrates providing sustained energy without blood sugar spikes
- Minimal fat content less than 1 gram per serving with beneficial fatty acid ratios
Vitamin and Mineral Content:
- B-vitamin complex exceptionally rich in niacin, riboflavin, and thiamine
- Vitamin D naturally occurring vitamin D2 supporting bone health
- Potassium abundance 484mg per 100 grams supporting cardiovascular health
- Selenium richness powerful antioxidant mineral for cellular protection
- Iron content supporting healthy blood formation and oxygen transport
Unique Bioactive Compounds:
- Beta-glucan polysaccharides immune-supporting compounds with proven benefits
- Ergothioneine rare antioxidant amino acid with exceptional cellular protective properties
- Triterpenes compounds with potential anti-inflammatory and liver-protective effects
- Phenolic compounds antioxidant substances protecting against oxidative stress
- Peptides bioactive proteins with various health-promoting effects
Specific Health Benefits and Therapeutic Applications
Scientific research reveals numerous health advantages associated with porcini mushroom consumption:
Immune System Enhancement:
- Beta-glucan activation stimulating immune cell function and pathogen recognition
- Antioxidant protection comprehensive cellular protection against free radical damage
- Anti-inflammatory effects reducing chronic inflammation throughout the body
- Antimicrobial properties natural compounds supporting defense against harmful microorganisms
- Seasonal wellness supporting immune function during challenging periods
Cardiovascular Health Support:
- Cholesterol management through soluble fiber and bioactive compounds
- Blood pressure regulation via potassium content and vascular support mechanisms
- Heart rhythm stability through mineral balance and electrolyte support
- Arterial health compounds supporting flexible, healthy blood vessel function
- Circulation enhancement improving blood flow and oxygen delivery
Metabolic and Digestive Benefits:
- Blood sugar stabilization preventing glucose spikes and supporting insulin sensitivity
- Digestive health prebiotic compounds supporting beneficial gut bacteria
- Satiety enhancement protein and fiber content promoting feelings of fullness
- Liver support compounds that may assist detoxification and liver function
- Weight management low-calorie, nutrient-dense food supporting healthy weight goals
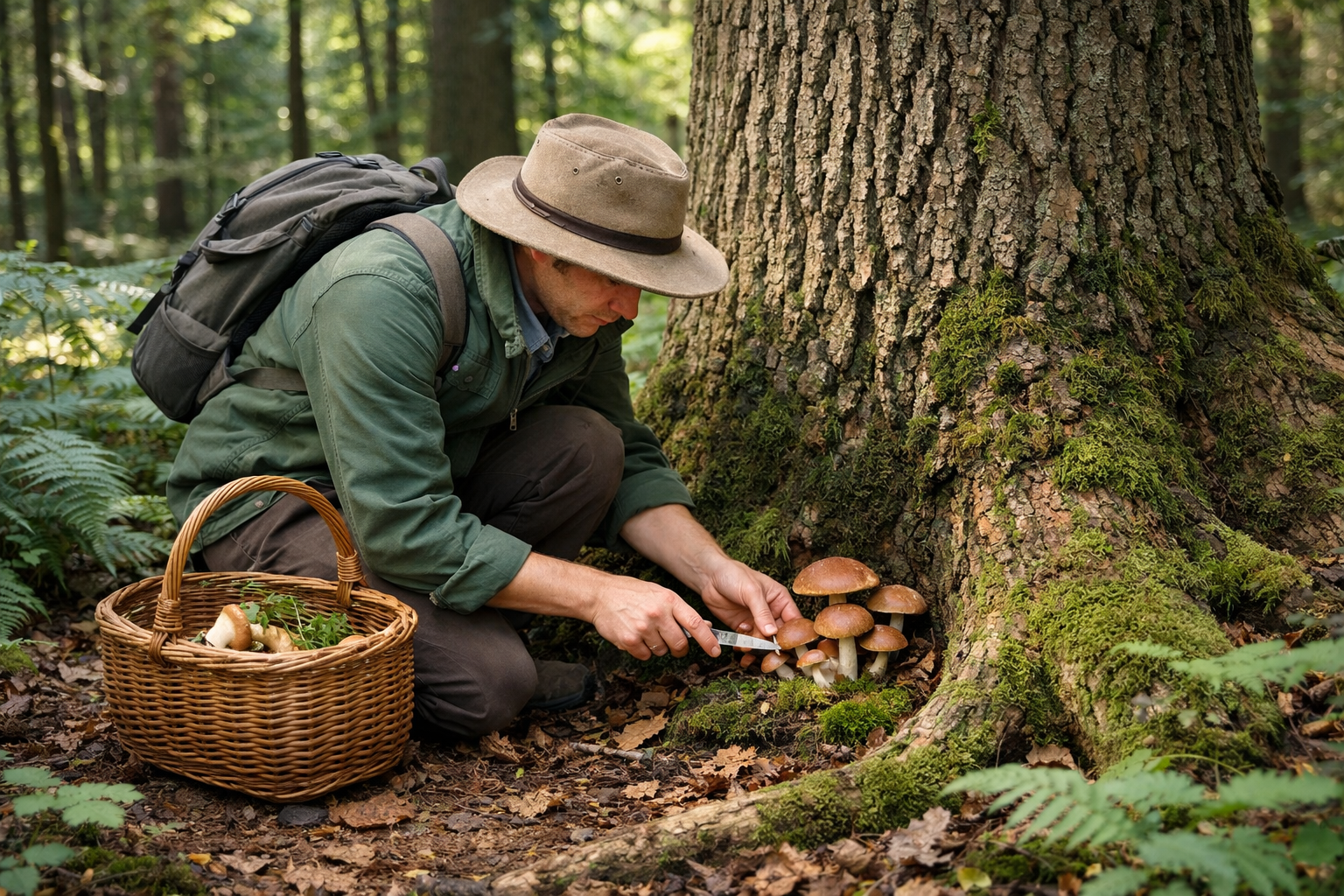
Foraging and Wild Harvesting Guidelines
Safe Foraging Practices
Responsible porcini mushroom foraging requires knowledge, preparation, and careful attention to safety:
Essential Safety Protocols:
- Positive identification never consuming any mushroom without 100% certainty
- Expert consultation working with experienced foragers or mycologists when learning
- Multiple identification sources using various field guides and resources for verification
- Gradual learning building identification skills over time with proper instruction
- Conservative approach avoiding any mushrooms that cannot be positively identified
Foraging Equipment and Preparation:
- Quality field guides comprehensive mushroom identification resources
- Mesh bags or baskets allowing spores to distribute during collection
- Sharp knife for clean cutting that doesn't damage the mycelium
- Camera or smartphone for documentation and later verification
- GPS device for marking productive locations for future visits
Sustainable Harvesting Techniques:
- Cutting vs. pulling using clean cuts to preserve underground mycelium networks
- Selective harvesting taking only mature specimens while leaving young mushrooms
- Quantity limits harvesting only what can be used to prevent waste
- Habitat preservation avoiding damage to surrounding vegetation and soil
- Spore dispersal allowing some mushrooms to mature and release spores
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Responsible foraging includes understanding legal requirements and ethical practices:
Legal Requirements:
- Permit requirements understanding local regulations for mushroom collection
- Private property obtaining permission before foraging on private land
- Public land rules following specific regulations for national forests and parks
- Seasonal restrictions observing closed seasons or protected areas
- Quantity limits adhering to legal harvest limits where applicable
Ethical Foraging Practices:
- Sustainable harvesting ensuring continued mushroom populations for future seasons
- Habitat protection minimizing environmental impact during collection
- Knowledge sharing teaching others responsible foraging practices
- Local community respecting traditional foraging areas and local customs
- Commercial considerations understanding impacts of commercial harvesting
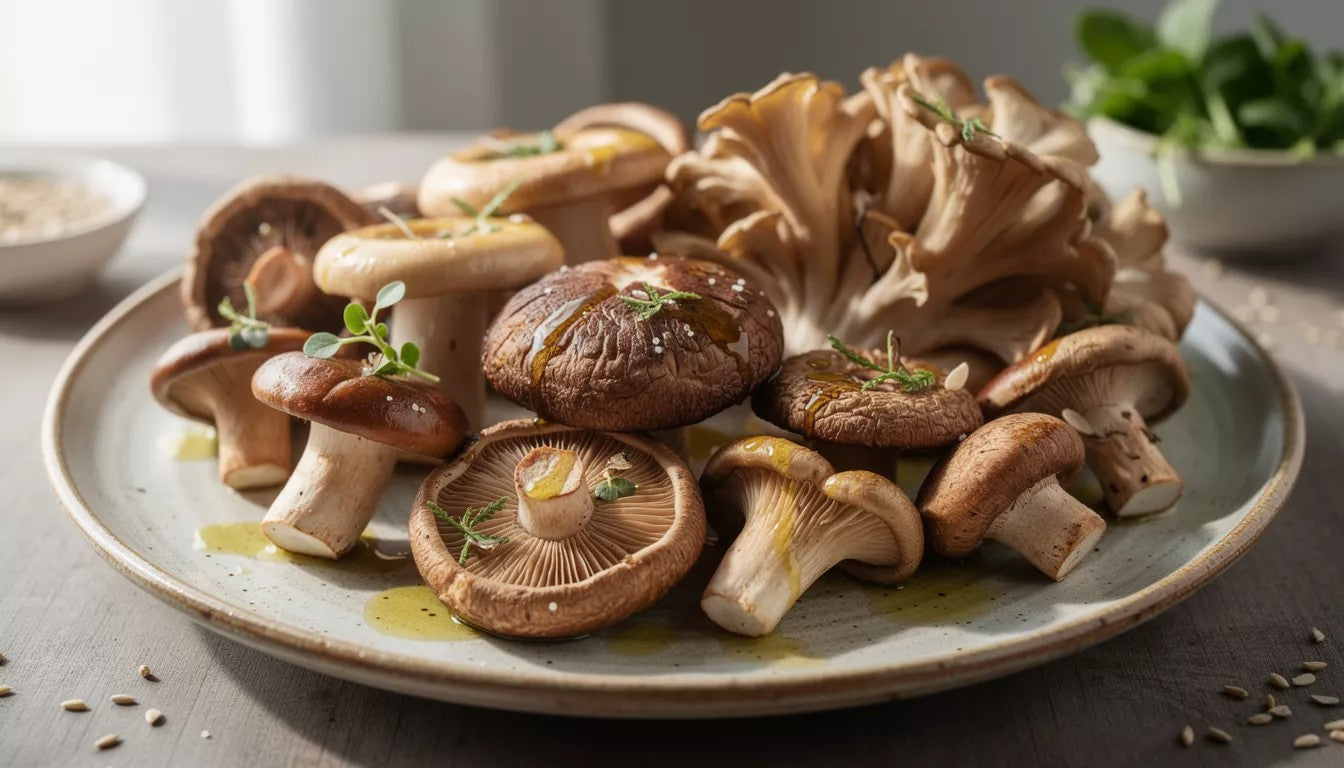
Culinary Applications and Cooking Techniques
Fundamental Preparation Methods
Proper preparation maximizes porcini mushroom flavor and texture potential:
Initial Cleaning and Preparation:
- Gentle cleaning using soft brush to remove dirt and debris
- Inspection protocol checking for insect damage or deterioration
- Trimming techniques removing damaged portions while preserving edible parts
- Pore removal deciding whether to remove or retain the pore layer based on use
- Size adjustment cutting to appropriate sizes for intended cooking methods
Pre-Cooking Considerations:
- Moisture management ensuring mushrooms are properly dried before cooking
- Temperature preparation bringing mushrooms to room temperature before cooking
- Seasoning strategies understanding how porcini respond to different seasonings
- Cooking vessel selection choosing appropriate pans and cookware
- Timing coordination preparing other ingredients to complement mushroom cooking
Traditional Italian Cooking Methods
Porcini mushrooms shine in classic Italian preparations that have been perfected over generations:
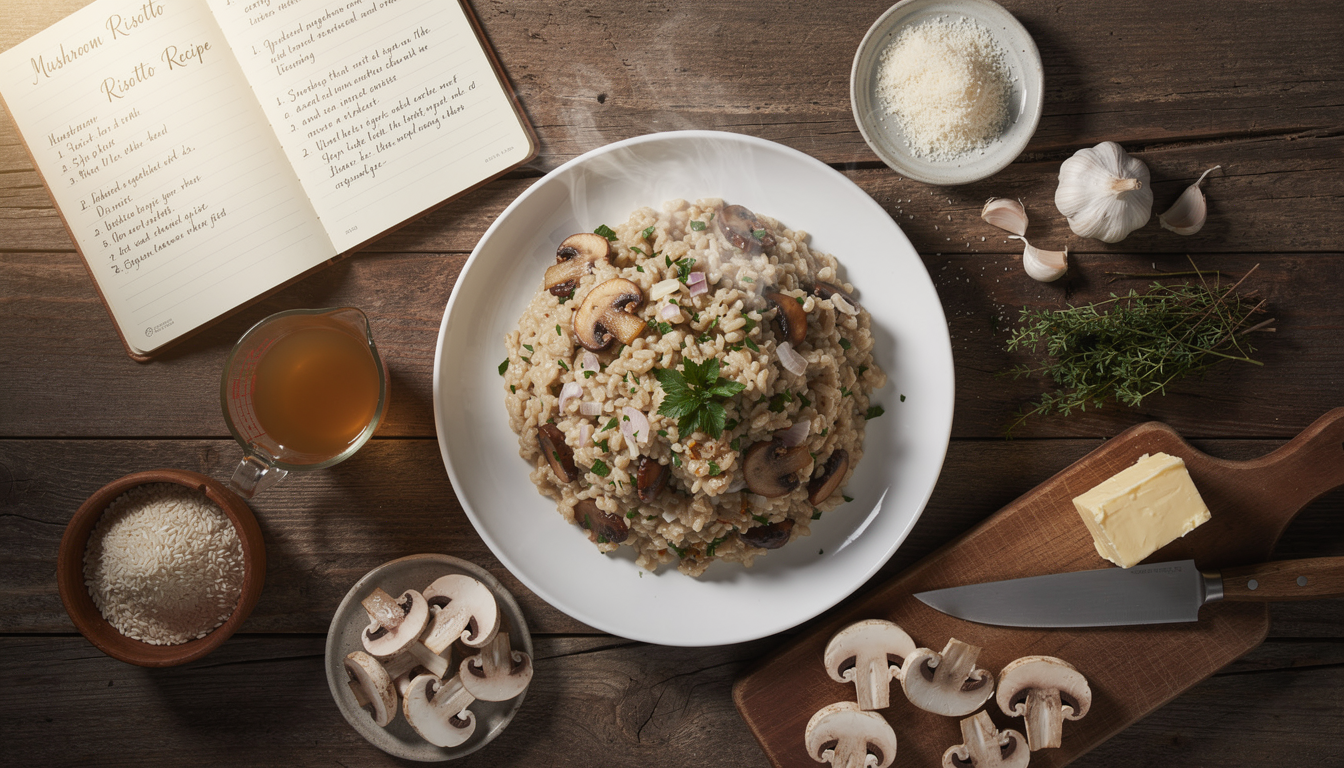
Risotto Applications:
- Porcini risotto classic preparation showcasing mushroom's earthy richness
- Stock integration using porcini-infused stocks for enhanced flavor
- Timing techniques adding mushrooms at optimal moments for texture and taste
- Cheese selections choosing complementary cheeses like Parmigiano-Reggiano
- Finishing touches final additions that enhance without overwhelming
Pasta Preparations:
- Simple aglio e olio highlighting porcini with garlic and olive oil
- Cream-based sauces rich preparations that complement mushroom earthiness
- Herb combinations traditional Italian herbs that enhance porcini flavors
- Pasta shape selection choosing pasta types that pair well with chunky mushrooms
- Sauce consistency achieving proper texture for optimal mushroom integration
Braising and Stewing:
- Slow-cooked applications long, gentle cooking that develops complex flavors
- Liquid selection using wines, stocks, and aromatics for braising
- Vegetable combinations traditional vegetables that complement porcini
- Seasoning development building flavors throughout the cooking process
- Serving suggestions traditional accompaniments and presentation styles
Modern Culinary Innovations
Contemporary chefs have developed new techniques that showcase porcini's versatility:
Molecular Gastronomy Applications:
- Porcini foam creating light, airy preparations that concentrate flavor
- Dehydration techniques using modern equipment for unique textures
- Flavor extraction advanced methods for capturing and concentrating taste
- Presentation innovations contemporary plating and serving techniques
- Texture manipulation creating unexpected textures while preserving flavor
Fusion Cuisine Integration:
- Asian applications incorporating porcini into stir-fries and Asian-inspired dishes
- Latin American fusion combining with Latin flavors and cooking techniques
- Mediterranean combinations pairing with Mediterranean ingredients and methods
- Modern European contemporary European techniques applied to porcini
- American regional incorporating into American regional cuisine styles
Preservation and Storage Techniques
Fresh Storage Methods
Proper storage significantly extends porcini mushroom freshness and quality:
Optimal Storage Conditions:
- Temperature control maintaining 32-36°F for maximum freshness retention
- Humidity management preventing excess moisture while avoiding dehydration
- Air circulation ensuring adequate ventilation around stored mushrooms
- Container selection using breathable materials that allow air movement
- Storage duration consuming fresh porcini within 3-5 days for best quality
Quality Maintenance:
- Daily inspection checking stored mushrooms for deterioration signs
- Moisture control adjusting storage conditions based on mushroom condition
- Damage removal trimming any deteriorated portions promptly
- Proper handling minimizing physical damage during storage and retrieval
- First-in-first-out using older mushrooms before newer acquisitions
Preservation Methods for Extended Storage
Various preservation techniques allow year-round enjoyment of porcini mushrooms:
Drying Techniques:
- Air drying traditional method using proper ventilation and temperature
- Dehydrator use modern equipment for consistent, controlled drying
- Oven drying low-temperature technique for home preservation
- Slice preparation cutting to appropriate thickness for even drying
- Quality assessment ensuring complete drying for long-term storage
Freezing Applications:
- Blanching preparation brief cooking before freezing for better texture
- Raw freezing freezing fresh mushrooms for specific applications
- Portion packaging freezing in convenient serving sizes
- Quality expectations understanding texture changes after freezing
- Usage applications best applications for frozen porcini mushrooms
Value-Added Preservation:
- Porcini powder creating concentrated seasoning from dried mushrooms
- Oil preservation storing in flavored oils for extended use
- Pickled preparations creating preserved mushrooms with enhanced flavors
- Salt preservation traditional salt-curing techniques
- Fermentation projects exploring fermented porcini preparations
Market Considerations and Economic Factors
Commercial Market Analysis
Understanding the porcini mushroom market helps inform purchasing and foraging decisions:
Pricing Dynamics:
- Premium pricing reflecting rarity, seasonality, and exceptional quality
- Fresh vs. dried significant price differences between fresh and preserved forms
- Import markets European dried porcini commanding premium prices
- Seasonal fluctuations dramatic price variations based on harvest success
- Quality grades different grades affecting pricing and applications
Supply Chain Factors:
- Limited availability seasonal and geographic constraints affecting supply
- Import dependency reliance on European sources for consistent supply
- Quality maintenance challenges in preserving quality during transport
- Certification requirements organic and wild-harvested certifications
- Traceability demands increasing requirements for supply chain transparency
Market Segments:
- Restaurant trade high-end establishments driving demand for premium products
- Retail markets specialty stores and gourmet food sections
- Online sales growing internet-based sales for specialty mushroom products
- Export opportunities international markets for wild-harvested porcini
- Value-added products processed forms commanding higher prices
Economic Opportunities
Various economic opportunities exist around porcini mushrooms:
Commercial Foraging:
- Professional harvesting commercial collection for restaurant and retail markets
- Permit requirements understanding licensing and regulatory requirements
- Quality standards meeting commercial quality and safety standards
- Market relationships developing relationships with buyers and distributors
- Seasonal planning managing seasonal income fluctuations
Value-Added Processing:
- Drying operations creating dried porcini products for extended markets
- Specialty preparations developing unique products for niche markets
- Private labeling creating branded products for retail distribution
- Educational services teaching foraging and cooking classes
- Tourism integration incorporating mushroom hunting into tourism offerings
Safety Considerations and Risk Management
Identification Safety
Accurate identification is crucial for safe porcini mushroom consumption:
Common Look-Alikes:
- Bitter bolete similar appearance but with bitter taste
- Devil's bolete red-pored species that may cause illness
- Other boletes various species with different edibility and safety profiles
- Identification challenges understanding subtle differences between species
- Regional variations recognizing geographic differences in bolete species
Safety Protocols:
- Multiple confirmation using various identification methods and sources
- Expert verification consulting experienced foragers or mycologists
- Gradual introduction starting with small amounts when trying new species
- Cooking requirements understanding proper cooking for safety
- Emergency preparedness knowing how to respond to adverse reactions
Food Safety Practices
Proper handling ensures safe consumption of porcini mushrooms:
Handling Protocols:
- Clean preparation maintaining sanitary conditions during processing
- Cross-contamination prevention keeping mushrooms separate from other foods
- Temperature control maintaining proper temperatures during storage and preparation
- Cooking requirements ensuring adequate cooking for safety and digestibility
- Storage safety following proper refrigeration and storage guidelines
Quality Assessment:
- Spoilage indicators recognizing signs of deterioration or contamination
- Safe consumption understanding when mushrooms should be discarded
- Allergic reactions recognizing potential mushroom allergies or sensitivities
- Medical considerations consulting healthcare providers about dietary changes
- Emergency protocols knowing how to respond to adverse reactions

Advanced Techniques and Professional Applications
Restaurant and Professional Use
Professional kitchens employ specialized techniques for porcini mushrooms:
Professional Preparation:
- Mise en place advanced preparation techniques for restaurant service
- Consistency standards maintaining uniform quality across servings
- Yield optimization maximizing usable product from expensive ingredients
- Cost control managing food costs while maintaining quality
- Menu integration incorporating porcini into diverse menu offerings
Advanced Cooking Techniques:
- Sous vide applications precise temperature cooking for optimal results
- Smoking techniques adding smoky flavors to enhance mushroom character
- Confit preparations slow cooking in fat for rich, tender results
- Reduction sauces concentrating flavors for intense mushroom essences
- Garnish applications using porcini as elegant finishing elements
Research and Development
Ongoing research continues to expand porcini mushroom applications:
Nutritional Research:
- Bioactive compound studies investigating health-promoting compounds
- Functional food applications developing mushroom-based health products
- Nutritional optimization enhancing nutritional content through processing
- Supplement development creating concentrated mushroom supplements
- Clinical studies researching therapeutic applications
Cultivation Research:
- Mycorrhizal cultivation attempts to cultivate porcini in controlled environments
- Habitat restoration projects to enhance wild porcini populations
- Genetic studies understanding genetic diversity and adaptation
- Climate change impacts studying effects of environmental changes
- Sustainable harvesting research on long-term sustainability practices
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Porcini Mushrooms
Porcini mushrooms represent the pinnacle of wild mushroom cuisine, offering an unmatched combination of exceptional flavor, substantial nutritional benefits, and endless culinary possibilities that have made them treasured ingredients for centuries. Their complex, nutty flavor profile and meaty texture provide foundations for countless culinary creations, from simple preparations that highlight their natural character to sophisticated dishes that showcase their versatility.
Understanding porcini mushrooms extends beyond mere culinary appreciation to encompass ecological awareness, foraging ethics, and sustainable harvesting practices that ensure these remarkable fungi remain available for future generations. Whether obtained through careful foraging, purchased from specialty markets, or incorporated into professional cooking applications, porcini mushrooms demand respect for their rarity, proper handling for their preservation, and skillful preparation for their optimal enjoyment.
The journey of mastering porcini mushrooms involves continuous learning, from developing identification skills and understanding seasonal patterns to exploring new cooking techniques and preservation methods. Each encounter with these magnificent fungi provides opportunities to deepen appreciation for their unique qualities while expanding culinary capabilities and nutritional awareness.
As interest in wild foods, sustainable foraging, and gourmet cooking continues to grow, porcini mushrooms will undoubtedly maintain their position as one of nature's most prized ingredients. Their ability to transform simple dishes into extraordinary culinary experiences, combined with their impressive health benefits and cultural significance, ensures that porcini mushrooms will continue to captivate food lovers, foragers, and chefs who appreciate the very best that nature has to offer.













Share:
Oyster Mushroom - Delicious, Nutritious, and Versatile
Golden Oyster Mushrooms - Vibrant and Nutritious Delight